In short, a furnace for ash determination is a specialized high-temperature oven designed for one specific task: burning away all the organic material in a sample to precisely measure the inorganic, non-combustible residue, known as ash. Unlike a standard lab furnace, its key feature is a system that promotes high airflow, which is critical for ensuring complete combustion and removing smoke.
The crucial difference is not just heat, but control. An ashing furnace is engineered to manage the combustion process with superior airflow, ensuring that the final ash weight is a true and accurate measure of a sample's inorganic content.
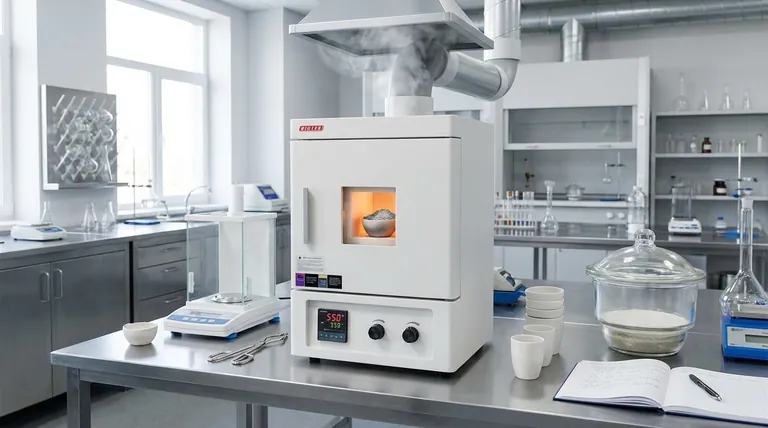

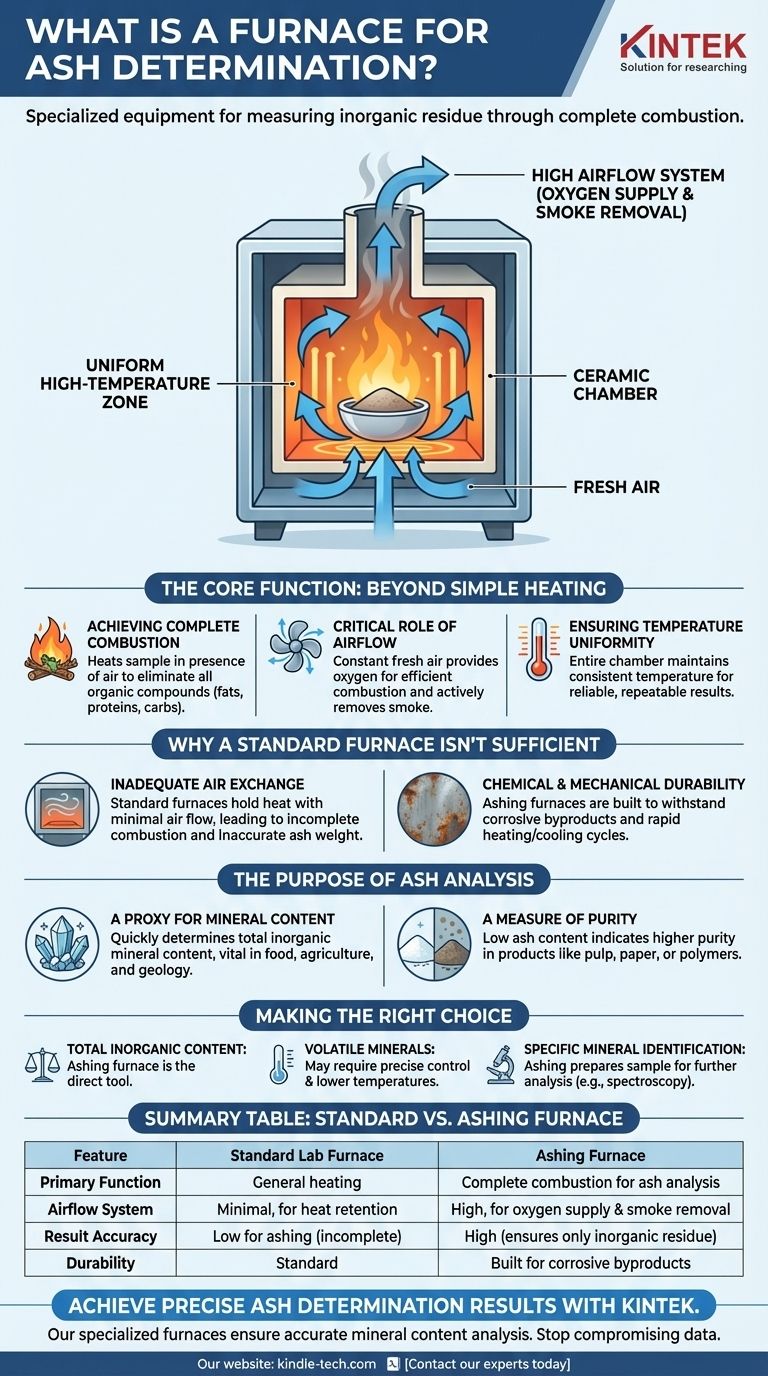
The Core Function: Beyond Simple Heating
The process of determining ash content is formally known as dry ashing. The furnace is the central piece of equipment for this analytical method, and its design is focused entirely on achieving accurate and repeatable results.
