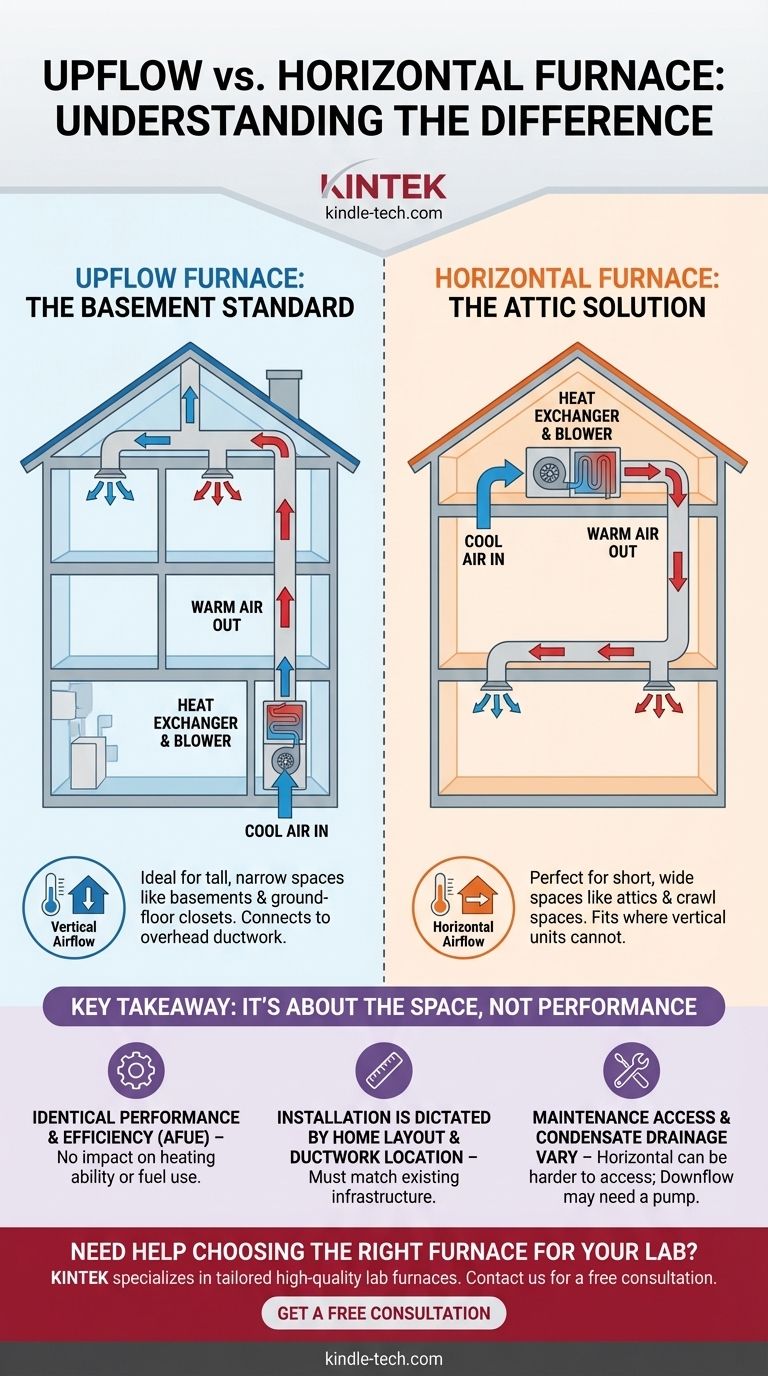
In short, the difference between an upflow and a horizontal furnace is the direction of air movement, which dictates where the unit can be installed. An upflow furnace stands vertically and pulls cool air from the bottom, heating it and pushing warm air out the top. A horizontal furnace lies on its side, pulling air from one end and pushing it out the other, making it suitable for spaces with low ceilings like attics.
The choice between an upflow or horizontal furnace is not about heating performance or efficiency. It is entirely determined by your home's physical layout and the location of your ductwork. The right furnace is the one that fits the designated space.

Understanding Furnace Airflow Configurations
A furnace's "configuration" simply refers to how it's built to move air. The internal components—the blower, heat exchanger, and controls—are arranged to direct airflow in a specific path: up, down, or sideways.
The Upflow Furnace: The Standard for Basements
An upflow furnace is the most common configuration. It stands upright and functions like a chimney for air.
