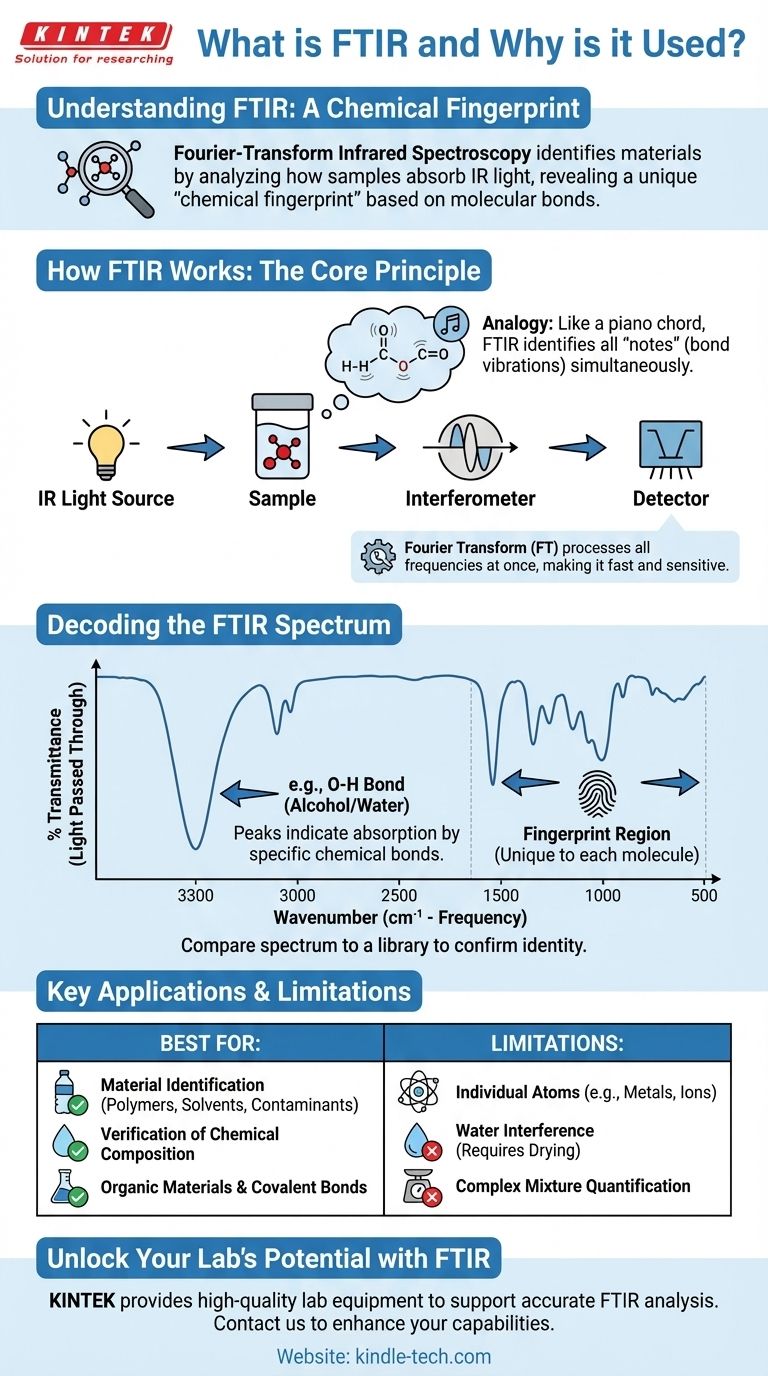
In analytical science, Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy is a powerful and widely used technique for identifying unknown materials and confirming the identity of known ones. It works by analyzing how a sample absorbs infrared light, which provides a unique "chemical fingerprint" based on the specific chemical bonds present within its molecules.
The core purpose of FTIR is not just to identify a substance, but to understand its fundamental molecular composition. By measuring which frequencies of infrared light a material absorbs, you can definitively identify the chemical bonds that make up the substance, enabling rapid and reliable material characterization.
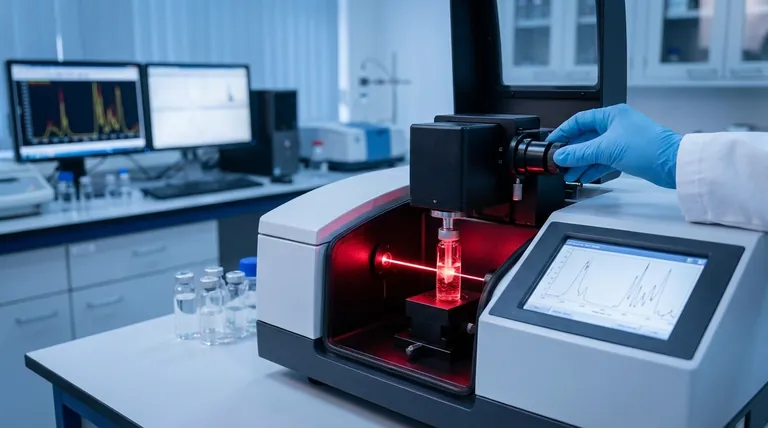

How FTIR Works: The Core Principle
FTIR is a form of vibrational spectroscopy. The entire process is based on a simple interaction: when infrared light hits a molecule, its chemical bonds can absorb that energy and vibrate in specific ways (stretching, bending, or rocking).
