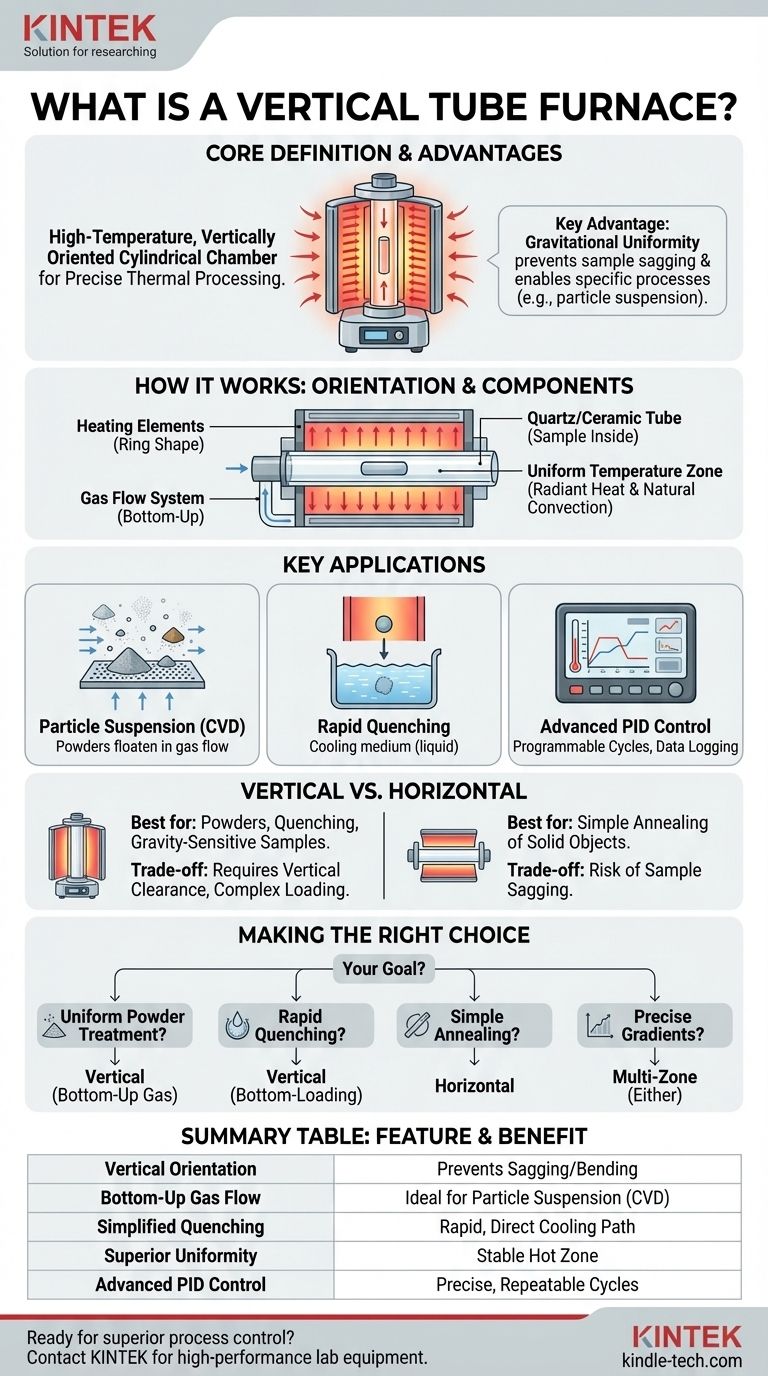
At its core, a vertical tube furnace is a high-temperature heating device distinguished by its vertically oriented cylindrical chamber. Materials placed inside this chamber are heated by surrounding elements, allowing for precise thermal processing in a controlled atmosphere. The vertical design is not arbitrary; it is engineered to provide exceptionally uniform temperature distribution and enable specific material processing techniques.
The decision to use a vertical tube furnace over a horizontal one is driven by the specific demands of your process. Its unique orientation is a deliberate design choice that excels at tasks requiring gravitational uniformity, particle suspension, or specific sample loading and unloading methods that are impractical in a horizontal setup.

How a Vertical Tube Furnace Works
Understanding the function of a vertical tube furnace begins with its defining characteristic: its orientation. This design directly influences its performance and ideal applications.
The Vertical Orientation
The furnace tube is positioned upright, with the sample loaded from either the top or bottom. This vertical alignment ensures that gravitational forces act uniformly on the sample, preventing issues like sagging or bending that can occur in horizontal furnaces with long or delicate materials at high temperatures.
