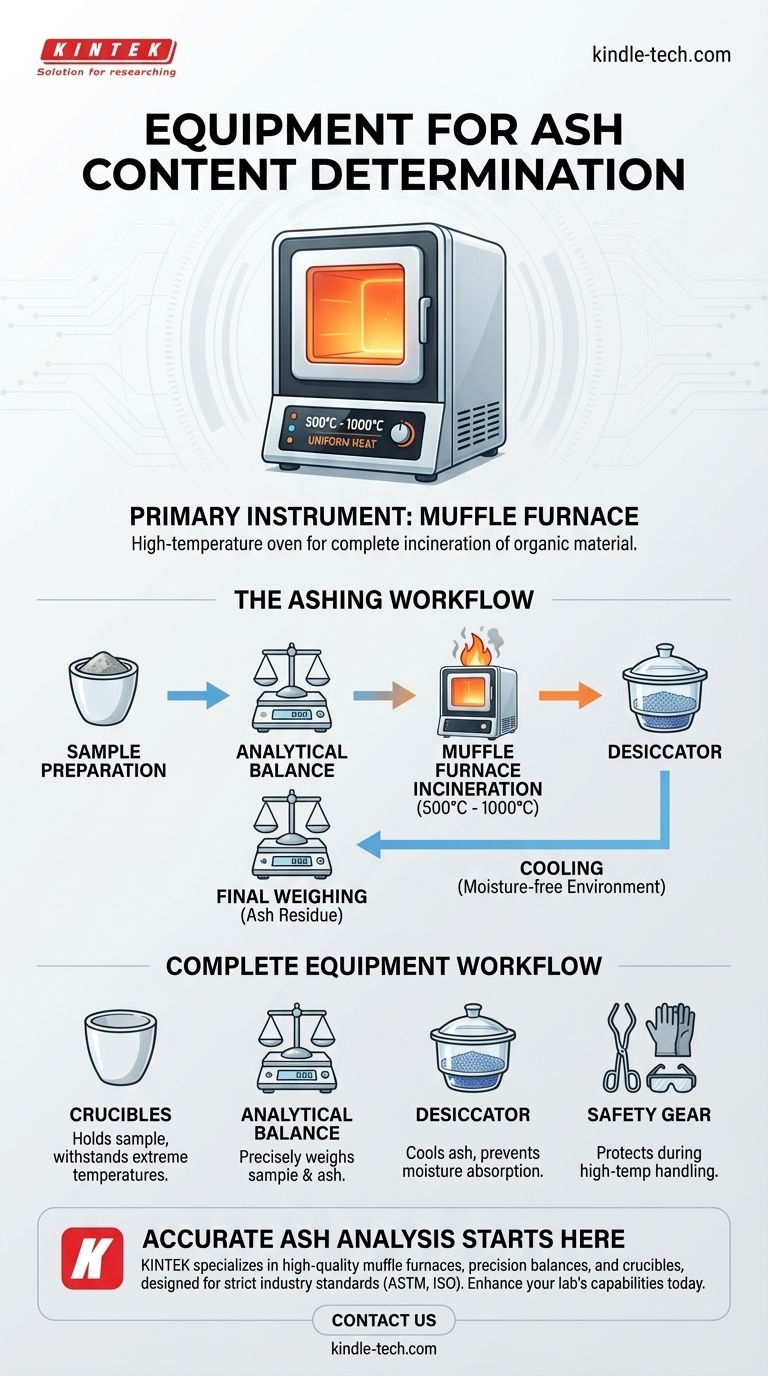
The primary instrument used for determining ash content is a muffle furnace. This is a high-temperature oven designed to completely incinerate the combustible, organic material within a sample. This process leaves behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue—known as ash—which can then be weighed to calculate its percentage of the original sample.
The core of ash analysis is not just a piece of equipment, but a process of controlled thermal decomposition. A muffle furnace provides the extreme, uniform heat necessary to isolate the inorganic residue that constitutes a sample's ash content.

Understanding the "Ashing" Process
To appreciate the equipment's role, it's essential to understand the goal: separating the organic from the inorganic. Ash content is a direct measure of the mineral and metallic impurities or inorganic fillers in a substance.
