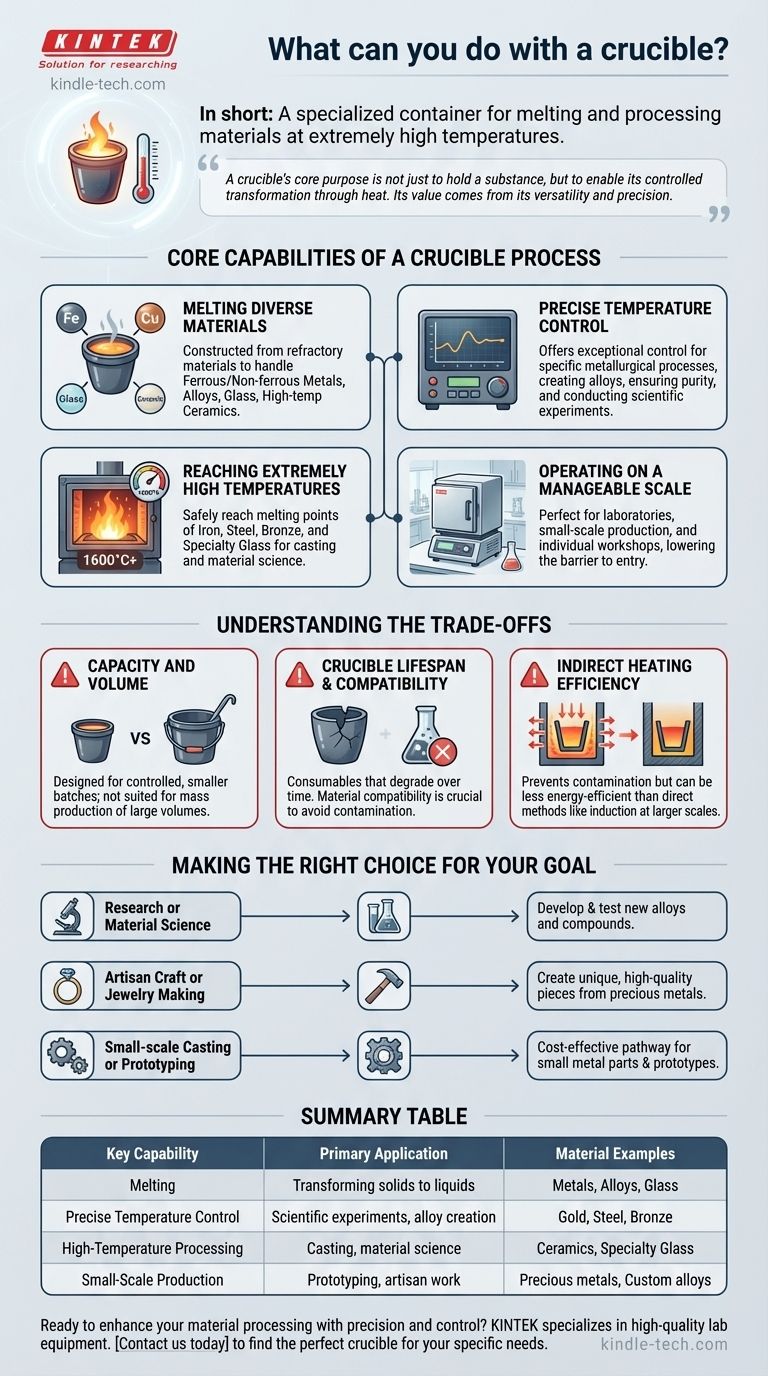
In short, a crucible is a specialized container used for melting and processing materials at extremely high temperatures. It is a fundamental tool for transforming solids into liquids, enabling a wide range of applications. Crucibles are designed to withstand thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making them essential for handling everything from metals and alloys to glass and ceramics.
A crucible's core purpose is not just to hold a substance, but to enable its controlled transformation through heat. Its value comes from its versatility across many materials and its precision, which is critical for laboratories, foundries, and artisan workshops.
