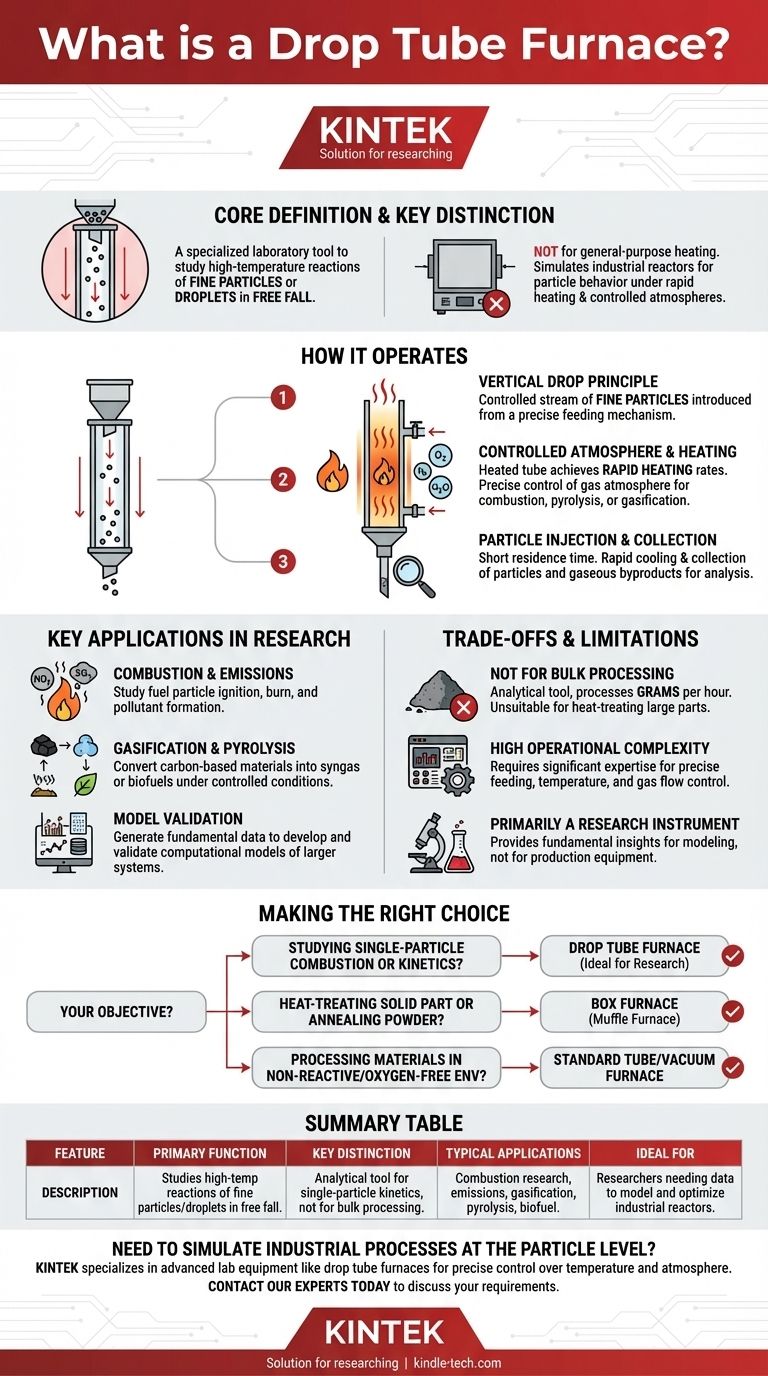
At its core, a drop tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed to study the high-temperature reactions of fine particles or droplets in a controlled environment. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats a stationary bulk sample, a drop tube furnace simulates processes like combustion or gasification by allowing particles to fall vertically through a heated column.
The crucial distinction is that a drop tube furnace is not for general-purpose heating. It is a highly specialized analytical tool used by researchers to investigate the behavior of individual particles under rapid heating and controlled atmospheric conditions, mimicking industrial-scale reactors.