Cool air is drawn into the unit through the bottom or lower side by the blower fan. The air then passes over the heat exchanger, where it is warmed, and is finally expelled through the top of the unit into your home's main duct system (the plenum).
This design is ideal for installations in basements or ground-floor utility closets, where the furnace can sit on the floor and feed ductwork located in the ceilings above.
The Horizontal Furnace: Designed for Attics and Crawl Spaces
A horizontal furnace is essentially an upflow unit designed to operate on its side. It is used in locations where vertical space is limited.
Air enters one side of the long, rectangular cabinet, is heated as it travels lengthwise across the heat exchanger, and exits through the other side.
This configuration is the only option for installations in tight spaces like attics or crawl spaces, where a tall, vertical unit would not fit.
The Downflow Furnace: A Necessary Variation
Though you didn't ask about it, a complete picture includes the downflow furnace. This unit is the mirror image of an upflow furnace.
It pulls air in from the top, heats it, and pushes it out the bottom. This design is used in homes without basements, where the furnace might be located in a closet on the first floor and the ductwork is run underneath in a crawl space or concrete slab.
How Airflow Dictates Installation Location
You cannot simply choose a configuration you prefer; you must select the one that matches your home's infrastructure. The furnace must align with your ductwork for the system to function.
Matching the Furnace to Your Ductwork
The furnace is the heart of a forced-air system. The return air ducts must feed into the furnace's intake, and the supply ducts must connect to its output.
An upflow furnace is designed to connect to return ducts at its base and supply ducts above it. A horizontal furnace is designed for ducts that run parallel to the floor in an attic or crawl space. Trying to install the wrong configuration would require a costly and inefficient re-engineering of your entire duct system.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Space
The decision is ultimately a practical one based on the installation space.
- Tall, narrow spaces (basements, closets) require a vertical unit, typically an upflow furnace.
- Short, wide spaces (attics, crawl spaces) require a horizontal furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the primary difference is physical orientation, there are a few secondary factors to consider that are consequences of the design.
Performance and Efficiency
For any given manufacturer and model line, the heating performance and energy efficiency (AFUE rating) will be identical between upflow, horizontal, and downflow versions. The internal components are the same. The choice has no impact on how well the furnace heats or how much fuel it consumes.
Installation and Maintenance
Horizontal installations in tight attics or crawl spaces can sometimes be more difficult and labor-intensive for technicians to access for repairs or maintenance compared to a freely accessible upflow unit in a basement.
Downflow furnaces have a unique requirement: they must be installed on a special, non-combustible base to protect the floor beneath them from the high heat, which can add a minor cost to the installation.
A Critical Detail: Condensate Drainage
High-efficiency furnaces (those with AFUE ratings of 90% or more) produce acidic water vapor, called condensate, that must be drained away.
In upflow and horizontal units, this drainage can typically be routed using gravity. However, in a downflow configuration, the drain exit is at the bottom of the unit, often requiring a condensate pump to lift the water up to a drain line. This adds a component that requires electricity and can potentially fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
The decision is straightforward once you identify the installation location and existing ductwork.
- If your furnace will be in a basement or a ground-floor closet: You almost certainly need an upflow furnace to connect to ductwork running overhead.
- If your furnace will be in an attic or crawl space: A horizontal furnace is the only configuration that will fit in the limited vertical space.
- If your furnace is on a main floor with ductwork in the slab or crawl space below: You will need a downflow furnace to push air downwards into the duct system.
Choosing the right furnace configuration is about matching the equipment to your home's unique layout, ensuring efficient and reliable airflow for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Airflow Direction | Ideal Installation Location | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upflow Furnace | Pulls air from bottom, expels from top | Basements, ground-floor closets | Connects to overhead ductwork |
| Horizontal Furnace | Pulls air from one side, expels from the other | Attics, crawl spaces | Fits in low-ceiling spaces |
| Downflow Furnace | Pulls air from top, expels from bottom | Main floor with slab/crawl space below | May require condensate pump |
Need Help Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Lab?
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is critical for efficient and reliable operation in your laboratory. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab furnaces tailored to your specific space and workflow requirements. Whether you need an upflow, horizontal, or custom configuration, our experts will help you find the perfect solution to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Contact us today to discuss your lab's heating needs and discover how KINTEK's reliable equipment can enhance your research and processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















