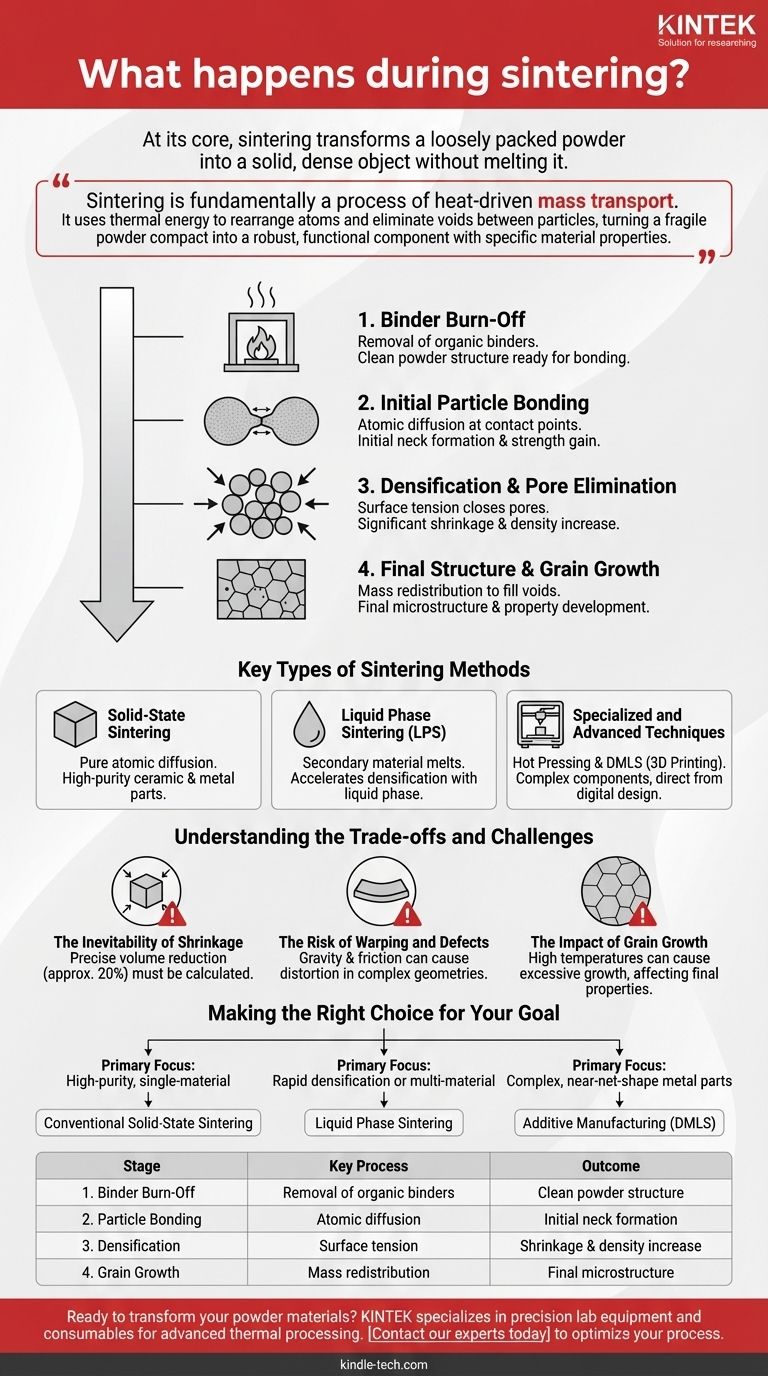
At its core, sintering transforms a loosely packed powder into a solid, dense object without melting it. The process involves heating a compacted powder, known as a "green body," to a high temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, the individual particles begin to fuse together through atomic diffusion, eliminating the empty spaces (pores) between them and causing the entire part to shrink and increase in density.
Sintering is fundamentally a process of heat-driven mass transport. It uses thermal energy to rearrange atoms and eliminate voids between particles, turning a fragile powder compact into a robust, functional component with specific material properties.

