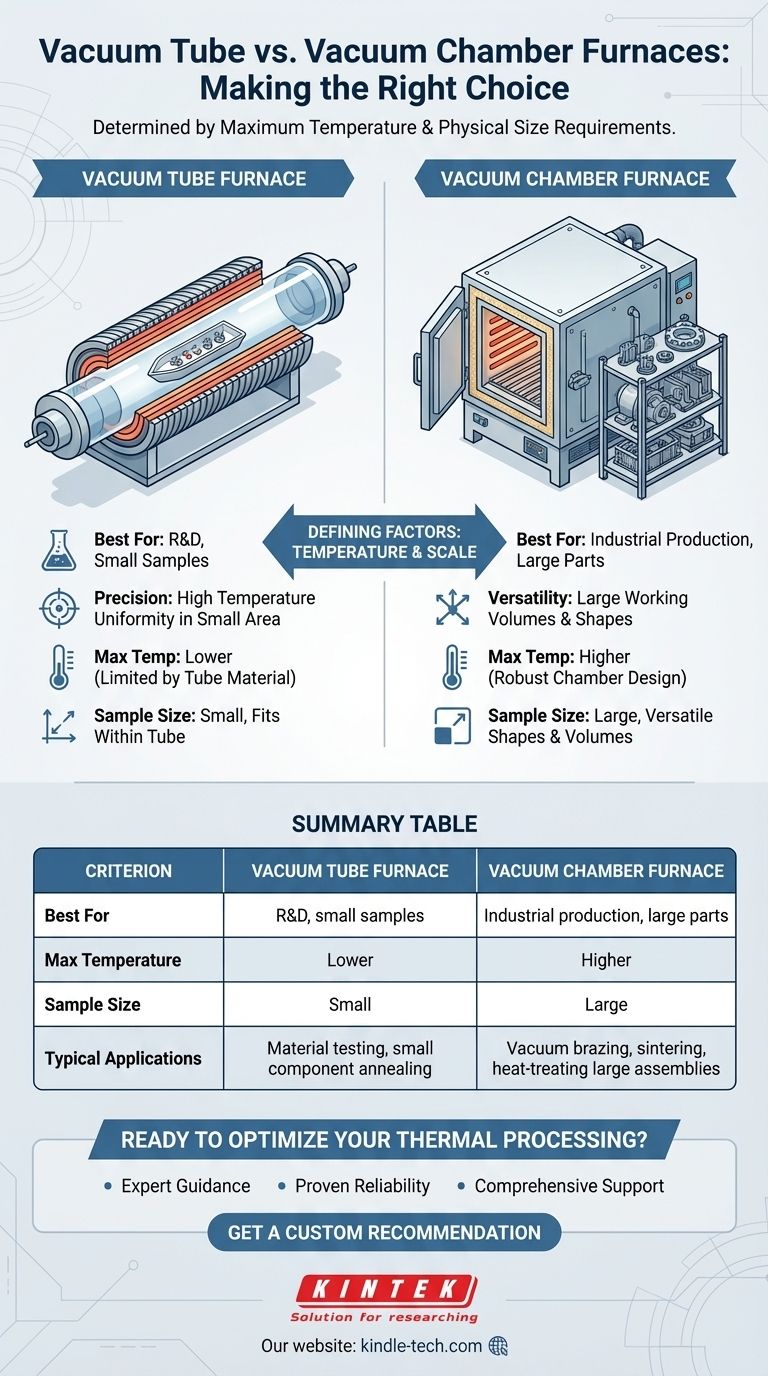
The choice between a vacuum tube furnace and a vacuum chamber furnace is determined by two primary criteria: the maximum temperature your process requires and the physical size of the items you need to heat. A vacuum chamber furnace is the necessary choice for applications that demand larger working volumes or higher temperatures than a tube furnace can provide.
While both furnaces create a controlled, high-purity heating environment, the decision is a fundamental trade-off. Vacuum tube furnaces offer precision for smaller-scale work, while vacuum chamber furnaces provide the necessary scale and temperature capabilities for larger industrial applications.
