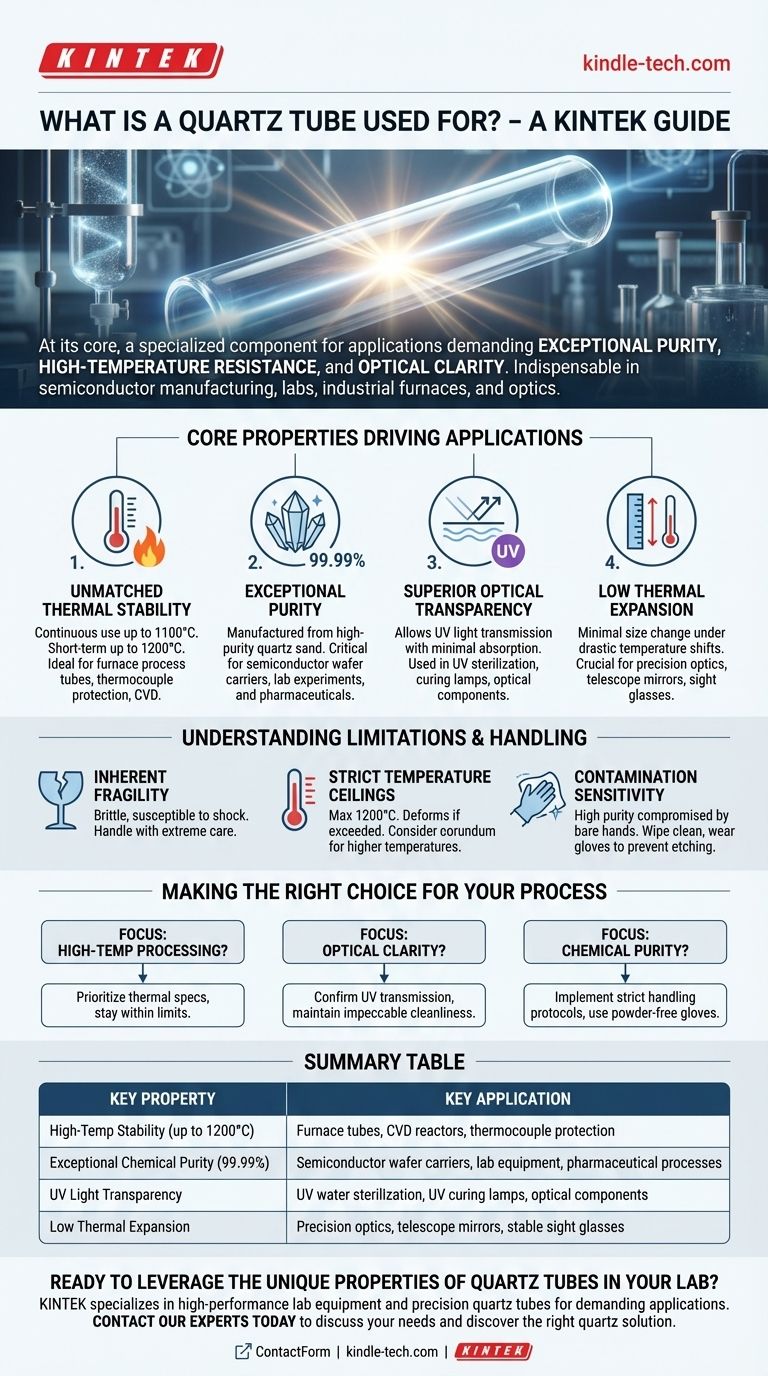
At its core, a quartz tube is a specialized component used in applications demanding exceptional purity, high-temperature resistance, and optical clarity. They are indispensable in processes ranging from semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory experiments to industrial furnaces and optical instruments. Their unique combination of properties makes them the material of choice where standard glass or ceramics would fail.
The true value of a quartz tube lies not in a single feature, but in its rare combination of three key properties: extreme thermal stability, unparalleled chemical purity, and transparency to specific light wavelengths like ultraviolet (UV). Understanding which of these properties is most critical for your goal is the key to using it effectively.