Core Components and Their Roles
A typical system consists of a few key parts. A high-purity quartz or ceramic tube contains the sample and the controlled atmosphere. Heating elements, often arranged in a ring shape, encircle this tube to provide heat. A gas flow system introduces gases, often from the bottom, to create the desired processing atmosphere or to suspend particles.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber and surrounding elements are designed for efficient, radiant heat transfer. This construction, combined with the natural convection currents within the vertical tube, creates a highly stable and uniform temperature zone along the sample's length, which is critical for consistent material processing.
Key Applications and Advantages
The vertical design makes this type of furnace uniquely suited for several advanced applications that are difficult to achieve with other furnace types.
Ideal for Particle Suspension and Deposition
For processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on powders, gas is introduced from the bottom of the tube. This flow can suspend the powder sample on a porous plate, creating a "fluidized bed" where each particle is uniformly exposed to the reactive gases and heat.
Superior for Quenching and Gravity-Sensitive Processes
Quenching, or rapid cooling, is simplified in a vertical furnace. A sample can be heated and then quickly dropped from the hot zone into a quenching medium (like water or oil) placed directly below the furnace, ensuring a rapid and uniform cooling rate.
Advanced Process Control
Modern vertical tube furnaces feature sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers. These allow for precise, programmable heating and cooling cycles with multiple temperature segments. Features like over-temperature protection and data logging are standard, ensuring both safety and process repeatability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vertical tube furnace is not the default choice for every application. Understanding its trade-offs compared to the more common horizontal furnace is key.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Furnaces
A horizontal furnace is often simpler and more cost-effective for basic annealing or heat treatment of stable, solid samples. The choice for a vertical furnace is made when the process benefits directly from its orientation, such as with powders, gravity-sensitive melts, or drop-quenching requirements.
Space and Accessibility
By nature, a vertical furnace requires more vertical clearance. Depending on the model, it may need to be mounted on a specialized stand or integrated into a larger processing rig. Sample loading can also be more complex, involving top-loading holders or bottom-loading mechanisms.
Sample Handling Nuances
While a horizontal furnace allows you to simply slide a sample boat into the tube, a vertical furnace may require specialized crucibles or holders to suspend the sample in the center of the hot zone. This can add a layer of complexity to the setup but is essential for the processes it enables.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace configuration requires matching the equipment's capabilities to your specific processing needs.
- If your primary focus is uniform powder treatment or deposition: A vertical furnace with bottom-up gas flow is the superior choice for fluidizing and processing particles.
- If your primary focus is rapid quenching: A bottom-loading vertical furnace provides the most direct and efficient path for dropping a sample into a quenching medium.
- If your primary focus is simple annealing of solid objects: A horizontal furnace is often more practical and cost-effective unless your sample is prone to sagging at high temperatures.
- If you require precise temperature gradients: Consider a multi-zone furnace (available in both vertical and horizontal configurations) to control temperature profiles along the sample length.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical tube furnace is a strategic decision to leverage gravity and thermal dynamics for a more controlled and uniform process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vertical Orientation | Uniform gravitational force prevents sample sagging/bending. |
| Bottom-Up Gas Flow | Ideal for particle suspension and fluidized bed processes like CVD. |
| Simplified Quenching | Sample can be dropped directly into a cooling medium for rapid cooling. |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Cylindrical design and natural convection create a stable hot zone. |
| Advanced PID Control | Ensures precise, programmable, and repeatable heating cycles. |
Ready to achieve superior process control for your lab's powder treatment, CVD, or quenching applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including vertical tube furnaces designed for precision and reliability. Our experts can help you select the right furnace configuration to meet your specific material processing goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why must metal membrane coatings undergo annealing in a tube furnace? Enhance Adhesion and Structural Integrity
- What is the role of a tube reduction furnace in tungsten oxide conversion? Master Metallic Film Production
- What role does a high-temperature tube atmosphere furnace play in Cr/CrxN conversion? Enhance Coating Durability
- How does a laboratory vacuum tube furnace contribute to the pyrolysis of leather scraps into porous carbon materials?
- What is the function of a quartz reaction tube in PROX activity testing? Ensure High-Purity Catalyst Performance
- What is the heating rate for alumina tubes? A Variable Schedule to Prevent Thermal Shock
- Why is a tube furnace required for Se/PPS mercury removal? Optimize Thermal Control for Flue Gas Research
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum tube furnace during creep testing? Ensure Data Integrity at 600-800ºC



















