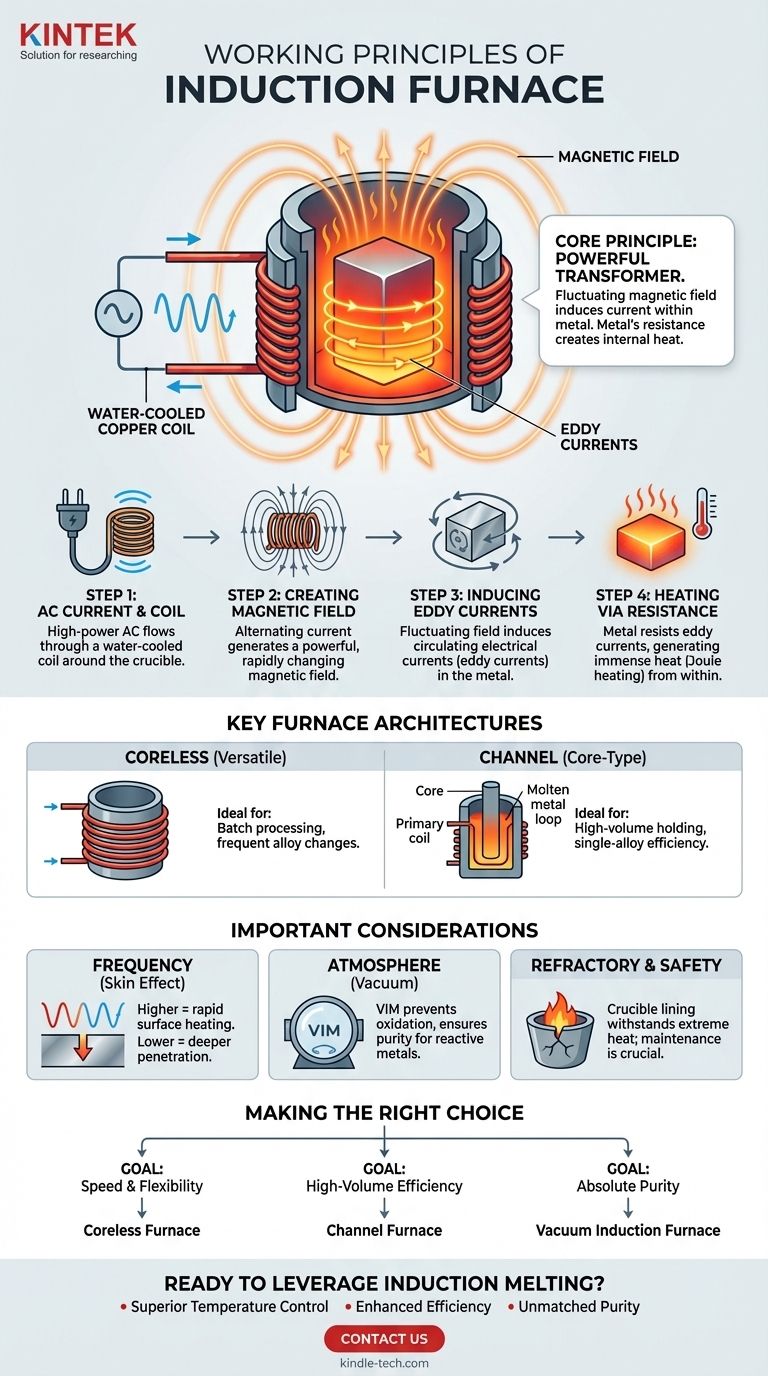
At its core, an induction furnace is a powerful transformer. It uses a fluctuating magnetic field to induce an electrical current directly within the metal to be melted. The metal's own electrical resistance to this internal current generates intense, rapid heat, melting it from the inside out without any external flame or heating element making contact.
The fundamental principle is not about applying heat to the metal, but about turning the metal into its own heat source. This is achieved by using electromagnetic induction, the same physical law that governs how electrical transformers work.
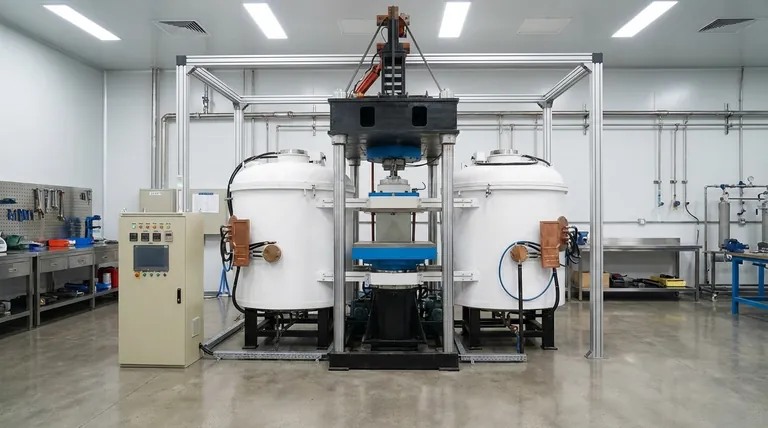

The Core Principle: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The entire process relies on the precise application of fundamental electromagnetic laws, turning electrical energy into heat with remarkable efficiency.
