At its core, the hot zone is the insulated, high-temperature heart of a vacuum furnace. It is a distinct internal chamber that contains the heating elements and the workpiece, effectively creating a furnace within the larger vacuum vessel to concentrate thermal energy and perform the actual heating process.
The hot zone is not just the area that gets hot; it is an engineered thermal and insulation system designed to deliver precise, uniform heat to a workpiece while protecting the outer furnace shell from extreme temperatures.
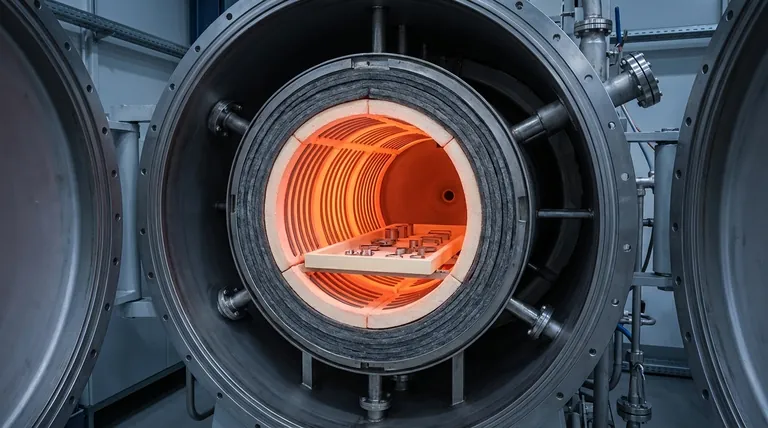
The Purpose of the Hot Zone: A Furnace Within a Furnace
A vacuum furnace's main body is a water-cooled steel vessel designed to hold a vacuum. The hot zone is a separate assembly suspended inside this "cold wall" shell. This design is critical for several reasons.
Containing and Focusing Heat
The primary function of the hot zone is insulation. It is constructed from layers of materials that reflect thermal radiation and prevent heat from escaping.
This creates an incredibly efficient environment, ensuring that the energy produced by the heating elements is directed at the workload, not lost to the surrounding furnace structure.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
By effectively trapping thermal energy, the hot zone allows for extremely stable and uniform temperatures across the entire workpiece.
This uniformity is non-negotiable for high-performance applications like brazing, sintering, and annealing, where even small temperature deviations can compromise the material's final properties.
Protecting the Furnace Structure
The outer furnace shell must remain cool to maintain its structural integrity and the vacuum-tight seals.
The hot zone acts as a thermal shield, keeping the intense heat (often exceeding 2000°F / 1100°C) contained and preventing it from damaging the vessel, controls, and vacuum pumps.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot Zone Materials
The materials used to construct a hot zone dictate its performance characteristics, cleanliness, and cost. The two most common designs are graphite-based and all-metal.
Graphite-Based Hot Zones
Graphite insulation (often rigid felt or board) and graphite heating elements are the industry standard for many applications.
- Pros: Excellent high-temperature performance, durable, and relatively cost-effective.
- Cons: Can produce fine carbon dust, which may not be suitable for ultra-high-purity applications. Can also react with certain sensitive materials.
All-Metal Hot Zones
These hot zones are built using layers of reflective metal sheets (like molybdenum or tungsten) as radiation shields, along with metallic heating elements.
- Pros: Extremely clean, producing no particulate, making them ideal for medical, electronic, and aerospace components. They can also achieve a higher vacuum level.
- Cons: Generally more expensive and have a lower maximum operating temperature compared to some graphite designs.
Matching the Hot Zone to Your Application
Choosing the right furnace begins with understanding your process requirements, which directly map to the hot zone design.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., medical implants, aerospace brazing): An all-metal hot zone is the superior choice to avoid any potential carbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or high-temperature processing (e.g., tool steel hardening, sintering): A graphite-based hot zone offers the best combination of high-temperature capability, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is maximum operational flexibility: Graphite remains the most versatile option, covering the widest range of temperatures and processes for most industrial applications.
Ultimately, understanding the hot zone's design and material is fundamental to controlling the outcome of your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite-Based Hot Zone | All-Metal Hot Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | General heat treating, high-temperature sintering | Medical, aerospace, ultra-high-purity applications |
| Temperature | High-temperature capability | Lower maximum temperature |
| Cleanliness | Potential for carbon dust | Extremely clean, no particulate |
| Cost | Cost-effective | More expensive |
Ready to Specify the Perfect Hot Zone for Your Application?
The right hot zone is critical for achieving precise temperature control, uniform results, and material integrity in your lab. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match your vacuum furnace's hot zone—whether graphite or all-metal—to your specific thermal processing needs, from research and development to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure your furnace delivers peak performance.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What are the advantages of using a Multi-zone Tube Furnace? Enhanced Thermal Uniformity for Diffusion Research
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity



