Shining Light on Molecules
An FTIR spectrometer shines a broad spectrum of infrared light through or onto a sample. The instrument's detector measures how much light passes through the sample at each specific frequency.
The frequencies that are absorbed by the sample correspond directly to the energies needed to excite its chemical bonds. Because different bonds (like C-H, O-H, or C=O) vibrate at different, characteristic frequencies, the resulting absorption pattern is unique to that molecule.
The Analogy: Identifying a Piano Chord
Think of a single chemical bond as a single piano key, which produces a specific note (frequency). A simple molecule is like a simple two-note chord, while a complex polymer is like an elaborate, multi-note chord.
FTIR doesn't just press one key at a time. It's like playing all the keys at once and using a sophisticated microphone and processor to instantly identify every single note within the resulting chord. This allows it to identify the entire "chord" (the molecule) very quickly.
The "Fourier-Transform" Advantage
The "FT" in FTIR refers to a mathematical process called a Fourier Transform. Instead of slowly scanning one frequency at a time, the instrument uses an interferometer to measure all frequencies simultaneously.
This creates a complex signal called an interferogram. The Fourier Transform is then used to convert this signal from the time domain into the familiar frequency domain, producing the final spectrum. This makes the process dramatically faster and more sensitive than older infrared methods.
Decoding the FTIR Spectrum
The output of an FTIR analysis is a graph called a spectrum. Understanding this graph is key to interpreting the results.
What the Graph Shows
The horizontal axis (x-axis) represents wavenumber (cm⁻¹), which is a unit of frequency for infrared light. The vertical axis (y-axis) typically represents percent transmittance, which is the amount of light that passed through the sample.
Where transmittance is low, absorption is high. These downward-facing spikes are called absorption bands or peaks.
The Significance of Peaks
Each peak in the spectrum indicates that a specific type of chemical bond absorbed energy at that frequency. For example, a strong, broad peak around 3300 cm⁻¹ is a classic indicator of an O-H bond, found in alcohols and water.
Chemists and material scientists use established correlation charts to match observed peaks to specific functional groups and bond types, effectively reconstructing the molecule's identity piece by piece.
The "Fingerprint Region"
While some peaks clearly identify specific functional groups, the region from approximately 1500 cm⁻¹ to 500 cm⁻¹ is known as the fingerprint region.
This area contains a dense, complex pattern of peaks unique to the molecule as a whole. Even very similar molecules will have distinct differences here, making it the most powerful region for confirming the exact identity of a compound by matching its spectrum against a library of known materials.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, FTIR is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application.
It Identifies Bonds, Not Atoms
FTIR excels at identifying covalent bonds, which are common in organic materials (plastics, oils, solvents) and many inorganic compounds. However, it cannot directly detect individual atoms like metals or ions in a salt (e.g., NaCl).
The Challenge of Water
Water is a very strong absorber of infrared light and its broad peaks can easily mask the signals from the actual sample. This is why samples must often be thoroughly dried, or special analysis techniques must be used for aqueous solutions.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Analysis
FTIR is primarily a qualitative tool—it is exceptionally good at answering "What is this?" However, it can be used for quantitative analysis ("How much of this is in my sample?"), but this requires careful calibration and a more controlled setup.
Complexity in Mixtures
Analyzing a pure substance is straightforward. Analyzing a mixture of several components is more challenging, as the peaks from different molecules can overlap, making the spectrum difficult to deconvolute without advanced software or complementary analytical techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
You can leverage FTIR most effectively by matching it to your specific analytical need.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification: FTIR is one of the fastest and most reliable methods available for verifying polymers, solvents, chemicals, and contaminants.
- If your primary focus is quantifying a component in a simple matrix: It is effective but requires careful development of a calibration curve using known standards.
- If your primary focus is analyzing unknown, complex mixtures: FTIR is an excellent first step for identifying major components, but you may need to combine it with other techniques like mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or chromatography for a full breakdown.
- If your primary focus is detecting trace metals or elemental composition: This is the wrong technique; you should use methods like Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) or X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF).
Ultimately, understanding FTIR is about knowing you have a powerful tool for rapidly decoding the chemical identity of the world around you.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | FTIR Capability |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Material identification & molecular composition analysis |
| Core Principle | Measures infrared light absorption by chemical bonds |
| Output | Spectrum showing unique "chemical fingerprint" |
| Best For | Organic materials, polymers, solvents, contaminants |
| Limitations | Cannot detect individual atoms; water can interfere |
Ready to unlock the power of FTIR analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your analytical needs. Whether you are identifying unknown materials, verifying polymer composition, or confirming chemical purity, the right tools are critical for accurate results.
Let our experts help you select the perfect FTIR spectrometer or accessories to enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can be your trusted partner in laboratory excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research


















