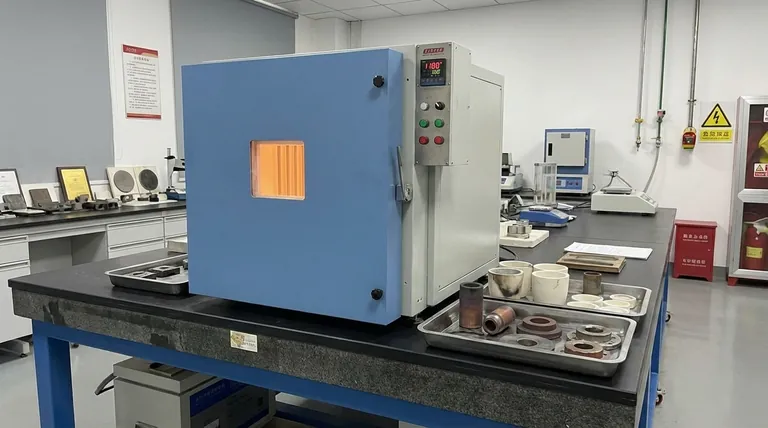
In short, a box furnace is a high-temperature oven used for a wide range of thermal processes. It serves as a fundamental tool in laboratories and industries for heat-treating metals, sintering ceramics, and conducting material analysis. Its simple, chamber-like design makes it exceptionally versatile for tasks requiring temperatures from moderate to very high.
The core value of a box furnace is not specialization, but versatility. It is the general-purpose workhorse for batch thermal processing, adaptable to countless materials and applications in research, development, and small-scale production.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Processing
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, provides a controlled, high-temperature environment. Its applications fall into several key categories.
Heat Treating Metals
This involves altering the physical and mechanical properties of metals.
Box furnaces are ideal for small steel parts and other metals, enabling processes like annealing (softening the metal), quenching (rapidly cooling to harden), and tempering (reducing brittleness after hardening).
Sintering and Firing Materials
Sintering is the process of using heat to fuse powders into a solid, coherent mass without melting them.
This is a primary application in fields like ceramics, metallurgy, and powdered materials. The furnace is used for everything from firing technical ceramics to sintering metal powders into a final part.
Material Analysis and Synthesis
In research settings, box furnaces are indispensable for testing and creating new materials.
Scientists and engineers use them for element analysis, determining the composition of a sample, and for synthesizing novel compounds like nanomaterials or specialized alloys that require high-temperature reactions.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of the box furnace means it is found in nearly every field that deals with materials science.
In Research and Academia
University labs and scientific institutes use box furnaces for foundational experiments. They are critical for everything from high-temperature experiments and material testing to developing new battery components or structural ceramics.
In Industrial Operations
Industrial and mining enterprises rely on box furnaces for both quality control and small-scale production. Applications include powder roasting, treating refractory materials, and performing heat treatments on small batches of manufactured parts.
Specialized Atmosphere Control
A more advanced variant, the box-type atmosphere furnace, allows for processing under a controlled gas.
This is critical for materials sensitive to oxygen. It is used for diffusion welding, treating single-crystal silicon, and the heat treatment of battery materials under a protective, inert atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly versatile, a standard box furnace is not the right tool for every thermal process. Understanding its limitations is key.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The "box" design is inherently for batch processing. You load a part or a set of parts, run the thermal cycle, and then unload them. This is different from a tube furnace, which can be configured for continuous processing of smaller samples.
Atmosphere Purity
A standard box furnace operates in ambient air. While sufficient for many tasks, it is unsuitable for processes requiring high purity. For materials that react with oxygen or nitrogen, a specialized atmosphere furnace or vacuum furnace is required to ensure process integrity.
Operational Diligence is Key
The quality of the result depends heavily on the operator. One must ensure the furnace is clean, monitor the temperature profile accurately, and, in atmosphere furnaces, verify the purity and flow rate of the protective gases. Residues from one process can contaminate the next.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your material, process, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is versatile, general-purpose heat treatment: A standard box furnace is your most flexible and cost-effective choice for a wide variety of materials and batch sizes.
- If your primary focus is processing materials in a specific, pure gas environment: An atmosphere furnace or a tube furnace is necessary to protect your materials from unwanted reactions.
- If your primary focus is treating materials that are extremely sensitive to any atmospheric gas: You must use a dedicated vacuum furnace, which removes all gases from the chamber.
Ultimately, understanding your specific material and process requirements is the key to selecting the right thermal processing tool.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treating | Annealing, Tempering, Hardening | Metallurgy, Manufacturing |
| Sintering & Firing | Fusing powders, Firing ceramics | Ceramics, Powder Metallurgy |
| Material Analysis | Elemental Analysis, Synthesis | Research & Development, Academia |
Ready to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your lab?
Whether you need a versatile standard box furnace for general heat treatment or a specialized atmosphere-controlled model for sensitive materials, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs. We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables that enhance your research and production capabilities.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the muffle furnace analysis? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing for Your Materials
- What critical role does a Muffle Furnace play in the surface protection of metal-supported membranes? Precision Heat!
- What is the function of an external heating high-temperature furnace in SCWG? Optimize Your Biomass Gasification Research
- Which instrument is used for ash determination? Choose the Right Tool for Accurate Results
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in Cu-TiO2 thin films? Achieve Precise Phase Transformation
- What function does a high-temperature sintering furnace serve in biomass carbonization? Unlock Superior MFC Performance
- What are the primary functions of a high-temperature muffle furnace in CaO catalyst production? Master Biodiesel Efficiency
- What conditions does a resistance furnace provide for oxidation tests? Achieve 1300°C Thermal Stability



















