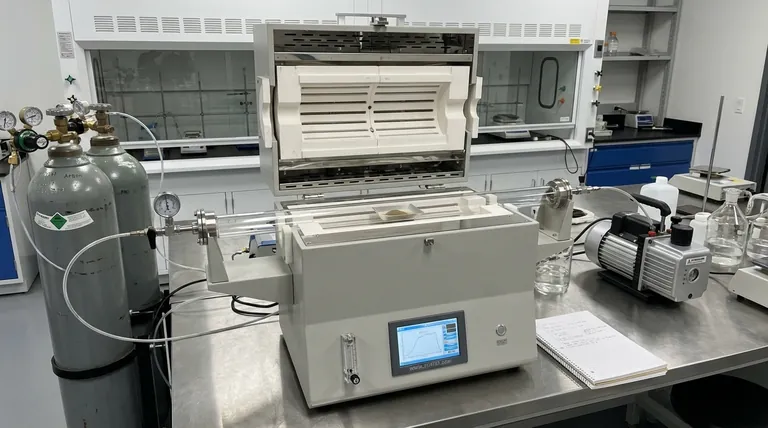
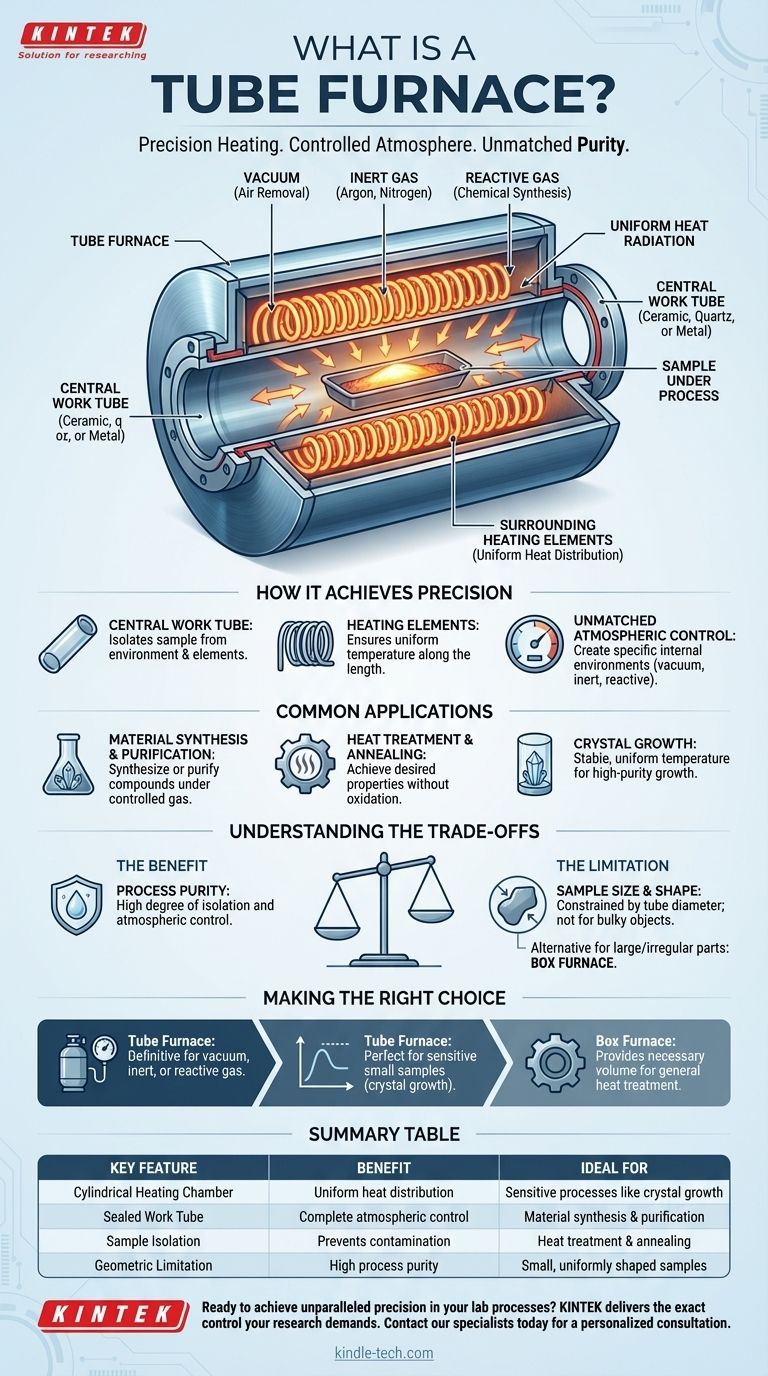
At its core, a tube furnace is a high-temperature electric heating device built around a central cylindrical chamber, or "tube." It is specifically designed to conduct processes that demand precise temperature control and, most critically, a highly controlled atmosphere around the sample. The design typically consists of heating coils embedded in an insulating matrix, which surround the work tube to ensure uniform heat distribution.
