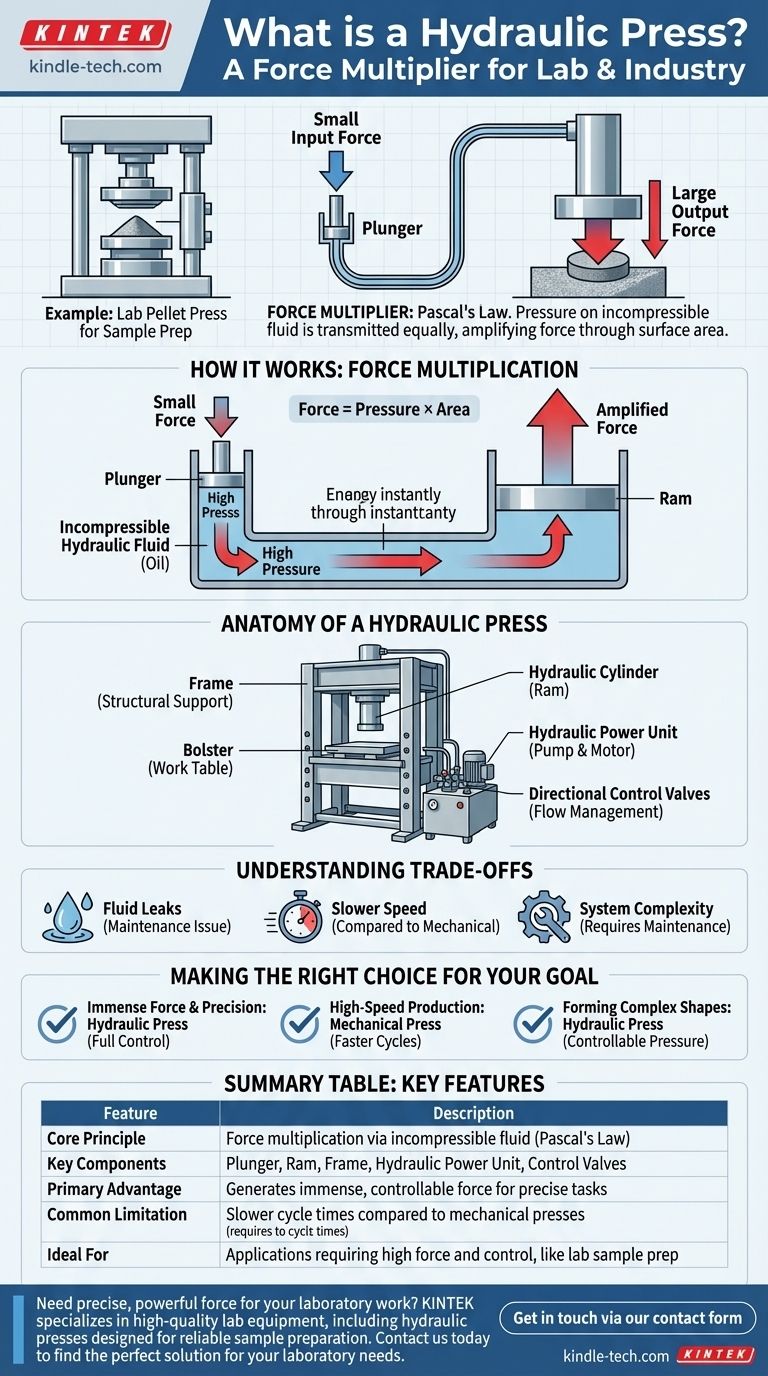
A common and specific example is a laboratory hydraulic press used for sample preparation, where immense force is applied to compress powdered material into a solid, thin pellet for analysis. This application showcases the machine's core ability to generate significant force in a compact and controlled manner.
A hydraulic press is not simply a machine for pressing things; it is a force multiplier. It leverages the principle of fluid dynamics to convert a small, manageable input force into a large, powerful output force, enabling tasks that would otherwise be impossible.

How a Hydraulic Press Achieves Force Multiplication
The power of a hydraulic press comes from a fundamental principle of fluid mechanics. It exploits the fact that pressure applied to a contained, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally throughout that fluid.