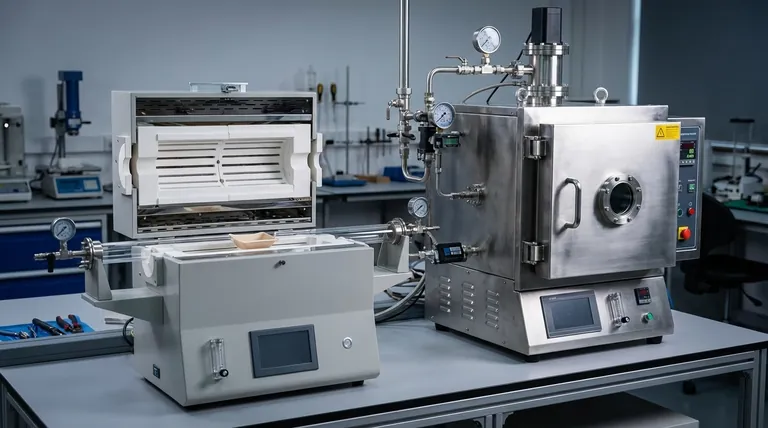

The Defining Factors: Temperature and Scale
The physical design of each furnace type dictates its capabilities and limitations. Understanding this core difference is the first step in making the correct selection.
The Role of the Vacuum Tube Furnace
A vacuum tube furnace centers around a ceramic or quartz tube that contains the sample and the controlled atmosphere. The heating elements are positioned around the outside of this tube.
This design is ideal for processing smaller samples with high precision. It excels in laboratory, research, and development settings where exact temperature uniformity over a small, well-defined area is critical.
The Role of the Vacuum Chamber Furnace
A vacuum chamber furnace, often called a cold wall furnace, is built around a large steel vessel. The insulation and heating elements are located inside this chamber.
This robust construction, often using carbon or stainless steel with secure door closures, allows for much larger processing volumes and significantly higher operating temperatures. It is the workhorse for industrial production.
Key Applications Driving the Decision
Your specific process goal will naturally point toward one furnace type. The application itself often has inherent size and temperature requirements.
Applications Suited for Tube Furnaces
These furnaces are the standard for small-scale, high-purity work. They are frequently used for material sample testing, annealing of small electronic components, and fundamental materials science research.
Applications Requiring Chamber Furnaces
Chamber furnaces are essential for large-scale industrial processes. Common uses include vacuum brazing of complex assemblies, vacuum sintering of production parts, and vacuum annealing or heat treatment of large metal components, including reactive metals like titanium.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Beyond the primary factors of size and temperature, you must consider the practical implications of operating each furnace type. These trade-offs involve precision, maintenance, and complexity.
Precision vs. Versatility
A tube furnace can provide exceptional temperature uniformity within its narrow tube, offering a high degree of control for sensitive processes.
A chamber furnace offers the versatility to handle a wide range of material sizes and cross-sections, but achieving precise uniformity across its entire large volume is a more complex engineering challenge.
Maintenance and Cleanliness
The furnace chamber must be kept extremely clean to prevent contamination. After each cycle, the furnace should be wiped down to remove debris.
While this applies to both types, the larger internal surface area and complexity of a chamber furnace can make inspection and cleaning more involved. You must check for "hot spots" or scorch marks that indicate improper cooling.
Cost and Complexity
The scale and robust engineering of chamber furnaces mean they represent a higher capital investment. Their systems are often more complex, sometimes requiring advanced controls and specialized pumps to achieve the desired vacuum levels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, align the equipment's capabilities directly with your process objectives.
- If your primary focus is research, material sample testing, or processing small, high-value components: A vacuum tube furnace offers the necessary precision and control in a smaller footprint.
- If your primary focus is industrial production, heat-treating large parts, or brazing complex assemblies: A vacuum chamber furnace is required to accommodate the necessary scale and temperature demands.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures for advanced materials: You will almost certainly need a specialized vacuum chamber furnace designed for extreme heat.
Ultimately, understanding the direct relationship between your process scale and required temperature will guide you to the correct furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Criterion | Vacuum Tube Furnace | Vacuum Chamber Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | R&D, small samples, high precision | Industrial production, large parts, high temperatures |
| Max Temperature | Lower (limited by tube material) | Higher (robust chamber design) |
| Sample Size | Small, fits within a tube | Large, versatile shapes and volumes |
| Typical Applications | Material testing, annealing small components | Vacuum brazing, sintering, heat-treating large assemblies |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Choosing the right vacuum furnace is critical to your success. Whether you are conducting precise R&D with small samples or scaling up for industrial production, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you select the ideal furnace based on your specific temperature, size, and application requirements.
- Proven Reliability: From benchtop tube furnaces for the lab to heavy-duty chamber furnaces for the factory floor, our equipment is built for performance and durability.
- Comprehensive Support: We provide full support from installation and training to maintenance, ensuring your furnace operates at peak efficiency.
Don't let equipment limitations hinder your process. Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect vacuum furnace solution for your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















