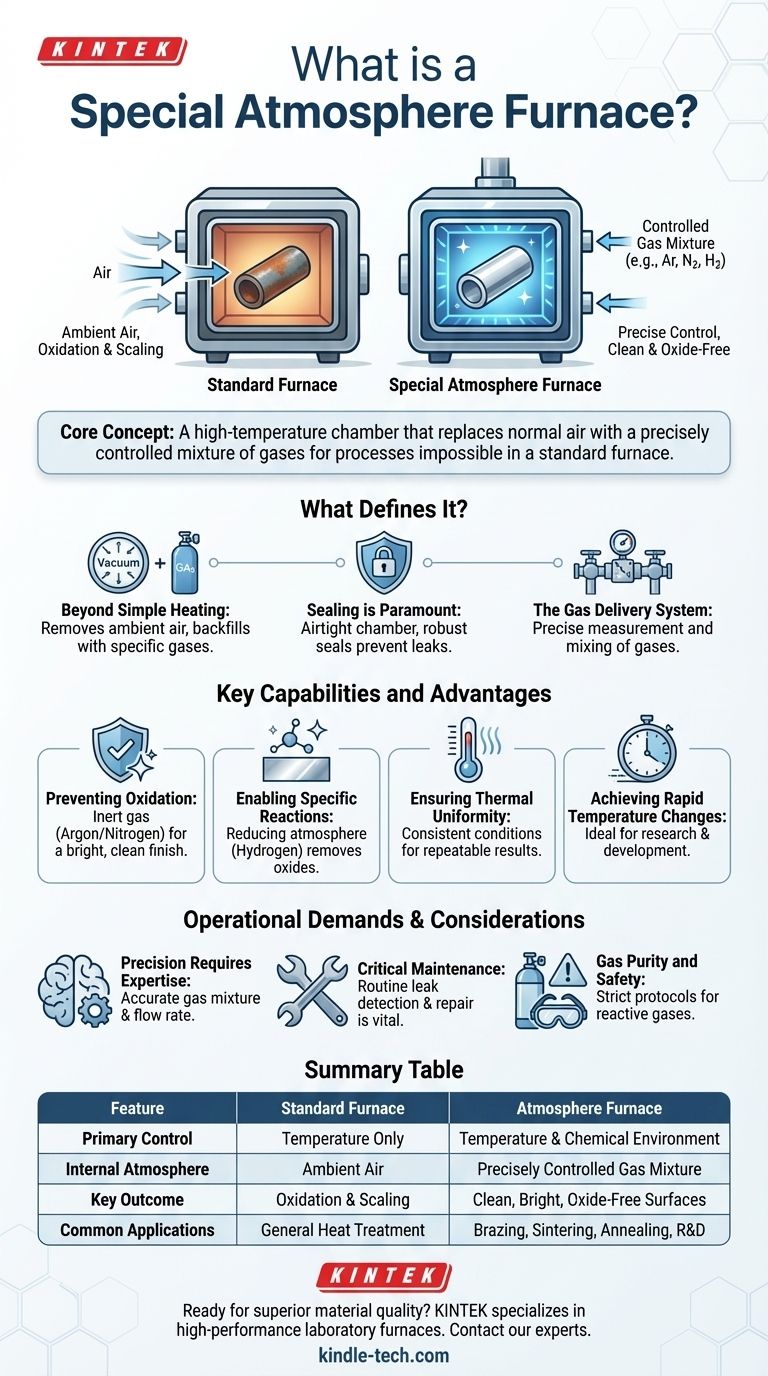
In essence, a special atmosphere furnace is a high-temperature chamber that replaces the normal air inside with a precisely controlled mixture of gases. This engineered environment is the furnace's defining feature. It allows for thermal processes that are impossible in a standard furnace, such as preventing oxidation or enabling specific chemical reactions on a material's surface.
