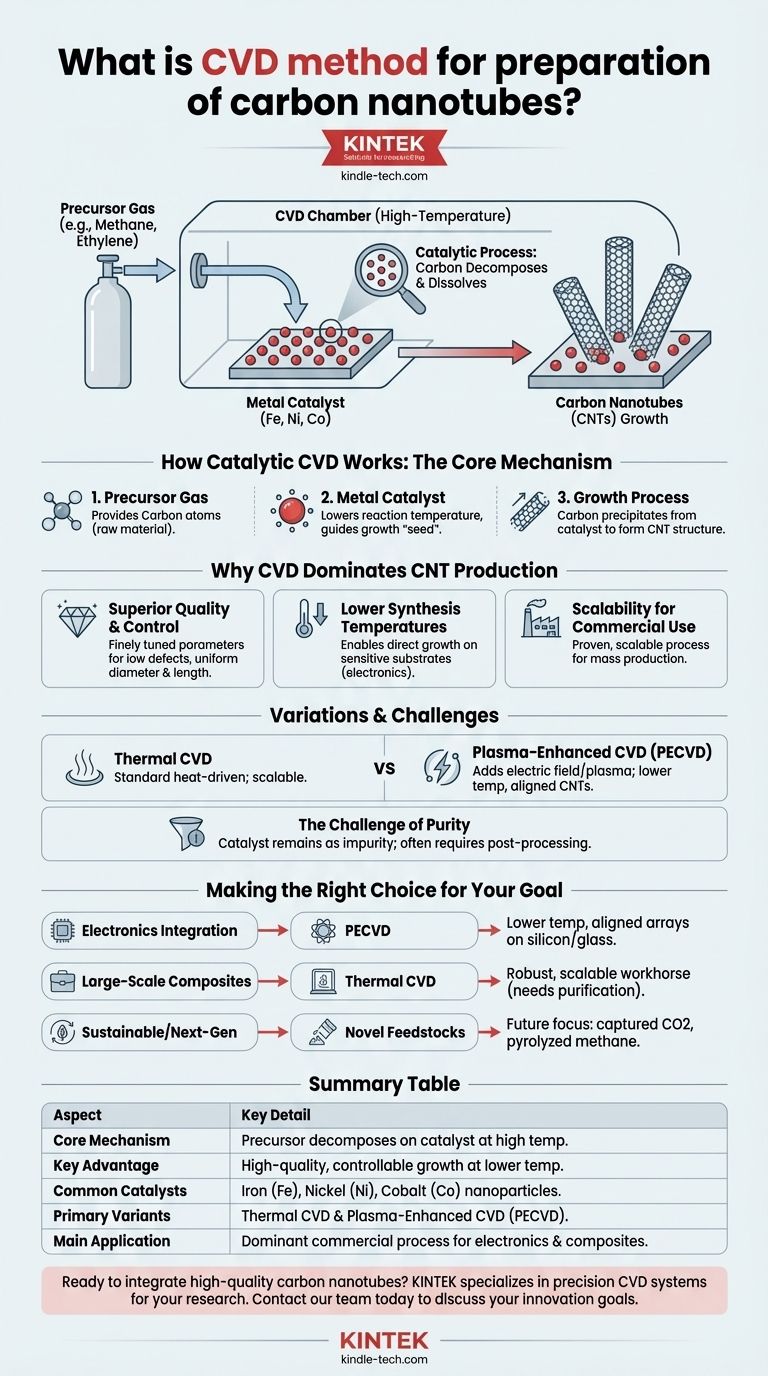
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a method for growing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) by introducing a carbon-containing gas into a high-temperature chamber where it decomposes. With the help of a metal catalyst, the liberated carbon atoms then assemble into the hollow, cylindrical structure of nanotubes on a surface, or substrate. This process is highly controllable, making it the leading approach for producing high-quality CNTs for advanced applications.
While older methods exist, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) has become the dominant commercial process for producing carbon nanotubes. Its key advantage lies in its ability to controllably grow high-quality materials at lower temperatures by using a catalyst, making it ideal for integration into electronics and other sensitive systems.