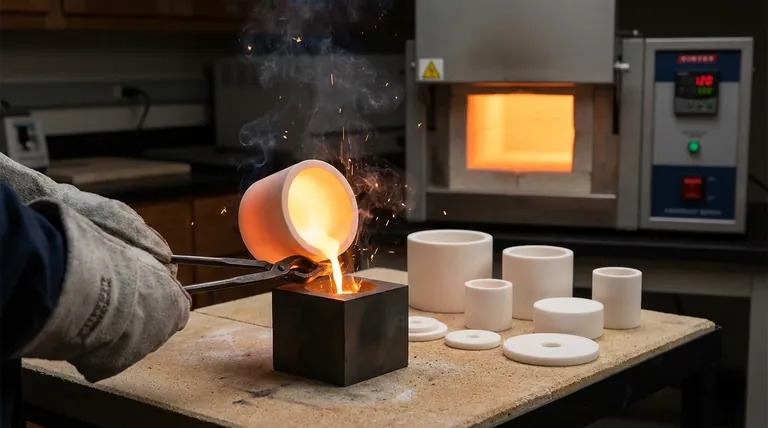

Core Capabilities of a Crucible Process
The decision to use a crucible is driven by a need for control and material integrity at high temperatures. Its design and the furnaces they are used in offer several key advantages.
Melting a Diverse Range of Materials
A crucible's primary function is melting. Because they are constructed from refractory materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or ceramic, they can handle an incredibly wide variety of substances.
This includes ferrous and non-ferrous metals, custom alloys, various types of glass, and high-temperature ceramics. This versatility makes them invaluable in both industrial and experimental settings.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
Crucible furnaces offer exceptionally precise temperature control. This is not just about getting something hot; it's about hitting and holding specific temperatures required for metallurgical processes.
This precision is critical for creating alloys with specific properties, ensuring the purity of a melt, or conducting scientific experiments where temperature is a key variable.
Reaching Extremely High Temperatures
Many valuable industrial and creative processes require temperatures far beyond what a standard oven or kiln can produce.
Crucible furnaces are engineered to safely reach the high melting points of materials like iron, steel, bronze, and specialty glass, making them essential for casting and material science.
Operating on a Manageable Scale
While large-scale industrial melting exists, many crucible furnaces are compact. This makes them perfectly suited for small-scale production, laboratories, and individual workshops.
Their manageable size, relative ease of operation, and cost-effectiveness lower the barrier to entry for high-temperature material processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the crucible process is not universally optimal. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Capacity and Volume
The "small-scale" advantage is also a limitation. Standard crucible furnaces are designed for controlled, smaller batches and are not suited for the mass production of large volumes of molten material, where larger, direct-heating furnaces are more efficient.
Crucible Lifespan and Compatibility
Crucibles are consumables. They degrade over time and can crack from repeated thermal shock if handled improperly.
Furthermore, not every crucible material is compatible with every substance. Using the wrong crucible can lead to contamination of the melt or rapid degradation of the crucible itself.
Indirect Heating Efficiency
In a crucible furnace, the heat is applied to the crucible, which then transfers that heat to the material inside. This indirect heating is excellent for preventing contamination.
However, it can be less energy-efficient than methods that heat the material directly, such as an induction furnace, especially at larger scales.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A crucible is the right tool when your objective requires controlled melting of specific material quantities.
- If your primary focus is research or material science: The precise temperature control and suitability for small batches make crucible furnaces ideal for developing and testing new alloys and compounds.
- If your primary focus is artisan craft or jewelry making: The ability to melt precious metals and custom alloys in manageable amounts is perfectly suited for creating unique, high-quality pieces.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting or prototyping: The cost-effectiveness and ease of use provide a powerful pathway for creating small metal parts, replacement components, or functional prototypes.
Ultimately, a crucible empowers you to transform raw materials into refined substances with a high degree of precision and control.
Summary Table:
| Key Capability | Primary Application | Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Melting | Transforming solids to liquids | Metals, Alloys, Glass |
| Precise Temperature Control | Scientific experiments, alloy creation | Gold, Steel, Bronze |
| High-Temperature Processing | Casting, material science | Ceramics, Specialty Glass |
| Small-Scale Production | Prototyping, artisan work | Precious metals, Custom alloys |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision and control? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including crucibles and furnaces designed for durability and exact temperature management. Whether you're in research, jewelry making, or small-scale casting, our solutions ensure purity, efficiency, and reliable performance. Contact us today to find the perfect crucible for your specific needs and achieve superior results in your high-temperature applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are High-purity Alumina Crucibles selected for corrosion testing? Ensure Data Fidelity in Molten Salt Experiments
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles necessary for liquid lead corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Data
- What are the advantages of using alumina crucibles for the TGA of modified alkyd resins? Ensure Accurate Results
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data



















