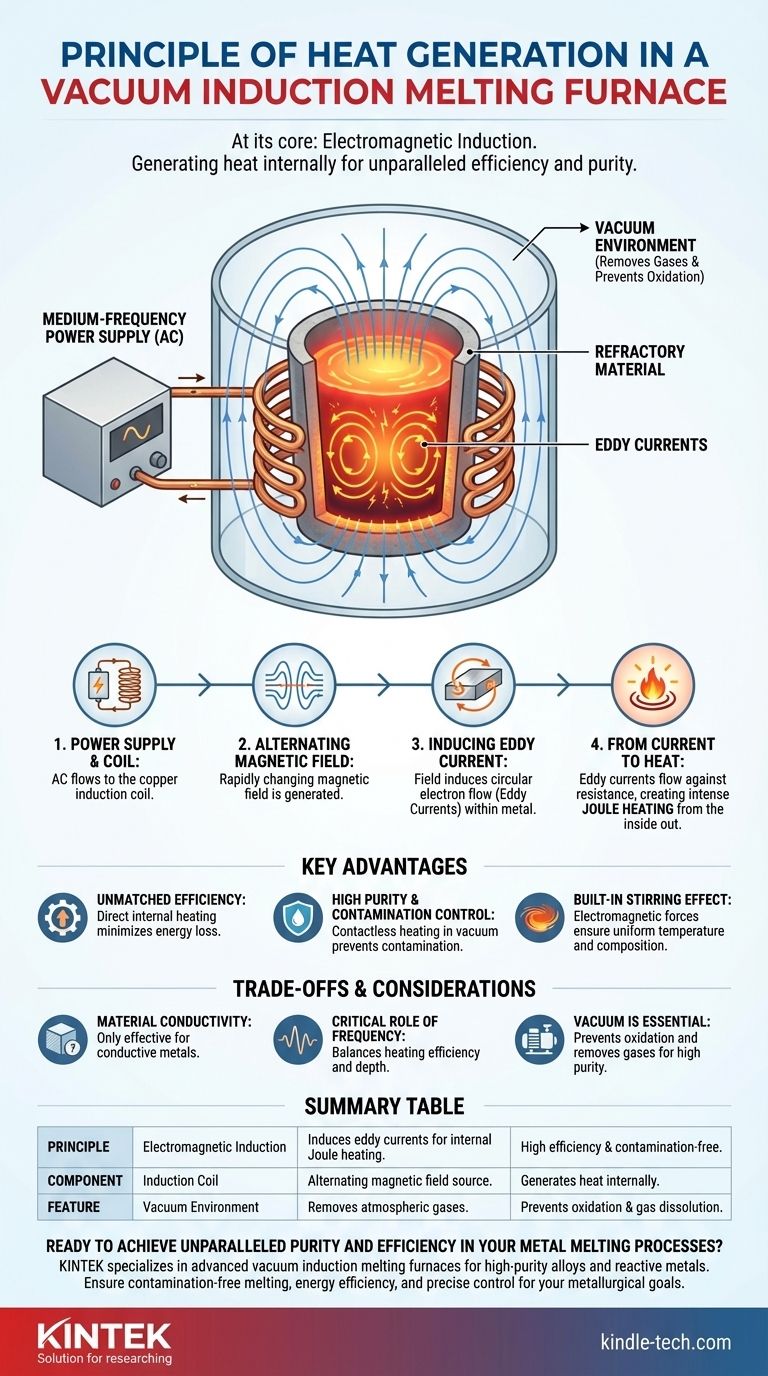
At its core, the principle used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace is electromagnetic induction. This process uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to induce strong electrical currents—known as eddy currents—directly within the metal charge, causing it to heat up and melt from the inside out.
Unlike traditional furnaces that apply heat externally, an induction furnace effectively turns the metal itself into the heating element. This internal heating method is fundamentally more efficient and cleaner, as the heat is generated precisely where it's needed without direct contact from a heat source.
