In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly controlled process for creating high-purity, high-performance solid materials, typically in the form of thin films. The technique involves introducing reactive gases, known as precursors, into a chamber. These gases then undergo a chemical reaction on or near a heated surface (the substrate), depositing a solid layer onto that surface.
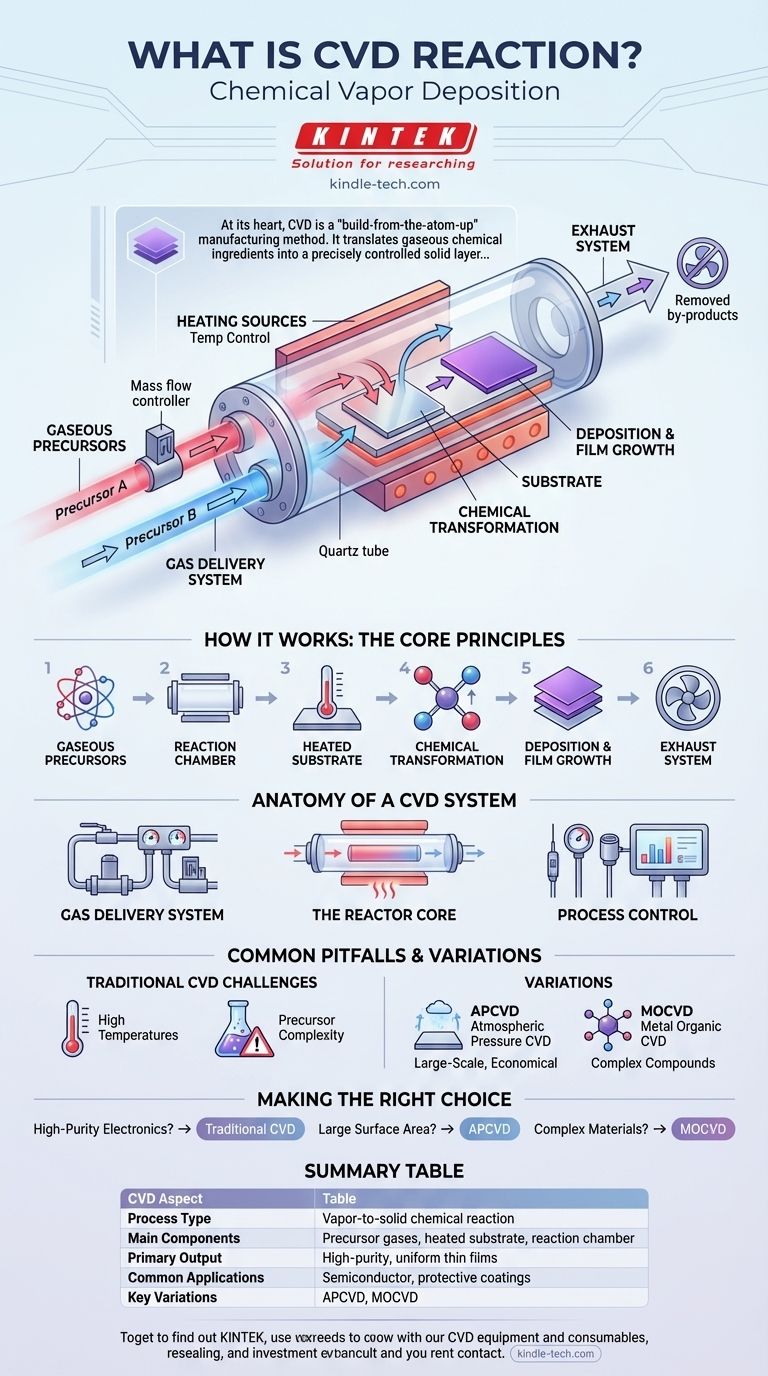
At its heart, CVD is a "build-from-the-atom-up" manufacturing method. It translates gaseous chemical ingredients into a precisely controlled solid layer, enabling the creation of advanced materials that are often impossible to form otherwise.
How a CVD Reaction Works: The Core Principles
The CVD process can be broken down into a series of fundamental steps, each occurring within a highly controlled environment. It is a true example of a vapor-to-solid reaction.
The Gaseous Precursors
The process begins with two or more gaseous raw materials. These precursors contain the specific atoms needed to form the final solid material.
The Reaction Chamber
These gases are introduced into a specialized reaction chamber, often a quartz tube. This chamber isolates the reaction from the outside atmosphere to prevent contamination.
The Heated Substrate
Inside the chamber is a substrate, which is the material to be coated. This substrate is heated, providing the thermal energy required to trigger the chemical reaction.
The Chemical Transformation
When the precursor gases come into contact with the hot substrate, they chemically react or decompose. This reaction forms the desired solid material and often creates gaseous by-products.
Deposition and Film Growth
The newly formed solid material deposits directly onto the substrate surface. This process builds up layer by layer, creating a thin, uniform film with high purity.
The Exhaust System
The gaseous by-products, which may be harmful, are safely removed from the chamber through an exhaust system that treats them before release.
Anatomy of a CVD System
A typical CVD system is composed of several critical components working in concert to ensure a precise and repeatable process.
Gas Delivery System
This includes the source of the precursor gases and stainless steel feed lines. Mass flow controllers are used to regulate the flow of each gas with extreme precision.
The Reactor Core
This is the central chamber where the reaction occurs, typically a quartz tube surrounded by heating sources. It is designed to maintain a stable temperature and pressure.
Process Control
Temperature and pressure sensors are essential for monitoring the conditions inside the reactor. This data allows for tight control over the film's properties.
Common Pitfalls and Variations
While powerful, the CVD process has specific requirements and has been adapted into many forms to suit different needs.
The Need for High Temperatures
Traditional CVD requires a heated substrate, which can make it unsuitable for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures.
Precursor Complexity
The choice of precursor gases is critical. They can be expensive, difficult to handle, or hazardous, requiring specialized safety protocols.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
Some CVD processes can be carried out at normal atmospheric pressure. This method, APCVD, is often used for less-demanding, large-scale applications, such as forming tin oxide coatings on hot glass.
A Family of Techniques
CVD is not a single process but a foundational principle for many techniques. Variations include Metal Organic CVD (MOCVD), pyrolysis, and reduction, each tailored for specific materials and applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core reaction allows you to select the right approach for your specific manufacturing or research objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity thin films for electronics: Traditional CVD is the industry standard for creating the semiconductor-grade layers required for microchips.
- If your primary focus is coating a large surface area cost-effectively: Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) is often a more practical and economical choice.
- If you are working with complex organic or metallic compounds: A specialized variant like Metal Organic CVD (MOCVD) will likely be necessary.
Ultimately, mastering the CVD reaction is about precisely controlling a chemical conversation between a gas and a solid surface to build the materials of the future.
Summary Table:
| CVD Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Vapor-to-solid chemical reaction |
| Main Components | Precursor gases, heated substrate, reaction chamber |
| Primary Output | High-purity, uniform thin films |
| Common Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, protective coatings, advanced materials |
| Key Variations | APCVD (atmospheric pressure), MOCVD (metal organic) |
Ready to integrate CVD technology into your lab workflow? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise Chemical Vapor Deposition processes. Whether you need CVD systems for semiconductor research or coating applications, our solutions deliver the purity and control your work demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's advanced material needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition



