The defining feature of a tube furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to completely isolate a sample within a controlled environment. This makes it indispensable for processes that are sensitive to air or require a specific reactive or inert gas atmosphere.

How a Tube Furnace Achieves Precision
A tube furnace's effectiveness comes from its simple yet powerful design, which focuses on isolating the sample from both the outside world and the heating elements themselves.
The Central Work Tube
The sample or material being processed is placed inside the work tube. This tube, often made of ceramic, quartz, or metal, acts as the reaction chamber. It can be sealed at the ends with flanges.
This physical separation is what allows for the precise control of the internal environment, preventing contamination from the heating elements or the ambient air.
Surrounding Heating Elements
Heating elements are positioned around the exterior of the work tube. This cylindrical arrangement ensures that heat radiates inward evenly from all sides, creating a zone of highly uniform temperature along the length of the tube.
Unmatched Atmospheric Control
This is the primary reason for choosing a tube furnace. The sealed tube allows operators to create a specific internal atmosphere.
You can create a vacuum by pumping out all the air, introduce a flow of inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or use a reactive gas to participate in a chemical synthesis.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The unique capabilities of a tube furnace make it essential in both laboratory research and specialized industrial production.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are widely used to synthesize or purify inorganic and sometimes organic compounds. The ability to control the gas atmosphere is crucial for driving chemical reactions that would be impossible in open air.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
Processes like annealing, tempering, and hardening often require heating materials to a specific temperature in a controlled environment to achieve desired properties. A tube furnace prevents unwanted surface reactions like oxidation during these treatments.
Crystal Growth
Growing high-purity crystals requires an extremely stable and uniform temperature environment over a long period. The excellent temperature distribution and clean atmosphere of a tube furnace are ideal for these delicate processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a tube furnace presents a fundamental trade-off that dictates its use.
The Benefit: Process Purity
The isolation of the work tube guarantees a high degree of process purity and atmospheric control that is difficult to achieve in other furnace designs.
The Limitation: Sample Size and Shape
The primary constraint of a tube furnace is its geometry. The diameter of the tube inherently limits the size and shape of the samples you can process. It is not suitable for heating large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects.
For applications requiring the processing of larger batches or components without a need for strict atmospheric control, a box furnace is often a more practical alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating device depends entirely on the requirements of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is atmospheric control: The tube furnace is the definitive choice for any process requiring a vacuum, inert, or reactive gas environment.
- If your primary focus is temperature uniformity on a small sample: The cylindrical heating design provides exceptional consistency, making it perfect for sensitive applications like crystal growth or calibration.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped parts: A box or chamber furnace will provide the necessary volume and is more suitable for general-purpose heat treatment.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace means prioritizing precise environmental control and temperature uniformity over sample volume.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Heating Chamber | Uniform heat distribution | Sensitive processes like crystal growth |
| Sealed Work Tube | Complete atmospheric control (vacuum, inert, reactive gases) | Material synthesis & purification |
| Sample Isolation | Prevents contamination from heating elements/air | Heat treatment & annealing |
| Geometric Limitation | High process purity | Small, uniformly shaped samples |
Ready to achieve unparalleled precision in your lab processes?
A tube furnace from KINTEK delivers the exact control your research demands. Whether you're synthesizing new materials, annealing samples without oxidation, or growing high-purity crystals, our tube furnaces provide the uniform heating and atmospheric isolation critical for success.
Let KINTEK, your trusted lab equipment partner, provide the right solution for your specific needs. Our experts will help you select the ideal tube furnace configuration for your application.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and see how our tube furnaces can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and accelerate your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of tube or muffle furnaces in the study of phase transformations? Reverting Martensite
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- Why are stainless steel 1.4404 or glass preferred for continuous reactors in cyclooctene epoxidation? Expert Insights
- What are the primary considerations for using a quartz tube reactor in DMSTA? Ensure Analytical Precision
- What are the design requirements for a CsI tube furnace? Master the Vertical Bridgman Method
- What is the role of the atmosphere provided by a tube furnace during the carbon coating process of Li3V2(PO4)3?
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