### What is Ash?
Ash is the non-combustible residue left after a sample is completely burned. This residue consists of mineral oxides, such as silica, alumina, iron oxide, and calcium oxide, which were present in the original material.
### Why Measure Ash Content?
This measurement is a critical indicator of quality and composition in many industries. It's used to determine the purity of fuels, the mineral content of food products, and the amount of inorganic filler in plastics and polymers.
The Role of the Muffle Furnace
A standard oven cannot achieve the temperatures or control required for complete combustion. This is the specific purpose of the muffle furnace in ash analysis.
### How it Works
A muffle furnace is a front-loading box-type oven with an insulated chamber. It uses high-resistance heating elements to achieve extremely high and, crucially, uniform temperatures, often ranging from 500°C to over 1000°C (932°F to 1832°F). The "muffle" design ensures the sample is heated without being exposed to the direct flame of a fuel source.
### Key Features for Ashing
A furnace suitable for ashing must have precise temperature control to follow specific industry standards (like ASTM or ISO). It also requires excellent temperature uniformity throughout the chamber to ensure every part of the sample incinerates at the same rate, yielding a reliable and repeatable result.
The Complete Equipment Workflow
While the furnace is the central component, accurate analysis requires a set of supporting equipment to manage the sample before and after combustion.
### 1. Crucibles
Samples are placed in crucibles, which are ceramic or porcelain cups designed to withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with the sample or degrading.
### 2. Analytical Balance
A high-precision analytical balance is essential. The empty crucible is weighed, then weighed again with the sample before ashing, and finally weighed with the resulting ash. The difference in these weights is used to calculate the ash percentage.
### 3. Desiccator
After being removed from the hot furnace, the crucible and its ash contents must be cooled in a desiccator. This is a sealed container with a desiccant that provides a moisture-free environment, preventing the cooled ash from absorbing atmospheric water, which would artificially increase its weight.
### 4. Safety Equipment
Handling items at such high temperatures requires long tongs, heat-resistant gloves, and safety glasses to prevent severe burns and injury.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Simply owning a muffle furnace does not guarantee an accurate result. The integrity of the analysis depends on a strict, repeatable process.
### Ignoring Standard Methods
Different materials require different temperatures and heating durations. Failing to follow the specific standard method for your sample type (e.g., ASTM D482 for petroleum products) will produce a meaningless number.
### Sample Contamination
Using dirty crucibles or allowing the cooled ash to be exposed to open air can introduce contaminants or moisture, leading to inaccurate final weight measurements.
### Mineral Volatility
Be aware that at extremely high temperatures, some inorganic compounds can become volatile and turn to gas. This can cause an underestimation of the true ash content, a factor that must be considered when developing a testing method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your analytical objective determines which part of the process requires the most attention.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize a reliable muffle furnace with programmable controls to ensure you can consistently follow your specific industry standard.
- If your primary focus is material characterization: Your process is paramount. Standardize the use of your analytical balance, desiccator, and sample preparation to ensure maximum accuracy.
- If your primary focus is ensuring safety and repeatability: Invest in proper training and high-quality safety equipment, as consistent handling procedures are key to preventing both injuries and analytical errors.
Ultimately, accurate ash content determination is achieved through a controlled process, for which the muffle furnace is the essential centerpiece.
Summary Table:
| Equipment | Purpose in Ash Analysis |
|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Provides high, uniform heat for complete sample incineration. |
| Crucibles | Holds sample during ashing; withstands extreme temperatures. |
| Analytical Balance | Precisely weighs sample before and after ashing. |
| Desiccator | Cools ash in a moisture-free environment to prevent weight gain. |
| Safety Gear (Tongs, Gloves) | Protects the user when handling hot materials. |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable ash content analysis in your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including durable muffle furnaces, precision balances, and essential consumables like crucibles. Our products are designed to meet strict industry standards (ASTM, ISO), ensuring your quality control and material characterization processes are accurate, efficient, and safe.
Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab's needs and let our experts help you enhance your analytical capabilities.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing



















