In the context of carbon nanotubes, CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is the most common and versatile method used to synthesize, or "grow," high-quality carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in a controlled manner. The process involves introducing a carbon-containing gas onto a heated surface (substrate) where a metal catalyst causes the gas to decompose and reconstruct itself into the cylindrical, honeycomb-like structure of a nanotube.
The core challenge in creating carbon nanotubes is precisely arranging carbon atoms into a specific cylindrical shape. Chemical Vapor Deposition is the dominant solution because it uses a metal catalyst to enable this construction at much lower and more manageable temperatures than would otherwise be possible.
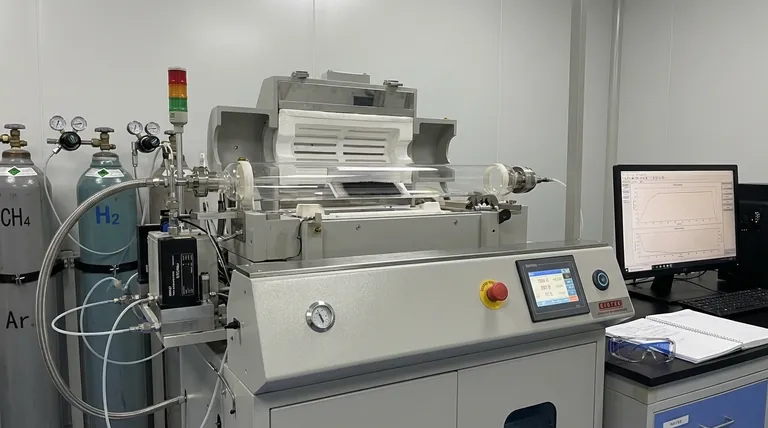

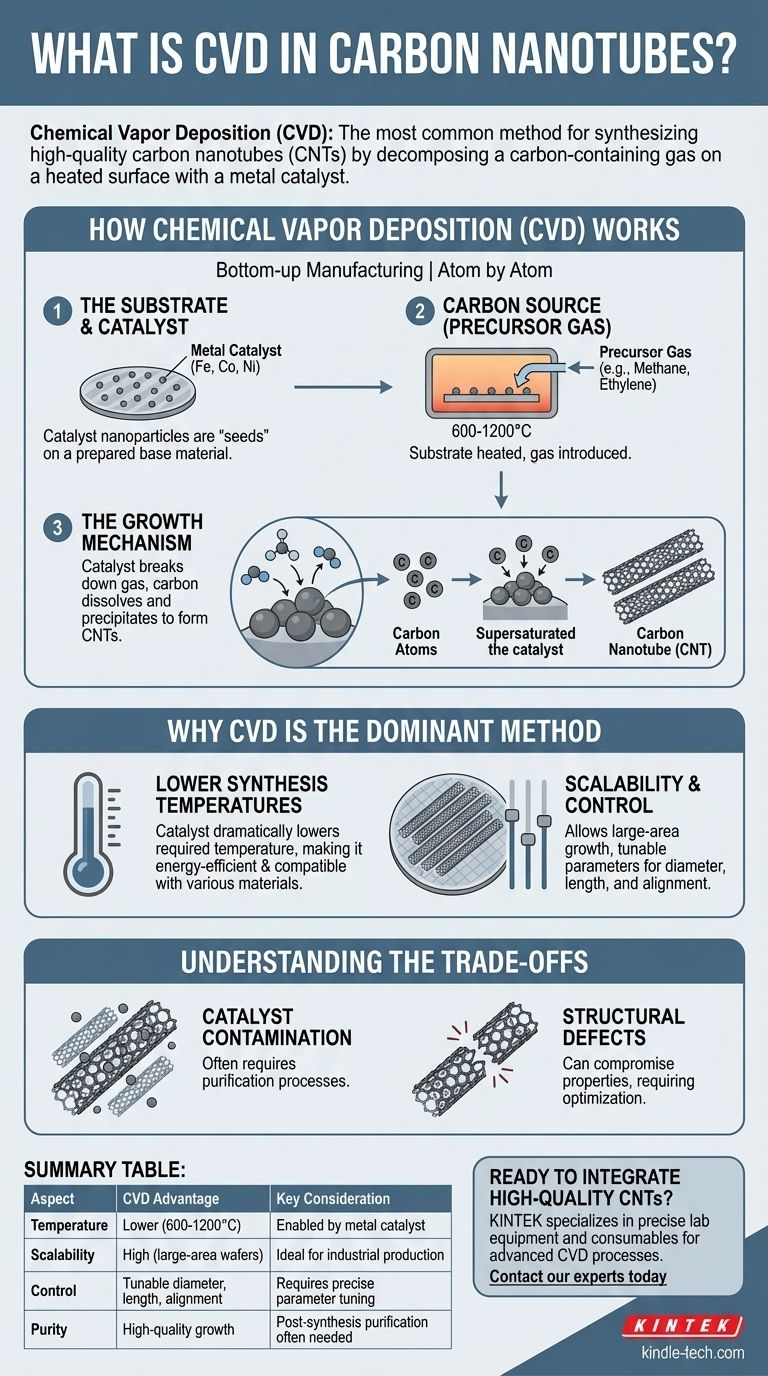
How Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Works for CNTs
The CVD process for growing CNTs is a bottom-up manufacturing technique, building the nanotubes atom by atom. It relies on a few fundamental components working together inside a reaction chamber, typically a high-temperature furnace.