The Core Properties Driving Quartz Tube Applications
The versatility of quartz tubes stems from a few fundamental characteristics of fused quartz. These properties directly enable their use in highly demanding technical environments.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Quartz tubes exhibit excellent resistance to high temperatures. They can be used continuously at temperatures up to 1100°C and for short-term applications up to 1200°C.
This makes them ideal for containing high-temperature processes. They are commonly used as furnace process tubes, thermocouple protection tubes (especially in molten metals), and in procedures like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Exceptional Purity
Manufactured from high-purity quartz sand, these tubes can reach a purity level of 99.99%. This near-absolute purity is critical in environments where contamination would ruin a process.
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on quartz for wafer carriers and processing chambers to prevent impurities from compromising microchips. It is also essential in laboratory and pharmaceutical settings where sample integrity is paramount.
Superior Optical Transparency
Fused quartz allows ultraviolet (UV) light to pass through it with very little absorption, a property that standard glass lacks.
This unique transparency makes it the only viable choice for applications like UV water sterilization systems, UV curing lamps, and optical components like lenses and sight glasses used in the UV spectrum.
Low Thermal Expansion
Quartz has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it changes size very little when subjected to drastic temperature changes.
This stability is crucial for creating precision optical components, such as mirror substrates for telescopes, where even microscopic changes in shape would distort the image.
Understanding the Limitations and Handling Requirements
While powerful, quartz is a specialized material with distinct trade-offs. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for successful implementation and safety.
Inherent Fragility
Quartz tubes are brittle and susceptible to breakage from physical shock. They must be handled with extreme care, avoiding violent vibrations, collisions, or impact.
This fragility requires special consideration during transportation, installation, and maintenance to prevent costly and dangerous failures.
Strict Temperature Ceilings
While highly heat-resistant, quartz has a definitive limit. Exceeding 1200°C will cause the material to soften and deform, compromising its structural integrity.
For applications requiring temperatures above this threshold, alternative materials like corundum tubes must be considered.
Contamination Sensitivity
The high purity of a quartz tube can be easily compromised. Before use, it must be wiped clean, and operators should always wear appropriate gloves.
Touching the surface with bare hands can transfer oils and salts that will etch into the material when heated, creating weak points and degrading performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting and using a quartz tube correctly depends entirely on your primary technical objective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing: Prioritize the tube's thermal specifications and ensure your process stays well within the 1100°C continuous use limit to ensure a long service life.
- If your primary focus is optical clarity: Confirm the material's transmission specifications for your required wavelength (especially in the UV spectrum) and maintain impeccable cleanliness to prevent surface contamination.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Implement strict handling protocols, including the use of powder-free gloves, to prevent any contamination that could compromise semiconductor or laboratory processes.
By matching the unique properties of quartz to your specific need, you can leverage its full potential for stable, reliable, and high-performance results.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Key Application |
|---|---|
| High-Temp Stability (up to 1200°C) | Furnace tubes, CVD reactors, thermocouple protection |
| Exceptional Chemical Purity (99.99%) | Semiconductor wafer carriers, lab equipment, pharmaceutical processes |
| UV Light Transparency | UV water sterilization, UV curing lamps, optical components |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Precision optics, telescope mirrors, stable sight glasses |
Ready to leverage the unique properties of quartz tubes in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision quartz tubes designed for demanding applications in semiconductor manufacturing, research, and industrial processes. Our products ensure the thermal stability, purity, and optical clarity your work requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover the right quartz solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia grinding jars necessary for solid electrolyte powders? Ensure High Purity & Ionic Conductivity
- What is the test for refractory material? Essential Tests for High-Temperature Performance
- Why is a benchtop magnetic stirrer used in electrocoagulation? Enhance Wastewater Treatment Efficiency
- What is the function of a laboratory magnetic stirrer? Enhance Yield & Uniformity in Thermal Extraction
- Why is a water-cooled copper hearth necessary? Protect Fe-Cu-O Melts from Contamination and Segregation
- What roles do high-purity quartz tubes and argon play in neutron diffraction? Ensure Sample Integrity and Signal Clarity
- What is the difference between single loop and multi loop controller? Choose the Right Control for Your Process
- What are the benefits of using zirconia (ZrO2) grinding jars and balls when milling sulfide-based solid electrolytes?



