The fundamental difference between a standard furnace and an atmosphere furnace is control. While a standard furnace only controls temperature, an atmosphere furnace gives you precise control over both the temperature and the chemical environment, preventing unwanted reactions and producing cleaner, higher-quality results.

What Defines an "Atmosphere" Furnace?
A standard furnace heats a material in the presence of ambient air, which is rich in oxygen. This inevitably leads to oxidation and other surface contamination. An atmosphere furnace is designed specifically to overcome this limitation.
Beyond Simple Heating
The core function is to create a specific chemical environment for the heating process. This is achieved by first removing the ambient air—often by creating a vacuum—and then backfilling the chamber with a specific gas or a carefully managed mixture of gases.
Sealing is Paramount
To maintain this controlled environment, the furnace chamber must be completely airtight. These furnaces feature robust seals, often using high-temperature resistant materials like silica gel rings on the furnace door, to prevent any leaks that would contaminate the internal atmosphere.
The Gas Delivery System
An atmosphere furnace includes a sophisticated gas handling system with an inlet and an outlet. This system allows for the precise measurement and mixing of gases, which is essential for the success of the thermal process and for safely exhausting the gases after treatment.
Key Capabilities and Advantages
The ability to control the internal atmosphere provides several distinct advantages over conventional heating methods, making these furnaces indispensable in advanced manufacturing and scientific research.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the most common application. By replacing oxygen with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), the furnace prevents the material from reacting with oxygen at high temperatures. This results in a bright, clean finish without scaling or discoloration.
Enabling Specific Chemical Reactions
Certain atmospheres are not just protective; they are reactive. A furnace using a reducing atmosphere, such as hydrogen, can actively remove oxides from a material's surface. This is critical for processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing where surface purity is vital.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
High-end atmosphere furnaces are engineered for exceptionally uniform temperature distribution. This ensures that the entire sample or workload is subjected to the exact same thermal conditions, leading to consistent and repeatable results.
Achieving Rapid Temperature Changes
Many models are designed for rapid heating and cooling cycles. This level of control over all thermal process parameters is ideal for materials science research and developing new manufacturing techniques.
Understanding the Operational Demands
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is a more complex piece of equipment than a standard oven and requires a higher level of operational discipline.
Precision Requires Expertise
The simple structure of the furnace belies the complexity of its operation. Achieving the correct gas mixture, flow rate, and pressure requires a clear understanding of the process. Precise gas measurement is not a suggestion—it is a requirement for success.
The Critical Role of Maintenance
The integrity of the atmosphere is entirely dependent on the integrity of the furnace seals. Routine preventative maintenance, especially thorough leak detection and repair, is absolutely critical. Even a minor leak can compromise the entire process, wasting time and expensive materials.
Gas Purity and Safety
The effectiveness of the process is directly tied to the purity of the gases used. Furthermore, handling reactive or flammable gases like hydrogen introduces significant safety protocols that must be strictly followed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on the required outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment where surface oxidation is not a concern: A standard, cost-effective box furnace is likely sufficient for your needs.
- If your primary focus is to heat a sensitive material without it oxidizing or discoloring: An atmosphere furnace using an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is actively cleaning, brazing, or sintering a material: You require a furnace capable of handling a reactive or reducing atmosphere like hydrogen.
Ultimately, an atmosphere furnace provides an unparalleled level of control, transforming the heating process from a brute-force tool into a precise instrument for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Control | Temperature Only | Temperature & Chemical Environment |
| Internal Atmosphere | Ambient Air (Oxygen-rich) | Precisely Controlled Gas Mixture |
| Key Outcome | Oxidation & Scaling | Clean, Bright, Oxide-Free Surfaces |
| Common Applications | General Heat Treatment | Brazing, Sintering, Annealing, R&D |
Ready to achieve oxidation-free results and superior material quality?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces and consumables. Our special atmosphere furnaces provide the precise control you need for brazing, sintering, and advanced materials research.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thermal processing requirements and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes



















