In short, all-ceramic restorations can be used for nearly every type of fixed dental prosthesis. This includes single crowns, veneers, inlays, onlays, fixed partial dentures (bridges), and implant-supported restorations. Their versatility, driven by significant advances in material science, allows them to be used in both the front (anterior) and back (posterior) of the mouth.
The decision to use an all-ceramic restoration has shifted from "can we?" to "which one and when?". The choice is no longer limited by possibility but is guided by a precise understanding of material properties, aesthetic demands, and the functional forces of each specific clinical case.

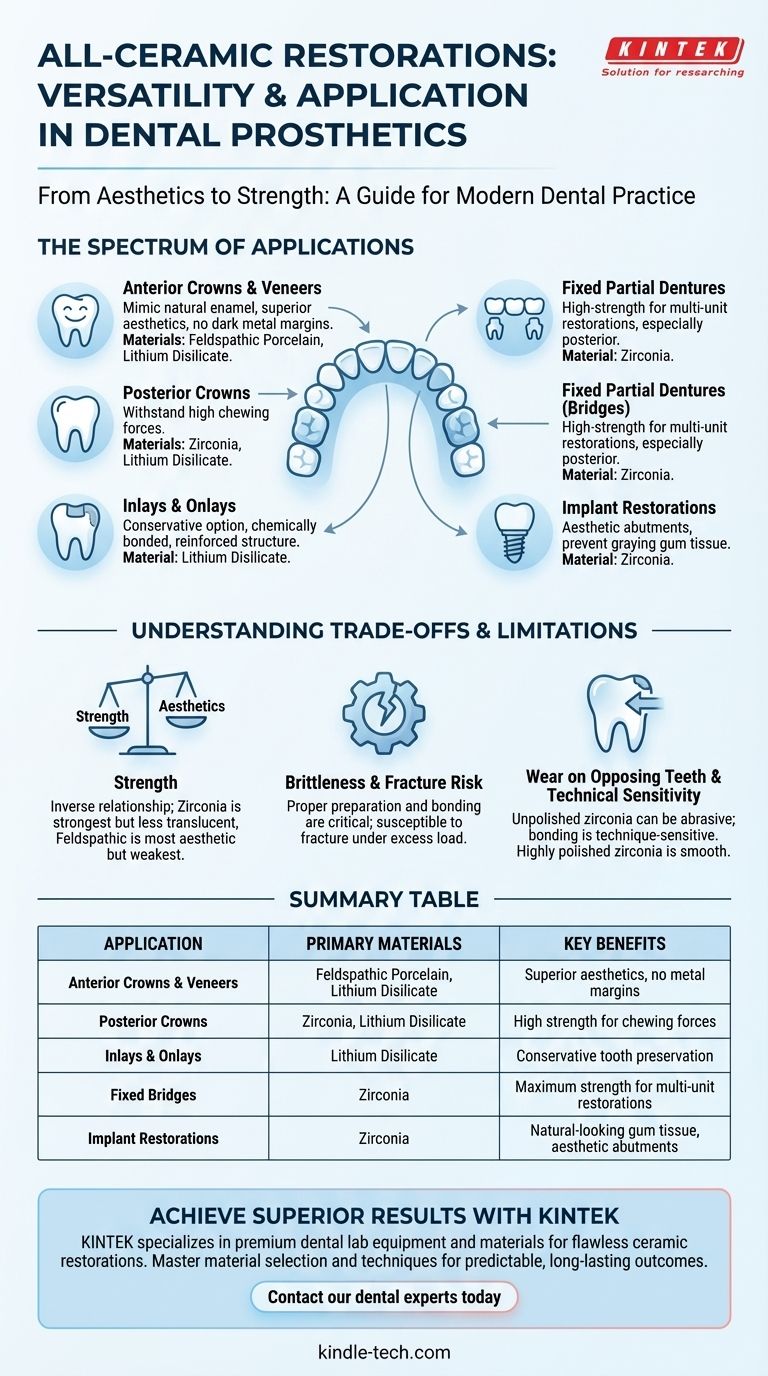
The Spectrum of All-Ceramic Applications
Modern ceramics have evolved from purely aesthetic, weaker materials into a class of high-strength, versatile solutions suitable for a wide range of demanding clinical situations.