Achieving Complete Combustion
The fundamental goal is to heat a prepared sample in the presence of air until it reacts with oxygen and combusts completely. This process is designed to eliminate all organic compounds, such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
The Critical Role of Airflow
This is the defining feature of an ashing furnace. A constant supply of fresh air provides the oxygen necessary for efficient combustion. Simultaneously, this airflow actively removes smoke and other byproducts created during the process, preventing them from contaminating the sample.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
For results to be reliable, the entire sample must be subjected to the same temperature. An effective ashing furnace is designed to provide a highly uniform temperature throughout the entire chamber, ensuring that one part of the sample doesn't burn differently than another.
Why a Standard Furnace Isn't Sufficient
Using a general-purpose laboratory oven or furnace for ash determination is a common mistake that leads to inaccurate data. The specialized design exists to overcome the specific challenges of the ashing process.
Inadequate Air Exchange
A standard furnace is typically designed to hold heat with minimal air exchange. For ashing, this is a critical flaw. Without sufficient oxygen, combustion will be incomplete, leaving behind organic material and artificially inflating the final ash weight.
Chemical and Mechanical Durability
The combustion process can release aggressive or corrosive substances. Ashing furnaces are built from materials that can withstand these chemical attacks as well as the mechanical stress of repeated, rapid heating and cooling cycles.
The Purpose of Ash Analysis
Understanding the furnace's function requires understanding the goal of the analysis itself. Ash determination is a critical quality control metric in many industries.
A Proxy for Mineral Content
The residual ash is primarily composed of inorganic mineral compounds. Measuring the ash content is a quick and effective way to determine the total mineral content of a sample, which is vital in food science, agriculture, and geology.
A Measure of Purity
In many contexts, ash is considered an impurity. For example, in analyzing pulp, paper, or polymers, a low ash content indicates a purer, higher-quality product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The method and equipment are chosen based on the specific information you need to extract from your sample.
- If your primary focus is determining the total inorganic content of a sample: An ashing furnace executing the dry ashing method is the most direct and appropriate tool for the job.
- If you are concerned about losing volatile minerals: You may need a furnace with highly precise temperature control to perform ashing at a lower temperature over a longer period.
- If your goal is to identify specific minerals within the ash: The ashing furnace is only the first step; it prepares the sample for further analysis by methods like spectroscopy.
Ultimately, using a purpose-built ashing furnace is the foundation for achieving accurate and defensible analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Lab Furnace | Ashing Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | General heating | Complete combustion for ash analysis |
| Airflow System | Minimal, for heat retention | High, for oxygen supply & smoke removal |
| Result Accuracy | Low for ashing (incomplete combustion) | High (ensures only inorganic residue remains) |
| Durability | Standard | Built to withstand corrosive byproducts |
Achieve precise and reliable ash determination results with KINTEK.
Our specialized ashing furnaces are engineered with the high airflow and uniform temperature control your laboratory needs for accurate mineral content analysis in food, agriculture, and material science. Stop compromising your data with inadequate equipment.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect ashing solution for your quality control needs. KINTEK specializes in durable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of a muffle furnace? Achieve Uncontaminated, High-Purity Heating
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity with Precise High-Temp Analysis
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it work? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab
- What is the operating temperature of a muffle furnace? From 200°C to 1800°C for Your Application



