How Catalytic CVD Works: The Core Mechanism
The most common form of CVD for nanomaterials relies on a catalyst to drive the reaction. This catalytic process is fundamental to its success.
The Role of the Precursor Gas
A carbon-bearing gas, known as a precursor, is fed into the reaction chamber. Common precursors include methane, acetylene, or ethylene. This gas serves as the raw material, providing the carbon atoms needed to build the nanotubes.
The Function of the Metal Catalyst
The substrate is coated with a thin layer of metal nanoparticles, such as iron, nickel, or cobalt. This catalyst is the critical component; it dramatically lowers the temperature required to break down the precursor gas.
Without a catalyst, such reactions would require extremely high temperatures that could damage the substrate. The catalyst acts as a "seed" or template, initiating and guiding the growth of the nanotube structure.
The Growth Process
At a controlled temperature, the precursor gas decomposes on the surface of the catalyst particles. The carbon atoms dissolve into the catalyst, eventually precipitating out to form the cylindrical lattice of a carbon nanotube. The nanotube then grows outwards from the catalyst particle.
Why CVD Dominates CNT Production
Traditional methods like arc discharge and laser ablation are effective for small-scale synthesis but have been largely replaced by CVD for commercial production.
Superior Quality and Control
CVD is the most common technique for thin-film deposition because it produces high-quality materials. The process parameters—temperature, pressure, and gas flow—can be finely tuned to control the diameter, length, and uniformity of the CNTs, resulting in a low defect count.
Lower Synthesis Temperatures
The use of a catalyst allows CNTs to be grown at significantly lower temperatures than other methods. This is crucial for applications in electronics, as it allows nanotubes to be deposited directly onto sensitive substrates, like glass or silicon wafers, without causing damage.
Scalability for Commercial Use
CVD processes are well-established in the semiconductor industry and are inherently scalable. This has made CVD the dominant commercial process for producing CNTs in the quantities and qualities needed for modern applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, CVD is not without its complexities. Understanding its variations and challenges is key to successful implementation.
Thermal CVD vs. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
Thermal CVD is the standard method, relying solely on heat to initiate the reaction at the catalyst site.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) adds another element: an electric field is used to generate a plasma in the chamber. This plasma helps decompose the precursor gas, allowing for even lower deposition temperatures and often resulting in vertically aligned CNTs, which is highly desirable for applications like field emitters and electronic interconnects.
The Challenge of Purity
The metal catalyst, while essential for growth, remains as an impurity in the final product. For many high-performance applications, a post-processing step is required to remove these catalyst particles, adding complexity and cost to the overall process.
A Broadly Applicable Technique
The power of CVD is not limited to carbon nanotubes. The same fundamental process is used to synthesize a wide range of advanced nanomaterials, including graphene, carbon nanofibers (CNFs), and fullerenes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use CVD and its specific variant depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is integrating CNTs into electronic devices: PECVD is the superior choice, as its lower operating temperatures and ability to grow aligned arrays are ideal for fabrication on silicon or glass substrates.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production of high-purity CNTs for composites: Thermal CVD is a robust, scalable workhorse, though you must account for post-processing purification steps.
- If your primary focus is sustainable or next-generation synthesis: Investigating CVD processes that use novel feedstocks, like captured carbon dioxide or pyrolyzed methane, represents the future of the field.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of CVD is foundational to leveraging the transformative potential of carbon nanotubes in any application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Precursor gas decomposes on a metal catalyst at high temperature. |
| Key Advantage | High-quality, controllable growth at lower temperatures. |
| Common Catalysts | Iron (Fe), Nickel (Ni), Cobalt (Co) nanoparticles. |
| Primary Variants | Thermal CVD (standard) and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). |
| Main Application | Dominant commercial process for electronics and composites. |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? The CVD process is foundational, but choosing the right equipment and parameters is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis, including CVD systems. Our experts can help you select the ideal setup for your specific application, whether it's electronics integration or large-scale production. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















