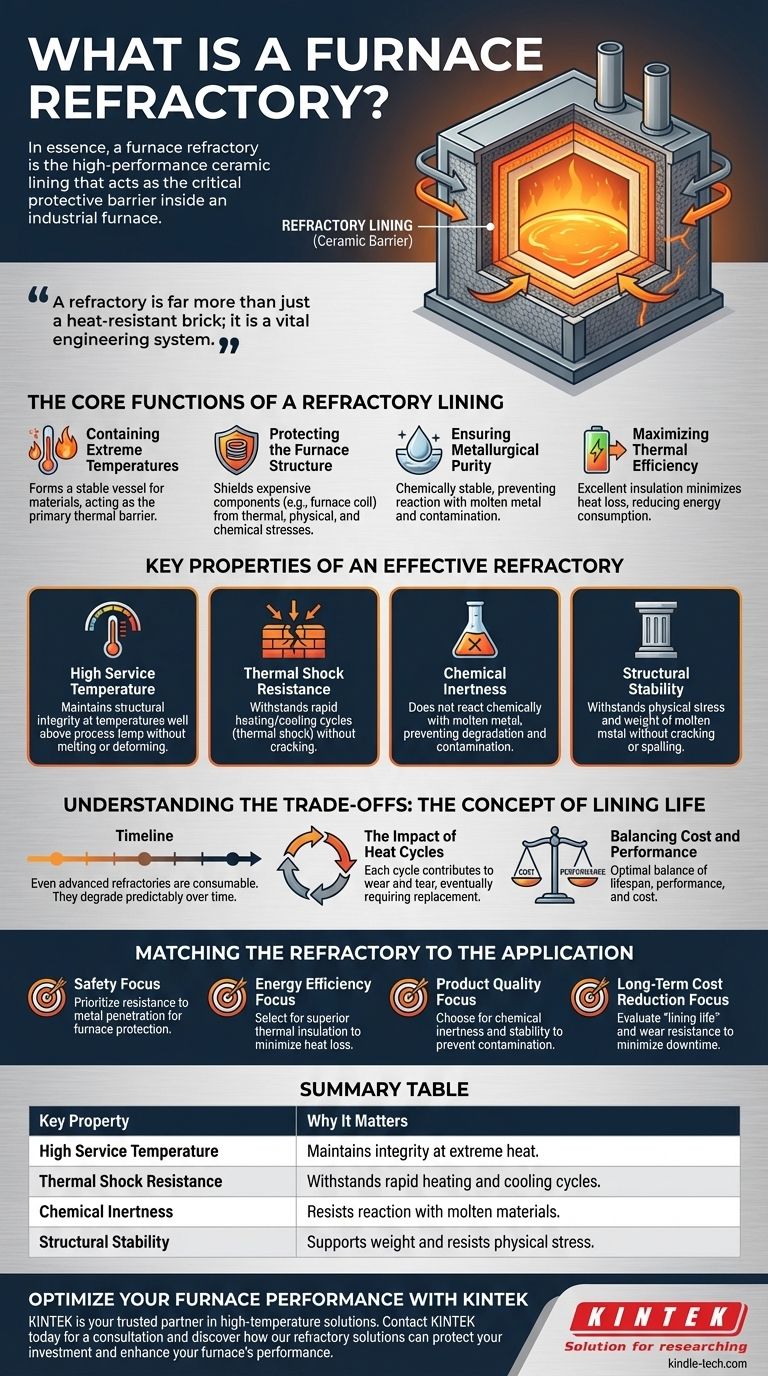
In essence, a furnace refractory is the high-performance ceramic lining that acts as the critical protective barrier inside an industrial furnace. This engineered material is designed to directly contain molten materials, such as aluminum or steel, while simultaneously shielding the furnace's structural components from extreme temperatures and chemical attack.
A refractory is far more than just a heat-resistant brick; it is a vital engineering system. Its core purpose is to contain immense heat, protect the furnace's expensive equipment, and ensure the purity of the final product, all while maximizing energy efficiency.

The Core Functions of a Refractory Lining
A refractory lining is a multi-function component that is indispensable for the safe and efficient operation of any high-temperature furnace.
