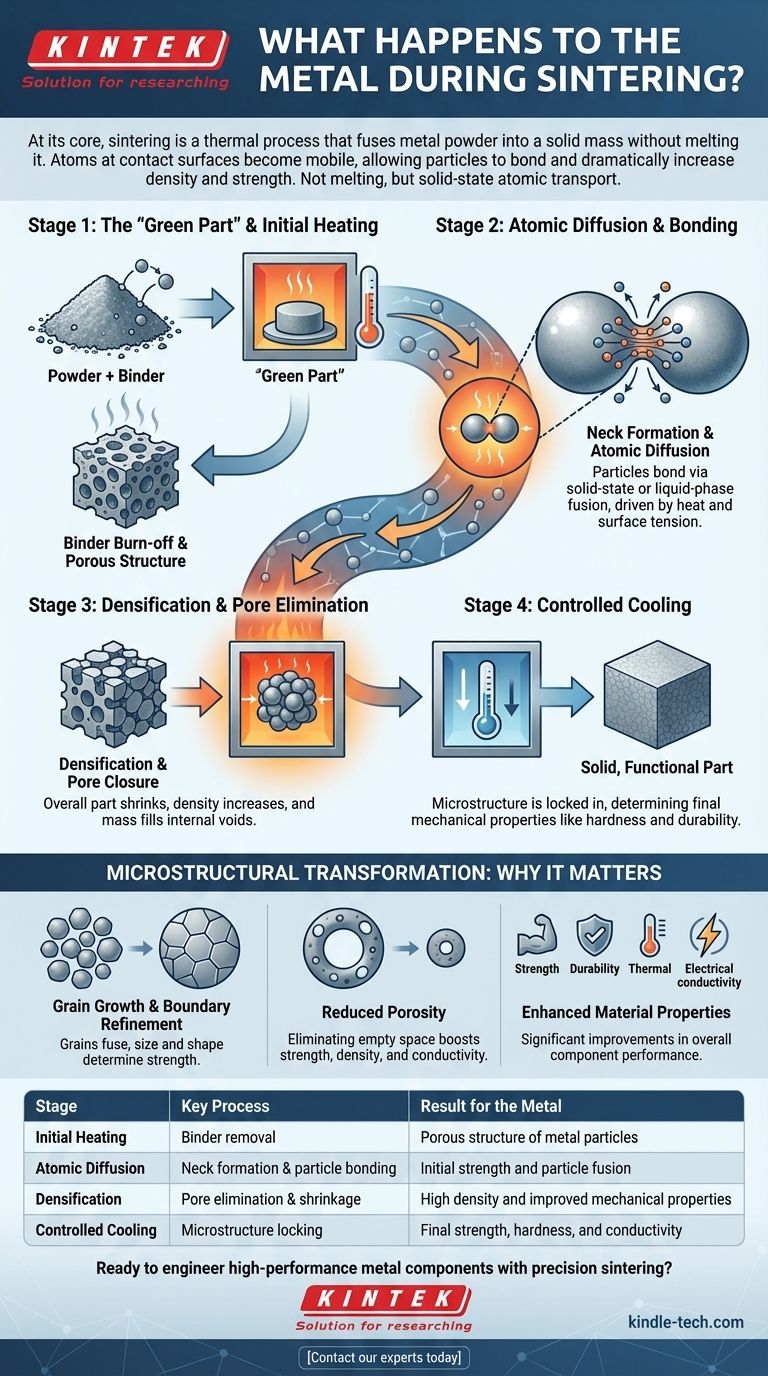
At its core, sintering is a thermal process that fuses metal powder into a solid mass without melting it. During this process, individual metal particles are heated to a point where atoms at their contact surfaces become mobile, allowing the particles to bond together, which reduces empty space and dramatically increases the material's density and strength.
The crucial takeaway is that sintering is not about melting. It is a solid-state atomic transport phenomenon where heat and pressure compel individual particles to fuse, fundamentally transforming a loose powder into a dense, engineered component.

The Sintering Process: A Microscopic Journey
To understand what happens to the metal, we must look at the process in distinct stages. It begins with a pre-formed shape and ends with a solid, functional part.
Stage 1: The "Green Part" and Initial Heating
Before the primary process begins, fine metal powders are blended and compacted into the desired shape, often using a binder like wax or polymer. This initial, fragile piece is known as the "green part."
