At its core, a graphite heater is a heating element manufactured from a high-purity carbon composite designed for high-temperature applications. It leverages the inherent properties of graphite to provide exceptional temperature uniformity, long-term stability, and mechanical strength within a furnace or heating system.
The central reason to choose a graphite heater is for its unwavering stability and uniformity in extreme heat. While its mass can affect initial heating speed and it requires careful handling, its longevity and process repeatability are often unmatched in demanding industrial environments.
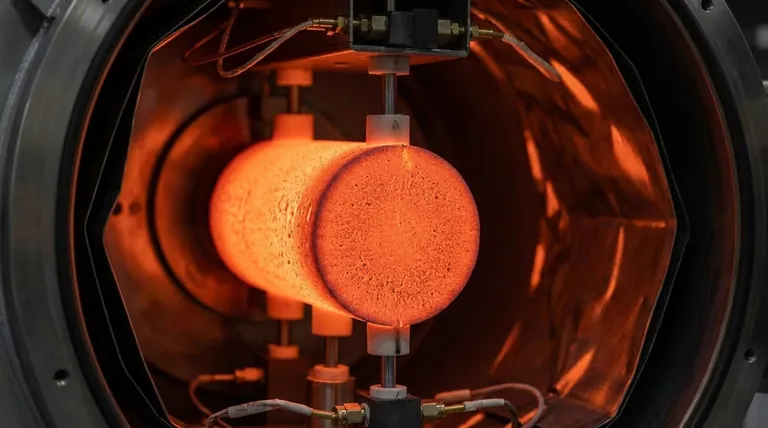
The Core Properties of Graphite Heating Elements
Graphite's unique characteristics make it a specialized material for high-temperature process heating. Understanding these properties is key to knowing when and why to use it.
Material Composition and Purity
Graphite heaters are produced from a carefully refined, high-purity carbon composite. This purity is critical, as it ensures consistent thermal and electrical performance and prevents the introduction of contaminants into the heating process.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
A key advantage of graphite is its ability to distribute heat evenly. This excellent thermal conductivity results in outstanding temperature uniformity across the heating zone, which is crucial for processes requiring precise thermal control.
Exceptional Mechanical Strength
Unlike many materials that weaken at high temperatures, graphite maintains its structural integrity. A graphite hearth is very rigid and holds its shape almost indefinitely, ensuring that the physical structure of the heating system remains stable through countless thermal cycles.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. The decision to use a graphite heater involves acknowledging its specific operational trade-offs.
Thermal Response and Mass
Graphite elements have a heavier mass compared to some alternatives. This can result in slightly slower heating rates, particularly at lower temperatures, as more energy is required to bring the element up to temperature.
However, the good thermal conductivity of graphite tends to minimize this effect, especially once the system reaches its target operational temperature.
Risk of Physical Damage
While structurally rigid, graphite can be brittle. Components like hearth rails are prone to chipping or cracking if subjected to sharp impacts during the loading and unloading of furnace materials. This necessitates careful handling procedures by operators.
Longevity and Process Repeatability
The combination of graphite's properties leads to two significant long-term benefits in an industrial setting.
Extended Service Life
Because graphite maintains its shape and strength under thermal stress, its heating elements have a very long operational life. This durability reduces downtime and the costs associated with frequent element replacement.
Unmatched Process Consistency
The stability of graphite directly translates to repeatability. A heating system that does not deform or degrade provides a consistent environment, ensuring that each production batch is processed under the exact same thermal conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of a graphite heater depends entirely on the priorities of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is process stability and uniformity: Graphite is an excellent choice due to its thermal conductivity and structural rigidity at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is longevity and minimal maintenance: The durability and long service life of graphite heaters make them ideal for reducing operational downtime.
- If your operation involves rough material handling: Be aware of graphite's brittle nature and ensure proper procedures are in place to prevent chipping and impact damage.
Ultimately, choosing a graphite heater is a decision for applications where precision, stability, and long-term reliability are the most critical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Purity | Consistent performance, no contamination |
| Excellent Thermal Conductivity | Superior temperature uniformity |
| High-Temperature Strength | Maintains shape and integrity |
| Long Service Life | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with reliable, high-performance equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing top-tier lab equipment, including robust graphite heating solutions designed for precision and longevity. Our graphite heaters deliver the temperature uniformity and process stability your demanding applications require.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring consistency and reliability to your laboratory processes.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of high-purity graphite electrodes in AC leaching? Powering Efficient Metal Recovery
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod selected as the EIS counter electrode? Ensure Data Integrity and Chemical Stability
- What technical advantages do carbon graphite electrodes offer for electroactive biofilms? Optimize Your Bio-Research
- What are the properties of graphite rods? Leverage High Conductivity for Extreme Applications
- What are the characteristics and applications of a graphite sheet electrode? Maximize Reaction Area for Bulk Electrolysis














