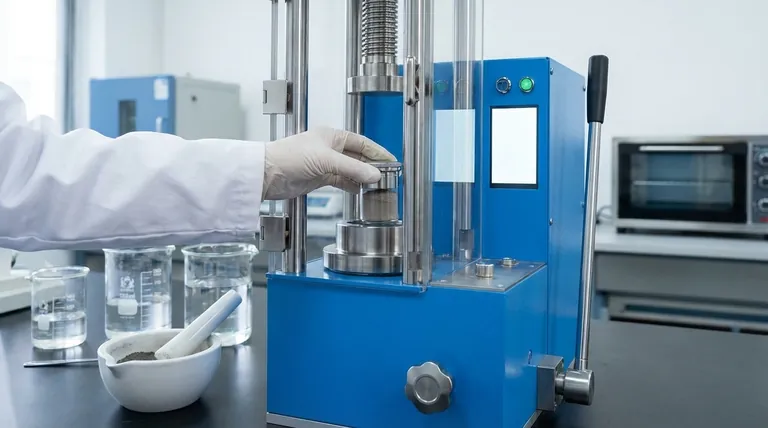
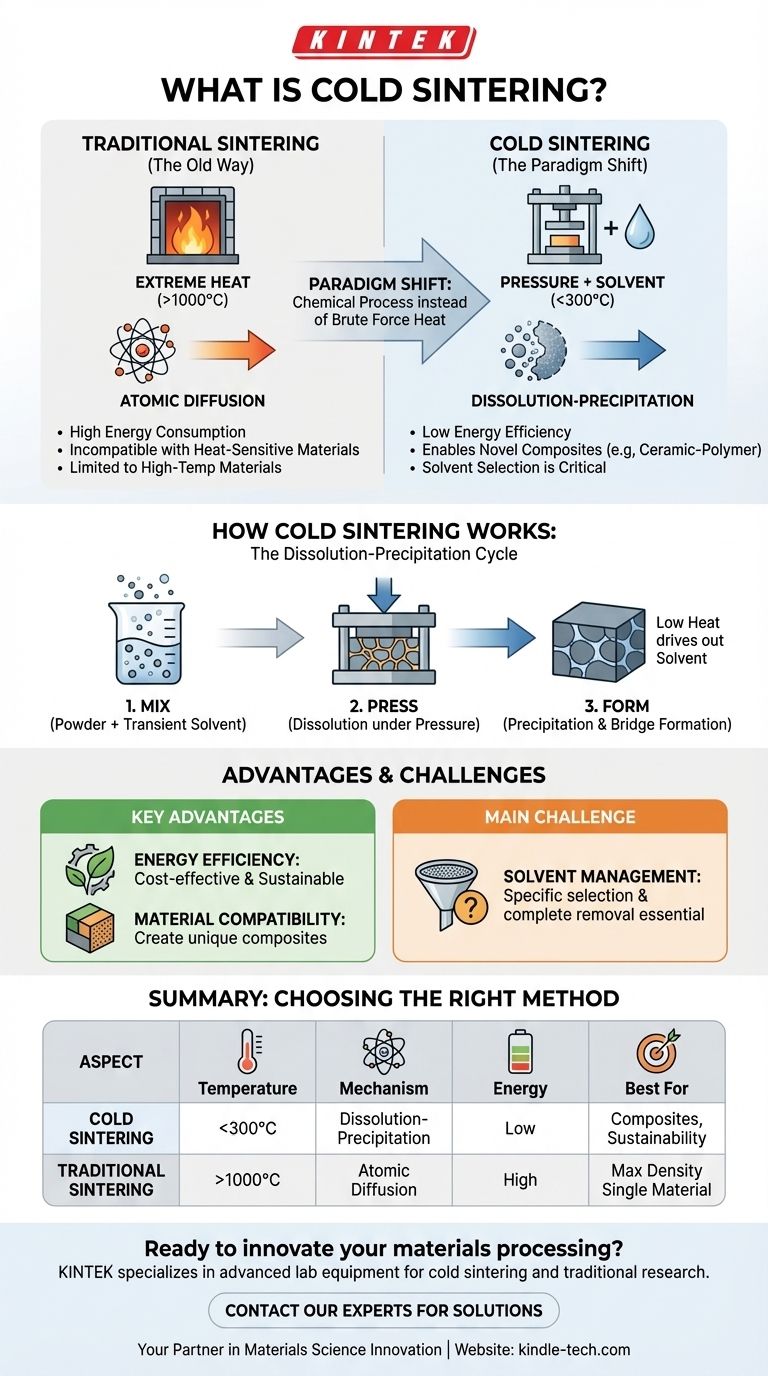
At its core, cold sintering is a manufacturing process that uses pressure and a temporary liquid solvent to compact and solidify powders into a dense mass at significantly lower temperatures than traditional methods. Unlike conventional sintering which relies on extreme heat to fuse particles, this technique leverages chemical processes to achieve a similar result.