How a Drop Tube Furnace Operates
A drop tube furnace, often called a drop tube reactor (DTR), provides a unique environment to isolate and study particle-level phenomena that are difficult to observe in large, complex systems.
The Vertical Drop Principle
The fundamental design involves a long, vertical tube, typically made of ceramic or a high-temperature alloy, that is externally heated. A precise feeding mechanism at the top introduces a steady, controlled stream of fine particles (like pulverized coal, biomass, or mineral powders) into the furnace.
These particles then fall, or are carried by a gas flow, down the length of the tube.
Controlled Atmosphere and Heating
The tube is heated to very high temperatures, often exceeding 1500°C. This setup is designed to achieve extremely rapid heating rates for the particles, closely simulating the conditions inside industrial boilers or gasifiers.
Crucially, the gas atmosphere inside the tube is precisely controlled. Researchers can introduce specific gases (like oxygen, nitrogen, or steam) to study reactions such as combustion, pyrolysis (thermal decomposition without oxygen), or gasification.
Particle Injection and Collection
After a very short residence time in the heated zone (typically just a few seconds), the particles and any gaseous byproducts are rapidly cooled and collected by a sampling probe at the bottom.
This collected material—both solid and gas—is then analyzed to understand how the particles transformed, what reactions occurred, and how efficiently the process worked.
Key Applications in Research
The unique capabilities of a drop tube furnace make it invaluable for specific areas of scientific and industrial research. Its primary purpose is to generate data that can be used to develop and validate computational models of larger systems.
Combustion and Emissions Studies
Researchers use drop tube furnaces to study how fuel particles, such as pulverized coal or biomass, ignite and burn. This helps in understanding pollutant formation (like NOx and SOx) and developing strategies for cleaner, more efficient combustion.
Gasification and Pyrolysis Research
By controlling the atmosphere, a DTR can be used to study gasification, where carbon-based materials are converted into a useful synthesis gas (syngas). It is also used to investigate pyrolysis, which is a key step in biofuel production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a drop tube furnace is a specialized instrument with clear limitations. Understanding these is key to its proper application.
Not Designed for Bulk Processing
A drop tube furnace is an analytical tool, not a production furnace. It processes material in grams per hour, not kilograms or tons. It is entirely unsuitable for heat-treating parts or sintering large quantities of powder.
High Operational Complexity
Operating a DTR requires significant expertise. Achieving stable particle feeding, maintaining precise temperature profiles, and ensuring accurate gas flow control are all non-trivial challenges. The system is far more complex than a simple box or tube furnace.
Primarily a Research Instrument
The results from a DTR are meant to provide fundamental insights and data for modeling. While this information is critical for designing and optimizing industrial-scale reactors, the furnace itself is not a piece of production equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your objective. A drop tube furnace is a poor choice for general lab work but an essential tool for its niche.
- If your primary focus is studying single-particle combustion or gasification kinetics: A drop tube furnace is the ideal and often necessary tool for this research.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a solid part or annealing a powder sample: A box furnace (muffle furnace) provides the uniform, stable heating needed for bulk materials.
- If your primary focus is processing materials in a non-reactive or oxygen-free environment: A standard tube furnace with gas flow control or a dedicated vacuum furnace is the appropriate choice.
Ultimately, understanding the specific question you need to answer is the first step in selecting the right high-temperature equipment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Studies high-temperature reactions of fine particles/droplets in free fall. |
| Key Distinction | Analytical tool for single-particle kinetics, not for bulk processing. |
| Typical Applications | Combustion research, emissions studies, gasification, pyrolysis, biofuel production. |
| Ideal For | Researchers needing data to model and optimize large-scale industrial reactors. |
Need to simulate industrial processes at the particle level?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including specialized reactors like drop tube furnaces. Our solutions are designed for researchers who require precise control over temperature and atmosphere to study combustion, gasification, and pyrolysis kinetics.
Let us help you select the right equipment to accelerate your R&D. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