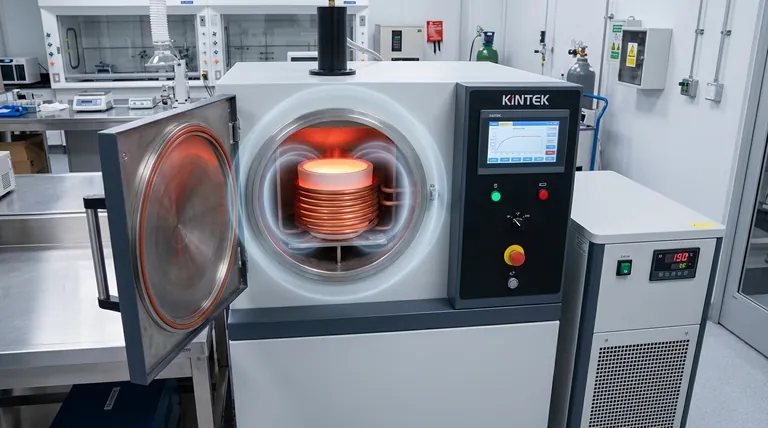

How Induction Heating Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand this process, it helps to think of the furnace as a large, specialized transformer where the metal being melted acts as a single-turn secondary coil.
The Power Supply and Induction Coil
The process begins with a medium-frequency power supply sending an alternating current (AC) to a copper induction coil. This coil is typically wrapped around a crucible containing the metal charge.
Generating an Alternating Magnetic Field
As the alternating current flows through the coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space occupied by the metal.
Inducing the Eddy Current
This alternating magnetic field continuously passes through the conductive metal charge. According to Faraday's Law of Induction, this induces an electromotive force, which creates a circular flow of electrons, or an eddy current, within the metal.
From Current to Heat
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As the strong eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate intense heat through a process known as Joule heating. This heat is generated directly within the material, causing it to rapidly reach its melting point.
Key Advantages of This Method
The principle of induction heating offers several distinct advantages, especially when combined with a vacuum environment.
Unmatched Efficiency
Because heat is generated inside the charge material, very little energy is lost to the surrounding environment. This makes induction melting highly efficient compared to methods that rely on external combustion or electric arcs.
High Purity and Contamination Control
There is no physical contact between the heating element (the coil) and the metal. This, combined with the vacuum which removes atmospheric gases, prevents contamination and is ideal for melting reactive metals and high-purity alloys.
The Built-in Stirring Effect
The same electromagnetic forces that induce the eddy currents also create a stirring action within the molten metal bath. This ensures the temperature and composition of the melt remain uniform, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, this method is not universal. Its effectiveness is governed by the laws of physics and the properties of the material being processed.
Material Conductivity is Key
Induction heating relies on the material being an electrical conductor. The principle is highly effective for metals but is not suitable for melting non-conductive materials like ceramics.
The Critical Role of Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current is a crucial parameter. A "medium frequency," as cited in the process, is chosen to balance heating efficiency with the depth of magnetic field penetration, ensuring the entire charge is heated evenly.
Why the Vacuum is Separate but Essential
The induction heating principle itself does not require a vacuum. However, for melting reactive or high-purity metals, the vacuum is essential to prevent oxidation and remove dissolved gases that would otherwise compromise the final product's quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this core principle helps clarify when a vacuum induction furnace is the optimal tool for a specific metallurgical goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The combination of contactless induction heating and a vacuum environment provides the cleanest possible melt, free from atmospheric and source contamination.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Heating the charge directly from within minimizes thermal losses, making it one of the most efficient methods for melting metals.
- If your primary focus is compositional uniformity: The natural electromagnetic stirring effect is a key benefit, ensuring a homogenous molten bath without mechanical parts.
Ultimately, vacuum induction melting leverages fundamental physics to create a precise, clean, and efficient internal heating element out of the very material you wish to melt.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Key Component | How It Works | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | Induction Coil | Alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents in the metal, generating internal heat via Joule heating. | High efficiency and contamination-free melting. |
| Vacuum Environment | Vacuum Chamber | Removes atmospheric gases to prevent oxidation and gas dissolution. | Ideal for reactive metals and high-purity alloys. |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Molten Metal Bath | Induced currents create a natural stirring action for uniform temperature and composition. | Consistent, high-quality alloy production. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and efficiency in your metal melting processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum induction melting furnaces designed for high-purity alloys and reactive metals. Our solutions ensure contamination-free melting, energy efficiency, and precise temperature control—perfect for laboratories focused on material purity and uniformity. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can enhance your metallurgical outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