The Substrate and Catalyst
First, a base material, or substrate, is prepared. This is the surface upon which the nanotubes will grow.
A thin layer of metal catalyst particles, such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, is then deposited onto this substrate. These nanoparticles are the crucial "seeds" for nanotube formation.
The Carbon Source (Precursor Gas)
Next, the substrate is heated to a high temperature (typically 600-1200°C), and a carbon-containing precursor gas, like methane, ethylene, or acetylene, is passed over it.
Without the catalyst, this process would require immensely higher temperatures to break the gas molecules apart.
The Growth Mechanism
The hot metal catalyst particles break down the precursor gas molecules into elemental carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms dissolve into the catalyst nanoparticle. Once the nanoparticle becomes supersaturated with carbon, the carbon begins to precipitate out, forming the stable, cylindrical lattice structure of a carbon nanotube.
Why CVD is the Dominant Method
While other methods like arc discharge and laser ablation exist, CVD has become the standard for both research and industrial production due to two significant advantages.
Lower Synthesis Temperatures
As the reference material notes, the catalyst is the key. It dramatically lowers the activation energy needed to decompose the carbon gas.
This allows CNTs to be grown at temperatures that are thousands of degrees lower than competing methods. This makes the process more energy-efficient and compatible with a wider range of materials, including those used in electronics.
Scalability and Control
CVD allows for the growth of CNTs directly on large-area wafers, making it suitable for mass production.
Furthermore, by carefully tuning process parameters—such as temperature, gas pressure, and catalyst type—engineers can exert significant control over the final product, influencing the nanotubes' diameter, length, and even alignment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, the CVD process is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations is critical for practical applications.
Catalyst Contamination
The most significant drawback is that the resulting nanotubes are often contaminated with residual metal catalyst particles.
These impurities can degrade the electrical and mechanical properties of the CNTs and typically require an aggressive, multi-step purification process after synthesis, which adds cost and complexity.
Structural Defects
The CVD process can introduce imperfections or defects into the carbon lattice of the nanotube walls.
These defects can compromise the exceptional theoretical strength and conductivity of the CNTs, preventing them from reaching their full potential in demanding applications.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The choice of a synthesis method is driven entirely by the requirements of the final application.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production for electronics or advanced composites: CVD is the most practical and scalable method, offering the best balance of quality, control, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research requiring the highest possible structural perfection: You might consider higher-energy methods, but you must accept the trade-offs of lower yield and difficulty in scaling the process.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition remains the most powerful and commercially viable technique for manufacturing carbon nanotubes for a vast range of applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Lower (600-1200°C) | Enabled by metal catalyst |
| Scalability | High (large-area wafers) | Ideal for industrial production |
| Control | Tunable diameter, length, alignment | Requires precise parameter tuning |
| Purity | High-quality growth | Post-synthesis purification often needed |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or production line? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced CVD processes. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for controlled CNT synthesis, from catalyst preparation to high-temperature furnaces. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve superior material outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision



