Step 1: The Alternating Current and Coil
It all begins with a power supply that sends a high-power alternating current (AC) through a large, often water-cooled, copper coil. This coil is typically wrapped around a crucible or chamber containing the conductive metal charge.
Step 2: Creating the Magnetic Field
As the alternating current flows and constantly reverses direction within the coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space at the center of the coil, where the metal is located.
Step 3: Inducing Eddy Currents
According to the laws of electromagnetism (specifically Faraday's Law of Induction), this fluctuating magnetic field induces circulating electrical currents within the conductive metal charge. These internal, circular currents are known as eddy currents.
Step 4: Heating via Resistance
The metal resists the flow of these induced eddy currents. This electrical resistance generates immense heat directly within the metal itself, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This heat rapidly raises the metal's temperature to its melting point and beyond.
The Built-in Stirring Effect
The same electromagnetic forces that induce eddy currents also create a powerful stirring action within the molten metal bath. This natural circulation ensures the melt is homogenous, which is critical for creating high-quality alloys of exact composition.
Understanding the Key Furnace Architectures
While the principle is the same, the physical design of the furnace can vary significantly, impacting its ideal application. These variations primarily concern how the magnetic field is coupled to the metal charge.
Coreless Induction Furnaces
This is the most common design. The induction coil directly surrounds a refractory-lined crucible containing the metal charge. There is no iron core connecting the coil and the metal.
This design is highly versatile, excellent for melting a wide range of metals, and ideal for applications requiring frequent changes in alloy composition (batch processing).
Channel (Core-Type) Induction Furnaces
This design functions much more like a traditional transformer. It has an iron core, a primary coil, and a secondary "coil" formed by a closed loop of molten metal.
The heat is generated in this specific molten metal loop and circulates into the main furnace bath. These furnaces are extremely energy-efficient but are best suited for holding and superheating very large volumes of a single type of metal, not for frequent alloy changes.
Common Pitfalls and Operating Considerations
Understanding the principles also means recognizing the operational nuances and limitations that arise from them.
The Importance of Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current is a critical parameter. Higher frequencies concentrate the current on the surface of the metal (the "skin effect"), leading to very rapid heating of smaller charges. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper, which is better for melting larger batches.
The Role of the Atmosphere
Most induction melting occurs in the open air. However, for reactive metals like titanium or superalloys, the process must be conducted in a vacuum induction furnace (VIM). By removing air and other gases, the vacuum prevents the molten metal from oxidizing or becoming contaminated, ensuring maximum purity.
Refractory and Safety
The heat is generated in the charge, not the furnace walls. However, the intense temperature of the molten metal means the refractory lining of the crucible is under extreme stress. Proper selection and maintenance of this lining are paramount to safe and efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific design of an induction furnace is chosen based on the desired outcome, from raw production to high-tech manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is speed and batch flexibility: A coreless furnace is the industry standard, allowing you to melt different alloys quickly and efficiently.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-alloy efficiency: A channel furnace offers superior energy performance for holding and processing large, continuous melts.
- If your primary focus is absolute material purity: A vacuum induction furnace is the only choice for creating high-performance, reactive alloys free from atmospheric contamination.
Ultimately, the induction furnace's working principle provides a clean, contained, and controllable method for melting metals with unparalleled precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| AC Power Supply | Generates high-frequency alternating current. |
| Water-Cooled Coil | Creates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. |
| Metal Charge | Acts as a secondary circuit; eddy currents generate internal heat (Joule heating). |
| Crucible/Refractory | Contains the molten metal and withstands extreme temperatures. |
Ready to leverage the precision of induction melting in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored for research and development. Whether you need the flexibility of a coreless furnace for alloy development or the ultimate purity of a vacuum induction furnace, our experts can help you select the right solution.
We provide:
- Superior Temperature Control: Achieve exact melting points for consistent, high-quality results.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Reduce energy consumption and melt times with direct internal heating.
- Unmatched Purity: Process reactive metals in a controlled atmosphere with our vacuum solutions.
Contact us today to discuss how an induction furnace from KINTEK can advance your materials science and metallurgy projects. Let's melt your challenges away!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of introducing hydrogen or argon gas into a vacuum hot pressing furnace during sintering or cooling?
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- How does the high-temperature and high-pressure environment provided by vacuum hot press equipment improve the interfacial bonding between Mo fibers and the TiAl matrix?



















