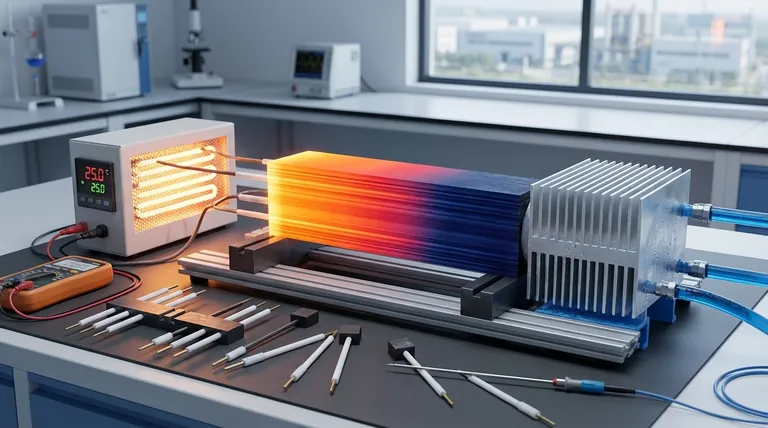
At room temperature, the thermal conductivity of graphite is not a single value but falls within a wide range, typically from 25 to 470 Watts per meter-Kelvin (W/m·K) for common industrial forms. Highly specialized forms like pyrolytic graphite can exhibit exceptionally high in-plane conductivity, reaching up to 2000 W/m·K, which surpasses even copper.
The key to understanding graphite's thermal conductivity is recognizing its profound anisotropy. The material's layered atomic structure causes it to conduct heat exceptionally well along its planes but poorly across them, making the "right" value entirely dependent on the type of graphite and the direction of measurement.
Why Graphite's Thermal Conductivity Varies So Widely
A single number for graphite's thermal properties is misleading. The value you use depends entirely on the material's specific grade and the intended application, as several factors dramatically alter its performance.
The Critical Role of Anisotropy
Graphite's structure consists of strongly bonded layers of carbon atoms (graphene sheets) that are weakly bonded to each other. This creates two distinct pathways for heat.
In-plane conductivity (basal plane) is extremely high. Heat travels rapidly along these layers with minimal resistance, similar to how water flows easily through a wide, open channel.
Through-plane conductivity (across the layers) is significantly lower. Heat must "jump" between the weakly bonded layers, creating a major bottleneck. This is akin to trying to cross a series of disconnected ravines.
The Impact of Form and Grade
Different manufacturing processes result in vastly different structures and, therefore, different thermal properties.
Pyrolytic Graphite is highly ordered, with its layers aligned in parallel. This results in extreme anisotropy, with in-plane conductivity often exceeding 1500 W/m·K (4x copper) and through-plane conductivity as low as 10 W/m·K (similar to stainless steel).
Isotropic Graphite is formed to have a more random grain orientation. This averages out the directional properties, resulting in a more uniform but lower overall conductivity, typically in the 85-130 W/m·K range in all directions.
Natural Graphite Flake has values that vary based on flake size and purity. Individual flakes have high in-plane conductivity, but when pressed together, the overall conductivity is limited by the poor through-plane transfer between them.
The Influence of Density and Purity
Higher density means fewer pores or voids within the material. Since voids act as insulators, a denser graphite part will generally have higher thermal conductivity.
Impurities and defects in the crystalline structure disrupt the pathways for heat transfer (phonon scattering). Therefore, higher purity grades of graphite typically exhibit superior thermal performance.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Simply comparing graphite to metals without context can lead to poor design choices. Its unique properties create specific trade-offs that must be understood.
Misconception 1: It's Always Better Than Copper
While the in-plane conductivity of high-grade pyrolytic graphite can be four times that of copper, its through-plane conductivity is often 20 to 40 times worse.
If your application requires heat to be pulled away from a source (through the material's thickness), a solid piece of copper or aluminum may be far more effective.
Misconception 2: Conductivity Always Increases with Temperature
This statement is generally incorrect for crystalline graphite around room temperature.
The thermal conductivity of most graphite forms peaks near or slightly below room temperature and then decreases as temperature rises further. This is because at higher temperatures, atomic vibrations (phonons) begin to scatter each other, impeding the flow of heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct form of graphite requires matching its anisotropic properties to the primary direction of heat flow in your application.
- If your primary focus is spreading heat across a surface (2D): Choose a highly oriented material like pyrolytic graphite sheet. Its exceptional in-plane conductivity is ideal for heat spreaders in electronics.
- If your primary focus is uniform heat transfer in all directions (3D): Choose an isotropic or molded synthetic graphite. This is best for applications like heating elements, crucibles, or molds where consistent temperature is key.
- If your primary focus is vertical heat transfer through a block: A high-density synthetic graphite block may work, but be aware that metals like copper or aluminum will almost always perform better for this specific task.
Ultimately, treating graphite as a simple number on a spec sheet is a mistake; understanding its directional nature is the key to leveraging its remarkable thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Graphite Type | Typical Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolytic Graphite | In-plane: 1500-2000, Through-plane: ~10 | Highly anisotropic, ideal for 2D heat spreading |
| Isotropic Graphite | 85-130 (all directions) | Uniform properties, good for 3D applications |
| Natural Graphite Flake | Varies widely with flake size/purity | High in-plane conductivity per flake |
| Common Industrial Graphite | 25-470 | Broad range, depends on density and purity |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right graphite material for your specific thermal management challenge?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of graphite products tailored for precise thermal applications. Our experts can help you leverage graphite's unique anisotropic properties to optimize your system's efficiency.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover the perfect graphite solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod selected as the EIS counter electrode? Ensure Data Integrity and Chemical Stability
- What are the properties of graphite rods? Leverage High Conductivity for Extreme Applications
- What are the potential risks when using a graphite electrode in electrochemical tests? Avoid Decomposition and Contamination
- What are the features and common uses of a graphite rod electrode? A Guide to Durable, Simple Electrochemistry
- What technical advantages do carbon graphite electrodes offer for electroactive biofilms? Optimize Your Bio-Research



















