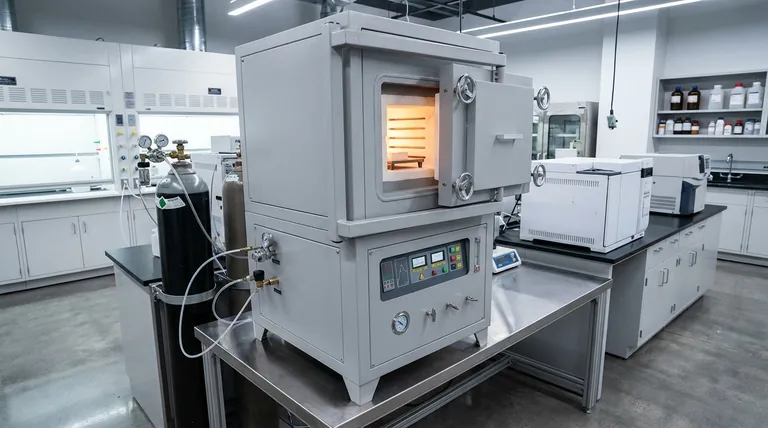
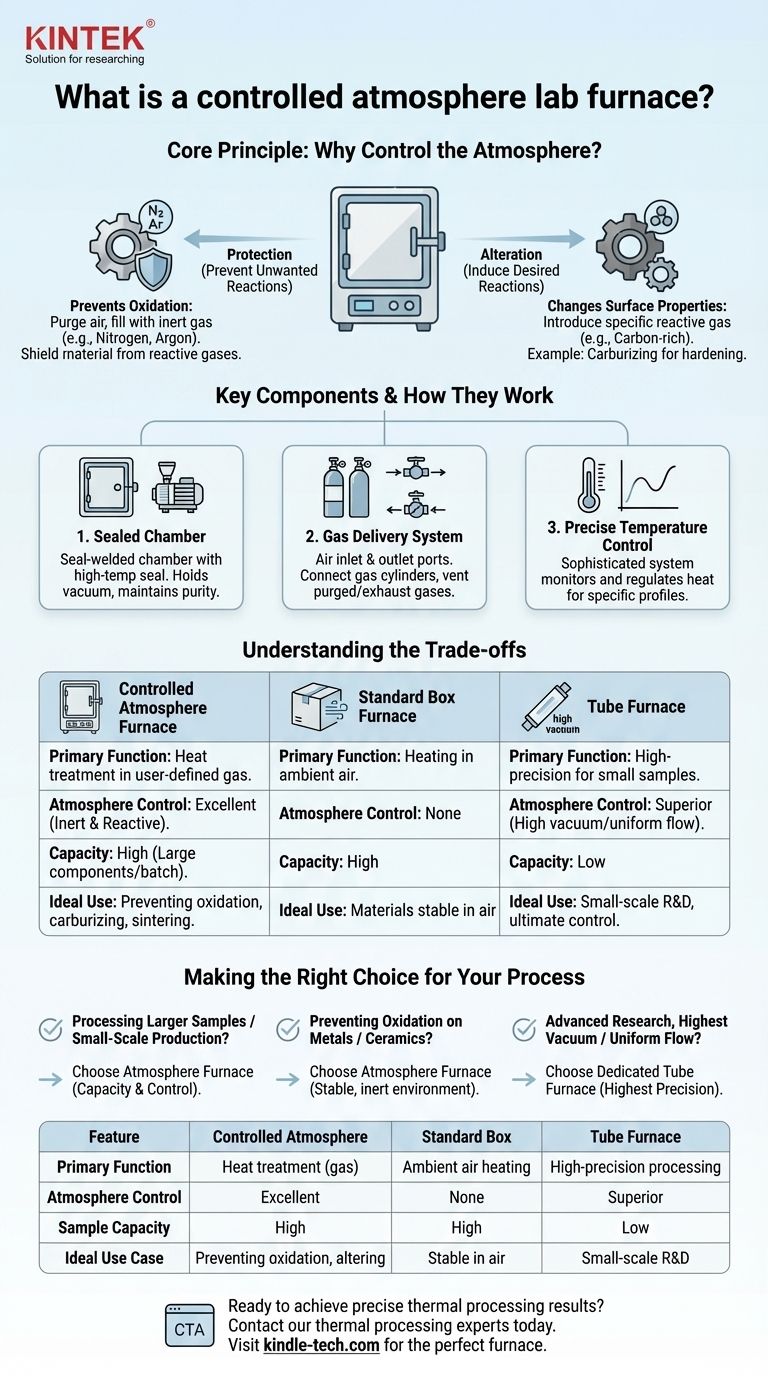
At its core, a controlled atmosphere lab furnace is a high-temperature oven that precisely manages the gaseous environment surrounding a material during heating and cooling. Instead of simply heating a sample in ambient air, this furnace allows you to replace the air with a specific, controlled gas. This is accomplished by using a tightly sealed chamber with gas inlets and outlets, combined with a sophisticated temperature control system.
