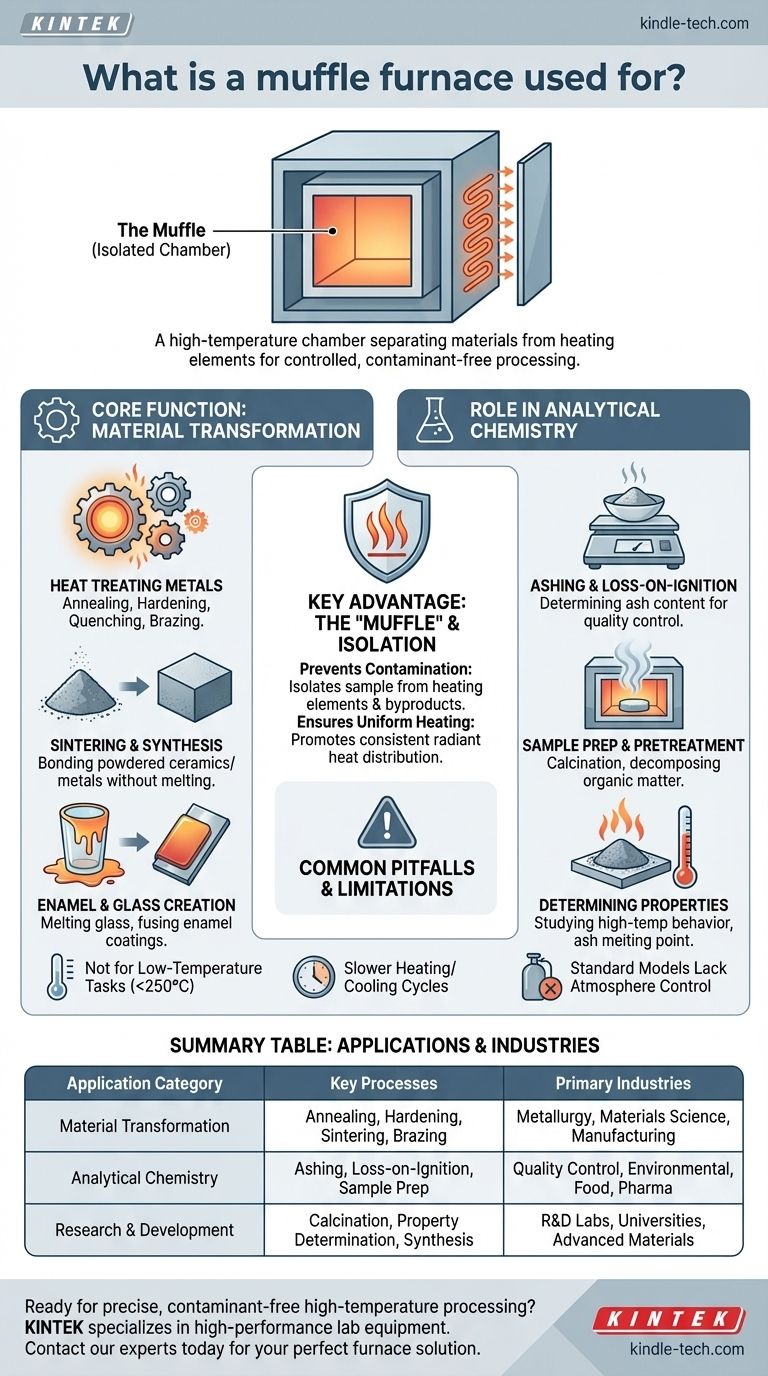
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature chamber used for transforming or analyzing materials in a controlled, isolated environment. Its applications range from heat-treating metals and sintering ceramics to performing critical analytical tests like determining the ash content in a sample for quality control. The key feature is an internal chamber—the "muffle"—that separates the material from the heating elements, preventing contamination.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a specialized tool for processes that demand extreme heat combined with high purity. Its core value lies in isolating the sample from the heating source, which is critical for both materials science and precise chemical analysis.

Core Function: High-Temperature Material Transformation
A primary use of a muffle furnace is to fundamentally alter the physical or chemical properties of a material through intense, controlled heat.
Heat Treating Metals and Alloys
Muffle furnaces provide the precise temperature control needed to change the mechanical properties of metals. This includes processes like annealing (softening), hardening (strengthening), quenching, and brazing (joining metals).
Sintering and Materials Synthesis
The furnace is essential for sintering, a process where powdered materials like ceramics or metals are heated to bond together without melting. This is used to create technical ceramics, special alloys, and other advanced materials.
Creating Enamel and Glass
The high, uniform temperatures are ideal for processes like melting glass for artistic or technical purposes and for fusing enamel coatings onto metal surfaces.
The Role in Analytical Chemistry and Research
The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace makes it an indispensable tool in laboratory settings where sample purity is paramount.
Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
One of its most common uses is ashing. A sample is heated until all organic and volatile substances burn away, leaving only the non-combustible ash. This process is critical for determining the ash content in food, chemicals, and environmental samples for quality control.
Sample Preparation and Pretreatment
In fields like medicine and environmental science, muffle furnaces are used to pretreat samples. This can involve calcination (heating to remove moisture and volatiles) or decomposing organic matter to prepare a sample for further chemical analysis.
Determining Material Properties
Researchers use muffle furnaces to study how materials behave at high temperatures. This includes determining the ash melting point of coal or identifying the chemical properties of materials destined for high-temperature applications.
Understanding the Key Advantage: The "Muffle"
The defining feature that separates this furnace from a simple oven is its design, which directly enables its specialized applications.
What the Muffle Does
The "muffle" is an insulating, high-temperature chamber that houses the sample. The heating elements are located outside of this chamber.
Preventing Contamination
This separation is the furnace's most critical advantage. It protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any gaseous byproducts of combustion. This ensures that the process is pure and the analytical results are accurate.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
The muffle design promotes radiant heating, which results in a highly uniform temperature distribution around the sample. This consistency is vital for repeatable experiments and reliable material treatments.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution for all heating tasks. Understanding its trade-offs is key to using it effectively.
Not for Low-Temperature Tasks
Using a muffle furnace for simple drying or applications below 250°C (about 480°F) is inefficient. A standard laboratory oven is faster and more energy-efficient for these tasks.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The same insulation that ensures temperature stability and uniformity also means the furnace takes a significant amount of time to heat up and cool down. This makes it less suitable for processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
Standard Models Lack Atmosphere Control
A basic muffle furnace operates with the ambient air inside the chamber. For processes that require an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation, a specialized, and more expensive, model is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct instrument, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (quality control, environmental analysis, ashing): The muffle furnace is essential for achieving a pure, contaminant-free environment to ensure accurate results.
- If your primary focus is materials science (sintering ceramics, creating alloys): The furnace's ability to deliver high, uniform temperatures is critical for synthesizing and developing new materials.
- If your primary focus is metalworking (hardening, annealing, brazing): The precise and stable temperature control is necessary to achieve the desired physical properties in metals and alloys.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process requires high heat without compromising the purity of your material.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering, Brazing | Metallurgy, Materials Science, Manufacturing |
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition, Sample Prep | Quality Control, Environmental, Food, Pharma |
| Research & Development | Calcination, Property Determination, Synthesis | R&D Labs, Universities, Advanced Materials |
Ready to achieve precise, contaminant-free high-temperature processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for the demanding needs of quality control, materials science, and research laboratories. Our solutions ensure the uniform heating and sample purity your work requires.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application, from ashing and sintering to heat treatment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- What is the difference between electric oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right High-Temp Lab Equipment



