Containing Extreme Temperatures
The most fundamental job of a refractory is to form a stable vessel for materials at temperatures far exceeding the melting point of the furnace's metal shell. It acts as the primary thermal barrier.
Protecting the Furnace Structure
This lining is the only thing standing between the molten metal and the furnace's induction system. It protects critical and expensive components, like the furnace coil, from thermal, physical, and chemical stresses that would otherwise cause catastrophic failure.
Ensuring Metallurgical Purity
An effective refractory must be chemically stable. It is designed to resist reacting with the molten metal it contains, preventing contamination from "slag" or other impurities that would degrade the quality of the final product.
Maximizing Thermal Efficiency
By providing excellent thermal insulation, the refractory lining minimizes heat loss to the outside environment. This containment of energy directly translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
Key Properties of an Effective Refractory
The extreme environment inside a furnace demands materials with a unique combination of properties. The quality of a refractory is defined by its ability to perform under these demanding conditions.
High Service Temperature
This is the most obvious requirement. The material must maintain its structural integrity at temperatures well above the process temperature without melting, softening, or deforming.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnaces are not always on; they are heated up and cooled down. A good refractory must withstand these rapid temperature changes—known as thermal shock—without cracking or failing.
Chemical Inertness
The refractory must not react chemically with the molten metal it holds. This prevents both the degradation of the lining and the contamination of the metal bath.
Structural Stability
Beyond just heat, the refractory must withstand the physical stress from the weight and movement of molten metal. It must not crack or shed pieces (spall) into the melt during operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Concept of Lining Life
Even the most advanced refractories are consumable materials. They are designed to wear out over time in a predictable way, sacrificing themselves to protect the furnace.
Inevitable Degradation
The constant assault of extreme heat, chemical attack, and physical stress means that every refractory lining will eventually degrade. This is an expected part of the furnace's operational cycle.
The Impact of Heat Cycles
The operational life of a refractory is often measured in "lining life" or the number of heat cycles it can endure. Each cycle of heating and cooling contributes to wear and tear, eventually requiring repair or complete replacement.
Balancing Cost and Performance
Choosing a refractory involves a critical trade-off. A cheaper initial installation might lead to a shorter lining life, causing more frequent downtime and higher long-term costs. The goal is to select a material that provides the optimal balance of performance, lifespan, and cost for a specific application.
Matching the Refractory to the Application
The ideal refractory choice depends entirely on the operational priorities of the furnace.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Choose a refractory with a proven record of resisting metal penetration to protect the furnace coil and structure.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize materials with superior thermal insulation properties to minimize heat loss and reduce consumption.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Select a refractory known for its chemical inertness and stability to prevent contamination of the molten metal.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost reduction: Evaluate the refractory's expected "lining life" and resistance to wear to minimize costly downtime and replacement frequency.
Ultimately, selecting the right refractory is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts furnace safety, efficiency, and profitability.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| High Service Temperature | Maintains integrity at extreme heat, well above the melting point of metals. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists reaction with molten materials to prevent product contamination. |
| Structural Stability | Supports the weight of molten metal and resists physical stress. |
Optimize Your Furnace Performance with the Right Refractory Solution
Selecting the correct refractory lining is a critical decision that directly impacts your furnace's safety, efficiency, and product quality. The wrong choice can lead to costly downtime, energy waste, and product contamination.
KINTEK is your trusted partner in high-temperature solutions. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-performance refractory materials tailored to your specific application—whether your priority is operational safety, energy efficiency, or product purity.
Let our experts help you:
- Extend Lining Life: Minimize downtime and replacement costs.
- Improve Energy Efficiency: Reduce heat loss and lower operational expenses.
- Ensure Product Quality: Prevent contamination with chemically inert materials.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our refractory solutions can protect your investment and enhance your furnace's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food industry? Essential for Accurate Food Ash Analysis
- What does a high ash content mean? A Guide to Material Quality & Contamination
- What is the importance of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What are the five common heat treatments of metals? Master the Processes for Precise Material Properties
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis



