The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Sintering is not a single event but a carefully controlled sequence of stages. Each stage plays a critical role in transforming the initial powder into a final, solid part.
Stage 1: Binder Burn-Off
Before high-temperature bonding can begin, any residual organic binders used to hold the powder in its initial shape must be removed. The component is heated slowly in a furnace to allow these binders to safely evaporate or burn off without damaging the part.
Stage 2: Initial Particle Bonding
As the temperature rises, atoms at the contact points between powder particles become more mobile. This atomic movement, known as diffusion bonding, creates small "necks" between adjacent particles, effectively tacking them together. The part begins to gain strength during this initial fusion.
Stage 3: Densification and Pore Elimination
The primary driver of sintering is surface tension, which works to minimize the high surface area of the individual pores. As the necks between particles grow, they pull the centers of the particles closer together. This collective action systematically closes the channels of pores, reducing the overall porosity and significantly increasing the part's density.
Stage 4: Final Structure and Grain Growth
In the final stage, mass is redistributed to eliminate the last remaining isolated pores. Atoms migrate along crystal boundaries to fill these voids, smoothing the internal structure. During this phase, the individual crystals, or grains, in the material may also grow, which can influence the final mechanical properties like strength and toughness.
Key Types of Sintering Methods
While the underlying principle remains the same, different methods are used to achieve specific outcomes for different materials and applications.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common form, where the material remains entirely in a solid state throughout the process. It relies purely on atomic diffusion to bond particles and is widely used for creating high-purity ceramic and metal parts.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In this technique, a small amount of a secondary material with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. During heating, this secondary material melts, creating a liquid phase that coats the solid particles. This liquid accelerates particle rearrangement and bonding, often resulting in faster and more complete densification.
Specialized and Advanced Techniques
Modern manufacturing employs several specialized methods. Hot Pressing combines heat with external pressure to accelerate densification. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is a 3D printing process that uses a laser to sinter metal powder layer-by-layer, creating complex components directly from a digital design.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Sintering is a powerful process, but it requires careful control to achieve the desired outcome. Understanding its inherent challenges is critical for success.
The Inevitability of Shrinkage
Because sintering eliminates porosity, a significant and predictable amount of shrinkage always occurs. This volume reduction, often around 20%, must be precisely calculated and accounted for when designing the initial "green" part to ensure the final component meets dimensional specifications.
The Risk of Warping and Defects
During the process, the part is in a mechanically weak state. Forces like gravity or friction with the furnace support can cause components, especially those with complex or unsupported geometries, to warp, sag, or distort.
The Impact of Grain Growth
While necessary for full densification, the high temperatures of sintering can also cause excessive grain growth. Overly large grains can sometimes negatively affect a material's final properties, such as making it more brittle. The process must be optimized to balance pore elimination with controlled grain size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering approach depends entirely on the desired material properties and the application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, single-material components: Conventional solid-state sintering is the standard, offering precise control over the final composition.
- If your primary focus is rapid densification or processing multi-material composites: Liquid phase sintering is often more efficient due to the accelerating effect of the molten phase.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, near-net-shape metal parts: Additive manufacturing techniques like DMLS, which integrate sintering, are the leading choice.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about controlling heat and mass transport to transform simple powders into highly engineered materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Binder Burn-Off | Removal of organic binders | Clean powder structure ready for bonding |
| 2. Particle Bonding | Atomic diffusion at contact points | Initial neck formation and strength gain |
| 3. Densification | Surface tension closes pores | Significant shrinkage and density increase |
| 4. Grain Growth | Mass redistribution to fill voids | Final microstructure and property development |
Ready to transform your powder materials into high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermal processing. Whether you are developing new materials in R&D or manufacturing robust parts, our sintering solutions provide the control and reliability you need to achieve consistent density, strength, and dimensional accuracy.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering challenges and help you optimize your process for superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