The crucial insight is that at high temperatures, chemical reactions accelerate dramatically. A controlled atmosphere furnace gives you command over these reactions, allowing you to either protect your material from the reactive gases in air or intentionally alter its properties using a specific gas.

The Core Principle: Why Control the Atmosphere?
The entire purpose of an atmosphere furnace is to manage chemical interactions on a material's surface at elevated temperatures. This function generally falls into two distinct categories: protection and alteration.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions (Protection)
Many materials, especially metals, will readily react with oxygen in the air when heated. This process, known as oxidation, can ruin a sample or component.
An atmosphere furnace prevents this by first purging the air from the chamber (often by pulling a vacuum) and then filling it with an inert gas, like nitrogen or argon. These gases do not easily react with other elements, creating a protective shield around the material.
Inducing Desired Reactions (Alteration)
Sometimes, the goal is not to prevent a reaction but to cause a very specific one. In these cases, a carefully chosen reactive gas is introduced into the furnace.
This is a fundamental technique in materials science for changing a material's surface properties. For example, introducing a carbon-rich gas can harden the surface of steel in a process called carburizing.
Key Components and How They Work
An atmosphere furnace integrates several key systems to achieve its function. It essentially combines the larger capacity of a box furnace with the environmental control of a tube furnace.
The Sealed Chamber
This is the most critical feature. The furnace chamber is seal-welded and features a door with a high-temperature resistant seal (like a silica gel ring). This robust sealing is what allows the furnace to first hold a vacuum and then maintain the purity of the introduced atmosphere.
The Gas Delivery System
The furnace is equipped with an air inlet and outlet. These ports allow you to connect gas cylinders to feed the desired atmosphere into the chamber and vent the purged air or exhaust gases safely.
The Precise Temperature Control System
Atmosphere control is useless without equally precise temperature control. A sophisticated system monitors and regulates the heat, ensuring the material follows a specific temperature profile that works in concert with the controlled atmosphere to achieve the desired result.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is not always the right choice. The decision depends on balancing capacity, cost, and the level of control required.
Atmosphere vs. Standard Box Furnace
A standard box furnace simply heats in ambient air. It is much simpler and less expensive but offers no protection against oxidation or other atmospheric reactions. You would choose a standard furnace only when your material is stable in air at high temperatures.
Atmosphere vs. Tube Furnace
This is a more nuanced comparison. A tube furnace is excellent for achieving a very high-quality vacuum and a highly uniform gas flow over a smaller sample. An atmosphere furnace offers a much larger chamber, making it suitable for bigger components or batch processing.
The primary trade-off is sample size versus ultimate control. For large-scale work, the atmosphere furnace is superior. For highly sensitive, small-scale research that demands the absolute best vacuum, a tube furnace may be more appropriate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace requires clearly defining your primary experimental or production goal.
- If your primary focus is processing larger samples or small-scale production: The atmosphere furnace provides the necessary capacity while still enabling crucial atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on materials like metals or ceramics: The ability to create a stable, inert environment is the most important feature of this furnace.
- If your primary focus is advanced research requiring the highest vacuum or most uniform gas flow: A dedicated tube furnace might offer more precision for your specific, smaller-scale experiments.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal processing equipment is about matching the tool's capabilities to your material's specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Controlled Atmosphere Furnace | Standard Box Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Heat treatment in a user-defined gas environment | Heating in ambient air | High-precision processing for smaller samples |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (Inert & Reactive gases) | None | Superior (Best for high vacuum/uniform flow) |
| Sample Capacity | High (Large components, batch processing) | High | Low |
| Ideal Use Case | Preventing oxidation, carburizing, sintering metals/ceramics | Materials stable in air | Small-scale R&D requiring ultimate control |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing results?
Whether your goal is to protect sensitive materials from oxidation or intentionally alter material properties through processes like carburizing, KINTEK's controlled atmosphere furnaces provide the reliable, sealed environment you need. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution for your specific application, from R&D to small-scale production.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