When placed in a furnace, the first step is a low-temperature bake to burn off or evaporate this binder. This leaves behind a porous structure of loosely-connected metal particles, ready for transformation.
Stage 2: Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
This is the heart of the sintering process. As the temperature rises to just below the metal's melting point, the atoms gain significant thermal energy.
At the points where particles touch, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries, forming small bridges or "necks." This phenomenon, driven by surface tension, is called atomic diffusion. The particles begin to merge.
There are two primary ways this fusion occurs:
- Solid-State Sintering: The primary metal particles themselves begin to fuse at their surfaces where they are in contact.
- Liquid-Phase Sintering: A secondary material with a lower melting point (like bronze mixed with tungsten) melts and flows into the gaps between the primary particles, acting as a cement.
Stage 3: Densification and Pore Elimination
As atoms continue to move and the necks between particles grow wider, the particles pull closer together. This systematically closes the gaps and pores between them.
The overall part shrinks in size, and its density increases dramatically. Mass is redistributed from the particles themselves to fill the internal voids, transforming the porous structure into a solid mass.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling
Once densification is complete, the part is cooled in a controlled manner. This final step is critical as it locks in the final microstructure of the material, such as specific crystalline structures, which dictates its ultimate mechanical properties like hardness and durability.
The Microstructural Transformation: Why It Matters
The changes that occur during sintering are not just cosmetic; they represent a fundamental re-engineering of the material at a microscopic level, which directly impacts its real-world performance.
Grain Growth and Boundary Refinement
Initially, each powder particle is a separate grain. Sintering causes these individual grains to fuse and grow into larger, interconnected crystalline structures. The shape and size of these final grains are a key determinant of the material's strength.
Reduced Porosity
The most obvious outcome of sintering is the reduction of porosity—the empty space between particles. Eliminating these voids is the primary source of the sintered part's enhanced strength, density, and thermal and electrical conductivity.
Enhanced Material Properties
The direct result of this transformation is a suite of improved properties. The final component is significantly stronger and more durable than the initial compacted powder. Its improved internal structure allows for better conduction of heat and electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is a process with specific characteristics and is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Incomplete Densification
Achieving 100% theoretical density is extremely difficult with sintering alone. Most sintered parts will retain a small amount of residual porosity, which must be accounted for in engineering calculations, especially for high-stress applications.
Process Control is Critical
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to the initial powder quality, furnace temperature, heating time, and atmospheric conditions. Inconsistent process control can lead to significant variations in performance.
It Is Not a Casting or Forging Process
Sintering creates a unique grain structure that is different from a part that has been melted and cast or one that has been mechanically forged. This is neither inherently better nor worse, but it produces different mechanical characteristics that must be understood for the specific application.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of manufacturing process should be driven entirely by the final goal for your component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex shapes: Sintering is an exceptional choice, as it minimizes material waste and can produce net-shape parts that require little to no machining.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum theoretical density: Processes like forging or hot isostatic pressing (which can be a secondary step after sintering) may be more suitable.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials like tungsten or molybdenum: Sintering is often the most practical and energy-efficient method available, as it avoids the extreme temperatures needed for melting.
Ultimately, understanding sintering empowers you to engineer material properties with precision, building a final component from the atomic level upward.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Result for the Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Heating | Binder removal | Porous structure of metal particles |
| Atomic Diffusion | Neck formation & particle bonding | Initial strength and particle fusion |
| Densification | Pore elimination & shrinkage | High density and improved mechanical properties |
| Controlled Cooling | Microstructure locking | Final strength, hardness, and conductivity |
Ready to engineer high-performance metal components with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for controlled sintering processes. Whether you are developing complex, net-shape parts or working with high-melting-point materials, our solutions help you achieve the exact density, strength, and material properties your project demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum oven utilized for ruthenium chloride pre-treatment? Ensure High-Precision Si-RuO2 Catalyst Preparation
- What is conduction in vacuum? Understanding Heat Transfer in the Absence of Matter
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven for NH4H2PO4-coated NCM811? Optimize Your Battery Precursor Prep
- What is the difference between gasification pyrolysis and combustion? Choose the Right Thermal Process
- Why is it important to hardening a steel? To Achieve Superior Strength and Wear Resistance
- What are the different types of annealing furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in Na3FePO4CO3 electrodes? Ensure Peak Performance with Advanced Purification
- What temperature is hardening heat treatment? Master the Critical Range for Superior Steel Hardness



