The central innovation of cold sintering is replacing the brute force of extreme heat with the finesse of a solvent-assisted chemical reaction. This dramatically lowers the energy required for densification and enables the creation of novel composite materials that would be destroyed by high temperatures.

The Problem With Traditional Sintering
To understand the value of cold sintering, we must first look at the conventional process it aims to improve. Traditional sintering is an energy-intensive but effective method for creating solid parts from powders.
The Role of Extreme Heat
Conventional sintering uses extremely high temperatures, often thousands of degrees, as its primary tool. This heat provides the thermal energy needed to drive the consolidation process.
The Mechanism of Atomic Diffusion
At these high temperatures, atoms in the powder particles become agitated and begin to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries between particles. This atomic movement effectively erases the gaps between the particles, fusing them into a single, solid piece without ever fully melting the material.
Inherent Limitations
This reliance on heat creates two major constraints. First, it requires an immense amount of energy, making it a costly process. Second, it is incompatible with materials that have low melting points or would degrade under extreme heat, such as polymers.
How Cold Sintering Works
Cold sintering bypasses the need for extreme thermal energy by introducing a different mechanism for material transport. The "cold" in its name is relative, typically referring to temperatures below 300°C.
The Key Ingredient: A Transient Solvent
The process begins by mixing the powder with a small amount of a liquid solvent. This solvent is "transient," meaning it is only present during the manufacturing step and is removed from the final product.
The Role of Pressure
This wet powder mixture is then placed under pressure. The pressure serves two functions: it forces the powder particles into close contact and, with the solvent, initiates a process of dissolution and precipitation.
The Dissolution-Precipitation Cycle
The solvent partially dissolves the surface of the powder particles. The applied pressure then effectively squeezes this dissolved material into the pores and gaps between the solid particles. As the solvent is driven out by low heat, the dissolved material precipitates, forming solid bridges that bind the particles together into a dense mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While innovative, cold sintering is not a universal replacement for traditional methods. The choice depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
Advantage: Energy Efficiency
The most significant advantage is the drastic reduction in energy consumption. By operating at hundreds of degrees instead of thousands, the process becomes far more cost-effective and sustainable.
Advantage: Material Compatibility
Cold sintering's low-temperature nature makes it possible to co-sinter materials with vastly different thermal properties. This opens the door to creating unique composites, such as ceramic-polymer blends, that are impossible to fabricate with conventional heat-based methods.
The Challenge: Solvent Selection and Removal
The choice of solvent is critical and highly specific to the powder material being used. Furthermore, ensuring the complete removal of the transient solvent from the final part is a key process hurdle that can affect the purity and properties of the finished product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sintering method requires a clear understanding of your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating novel composite materials: Cold sintering is uniquely suited for combining materials that cannot survive traditional high-temperature processing, such as ceramics and polymers.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy costs and environmental impact: The dramatically lower processing temperatures of cold sintering make it the clear choice for sustainable manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum theoretical density for a single high-temp material: Traditional high-temperature sintering often remains the most reliable method, as it avoids any potential for residual solvent contamination.
Ultimately, cold sintering represents a paradigm shift in materials processing, offering a low-energy pathway to fabricate materials that were previously difficult or impossible to create.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Cold Sintering | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Below 300°C | Often thousands of degrees |
| Primary Mechanism | Dissolution-precipitation under pressure | Atomic diffusion via extreme heat |
| Energy Consumption | Low | High |
| Material Compatibility | Excellent for composites (e.g., ceramic-polymer) | Limited to high-temperature materials |
| Key Challenge | Solvent selection and complete removal | High energy cost and thermal degradation risks |
Ready to innovate your materials processing?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge research and development. Whether you are exploring novel composite materials with cold sintering or optimizing traditional high-temperature processes, our expertise and product solutions can support your goals for energy efficiency and material innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help equip your laboratory for the future of materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What is the process of isostatic graphite? A Guide to High-Performance, Uniform Material Creation
- What is the difference between sintering and pressing? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy Processes
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- What is cold isostatic pressing examples? Achieve Uniform Density in Powder Compaction



