Anterior Crowns & Veneers
This is the classic application where aesthetics are paramount. All-ceramic materials can mimic the translucency, color, and fluorescence of natural tooth enamel with unmatched fidelity.
Because there is no metal substructure, there is no risk of a dark metal margin showing at the gumline, a common aesthetic problem with older porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns.
Posterior Crowns
Historically, the high chewing forces in the posterior mouth precluded the use of ceramics. However, the development of high-strength materials like zirconia and lithium disilicate has completely changed this.
These modern ceramics can withstand significant occlusal (biting) loads, making them a durable and aesthetic alternative to metal or PFM crowns for molars and premolars.
Inlays and Onlays
For teeth with damage that is too extensive for a simple filling but not severe enough to require a full crown, ceramic inlays and onlays are an ideal conservative option.
They can be chemically bonded to the remaining tooth structure, which reinforces the tooth and creates a very strong, sealed margin. This is often done with CAD/CAM technology (like CEREC) for a single-visit restoration.
Fixed Partial Dentures (Bridges)
Replacing missing teeth with a bridge places immense stress on the connector areas between the units. Only high-strength ceramics, primarily zirconia, are indicated for multi-unit bridges, especially in the posterior region.
For anterior bridges, aesthetics can be improved by using a strong zirconia framework layered with a more life-like porcelain.
Implant Restorations
All-ceramic materials are now the standard for aesthetic implant restorations. Zirconia is frequently used to create custom abutments (the connector between the implant and the crown) to provide a tooth-colored foundation, preventing the graying effect that a metal abutment can have on the overlying gum tissue.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly versatile, all-ceramic materials are not a universal solution. Success depends on understanding their inherent properties and limitations.
Strength vs. Aesthetics
There is generally an inverse relationship between a ceramic's strength and its translucency. The strongest material, zirconia, is traditionally the most opaque, while the most beautiful, feldspathic porcelain, is the weakest.
Modern materials like high-translucency zirconia and lithium disilicate strike an exceptional balance, but the fundamental trade-off still guides material selection.
Brittleness and Fracture Risk
Unlike metals, which can bend slightly under load, ceramics are brittle. If the restoration is not thick enough or if the tooth preparation is not designed correctly, they can fracture.
Proper clinical protocols for tooth preparation, bonding, and occlusal adjustment are absolutely critical to long-term success.
Wear on Opposing Teeth
Some monolithic (single-material) ceramics, particularly unpolished zirconia, can be abrasive and cause wear on the opposing natural teeth.
However, research has shown that a highly polished zirconia surface is exceptionally smooth and kind to the opposing dentition, making the final polishing step essential.
Technical Sensitivity
The long-term success of many all-ceramic restorations relies on the quality of the adhesive bond to the tooth. This bonding procedure is more complex and technique-sensitive than traditional cementation used for metal-based crowns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct ceramic is about matching the material's properties to the specific demands of the case.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics for anterior veneers: Feldspathic porcelain or a high-translucency lithium disilicate are the premier choices for their optical properties.
- If your primary focus is a single crown with an ideal blend of strength and beauty: Lithium disilicate (e.g., IPS e.max) is often the go-to material for both anterior and posterior applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a posterior bridge or for a patient with heavy grinding forces: A monolithic, high-strength zirconia restoration is the most durable and predictable all-ceramic option.
Ultimately, leveraging the full potential of all-ceramic restorations comes from a clear diagnosis of the functional and aesthetic needs of the patient.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior Crowns & Veneers | Feldspathic Porcelain, Lithium Disilicate | Superior aesthetics, no metal margins |
| Posterior Crowns | Zirconia, Lithium Disilicate | High strength for chewing forces |
| Inlays & Onlays | Lithium Disilicate | Conservative tooth preservation |
| Fixed Bridges | Zirconia | Maximum strength for multi-unit restorations |
| Implant Restorations | Zirconia | Natural-looking gum tissue, aesthetic abutments |
Ready to achieve superior results with all-ceramic restorations? KINTEK specializes in premium dental lab equipment and materials that empower technicians to create flawless ceramic crowns, bridges, and veneers. Our solutions help you master material selection, milling, and finishing techniques for predictable, long-lasting outcomes.
Contact our dental experts today to discuss how we can support your lab's success with cutting-edge ceramic solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia



