The Role of the Two Cylinders
A hydraulic press is built around two connected cylinders of different sizes. The smaller cylinder is called the Plunger, and the larger one is called the Ram.
A small force is applied to the Plunger. Because the Plunger's surface area is small, this generates high pressure in the hydraulic fluid.
The Incompressible Fluid
The system is filled with a hydraulic fluid, typically a specialized oil. This fluid is critical because it is nearly incompressible, meaning it doesn't lose volume under pressure.
When the Plunger applies pressure, the fluid transmits this pressure instantly and uniformly to every part of the system, including the much larger Ram.
The Result: Amplified Force
The Ram has a much larger surface area than the Plunger. Since the pressure is the same, the total force exerted by the Ram is proportionally larger.
This is how a small push on the Plunger results in a massive force from the Ram, capable of shaping metal or compressing dense materials.
The Anatomy of a Hydraulic Press
While the two-cylinder system is the heart of the press, several other components are essential for its structure and operation.
The Frame and Bolster
The frame is the heavy-duty structure that holds all the components together and withstands the immense forces generated during operation.
The table or bolster is the sturdy surface that supports the material being worked on, positioned directly under the Ram.
The Hydraulic Power Unit
This system, consisting of a pump, delivers high-pressure oil into the cylinders. The pump is the engine that creates the initial pressure in the hydraulic fluid.
The Hydraulic Cylinder (Ram)
The hydraulic cylinder or Ram is the component that moves and applies the amplified force to the workpiece. It is the primary "output" of the machine.
Directional Control Valves
Valves are used to manage the flow of hydraulic fluid. They direct the high-pressure oil to extend or retract the Ram, giving the operator precise control over the pressing operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, hydraulic presses are not the perfect solution for every application. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Potential for Fluid Leaks
Because the system operates under very high pressure, seals and hoses can wear out over time, leading to hydraulic fluid leaks. This can be a maintenance issue and an environmental concern.
Operating Speed
Compared to mechanical presses, hydraulic presses can have slower cycle times. The time it takes for the pump to move the fluid and build pressure can limit high-speed, high-volume production.
System Complexity
The hydraulic system, with its pumps, valves, filters, and fluid, requires regular maintenance to ensure reliability and safety. Neglecting this can lead to poor performance or catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right technology depends entirely on the specific requirements of your task.
- If your primary focus is immense force and precision: A hydraulic press is unparalleled, offering full force control throughout the entire stroke.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production: A mechanical press might be a better choice due to its faster cycle times for repetitive tasks.
- If your primary focus is forming complex shapes: The controllable pressure of a hydraulic press provides a distinct advantage over other technologies.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a foundational tool for applications demanding massive, controllable power in a reliable design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Force multiplication via incompressible fluid (Pascal's Law) |
| Key Components | Plunger, Ram, Frame, Hydraulic Power Unit, Control Valves |
| Primary Advantage | Generates immense, controllable force for precise tasks |
| Common Limitation | Slower cycle times compared to mechanical presses |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring high force and control, like lab sample prep |
Need precise, powerful force for your laboratory work?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for reliable sample preparation. Our machines deliver the controlled force you need to create perfect pellets for accurate analysis, ensuring your research and quality control processes are efficient and effective.
Contact us today to find the perfect hydraulic press solution for your laboratory needs. Get in touch via our contact form and let our experts help you enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the safety rules for a hydraulic press? Essential Protocols for Operator and Machine Safety
- What is the function of a laboratory mechanical press and stainless steel mold in L-proline sample preparation?
- What is KBr pellet technique? Master Solid Sample FTIR Analysis with Clear Pellets
- Why is a hydraulic press used to apply 380 MPa to battery bilayers? Achieve Superior Density & Safety
- Why is powder metallurgy limited to small parts? The Compaction & Cost Challenges Explained
- What is a pelletizing machine? Transform Raw Materials into High-Value Pellets
- What is uniaxial pressing of ceramics? A Guide to High-Volume Production of Simple Shapes
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized in the fabrication of Na3SbS4 pellets? Achieve High-Density Electrolytes



















