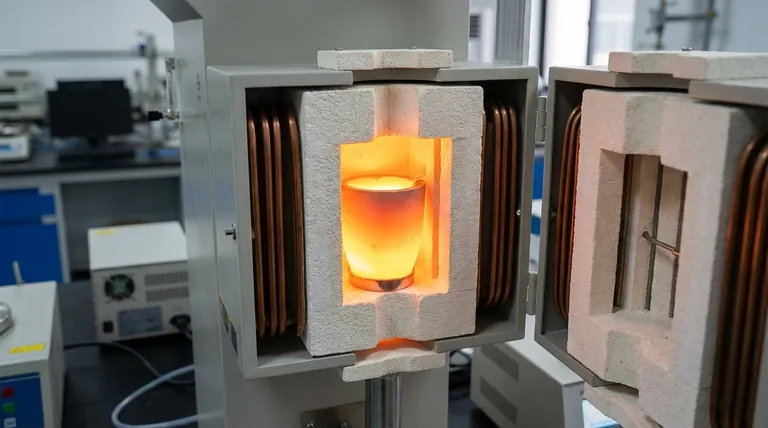
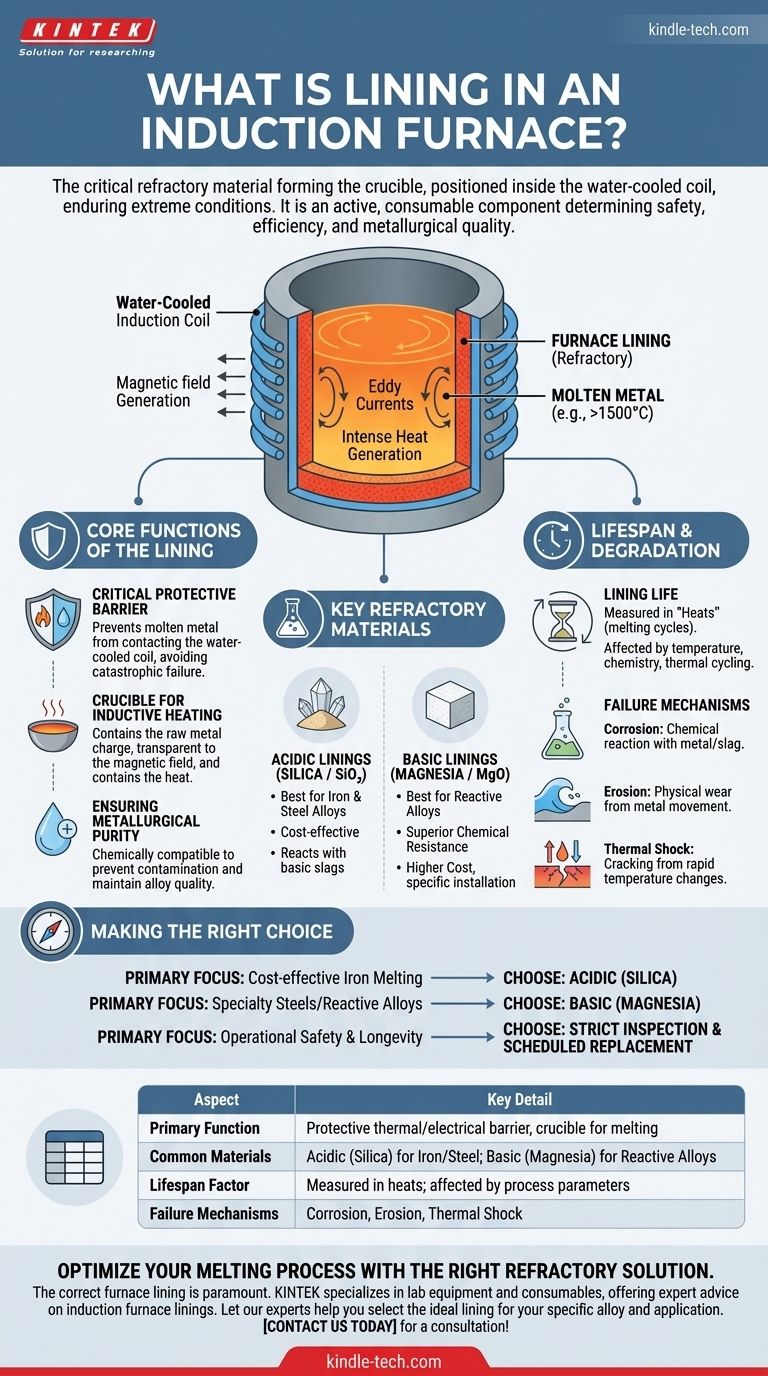
In an induction furnace, the lining is the critical refractory material that forms the crucible or container holding the molten metal. This lining is positioned inside the water-cooled copper induction coil and must withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and physical erosion while the furnace is in operation.
The furnace lining is not merely a passive container; it is an active, consumable component whose material composition and integrity directly determine the furnace's safety, efficiency, and the metallurgical quality of the final product.
The Core Function of the Furnace Lining
The lining serves as the central component where the entire melting process takes place. Its role is multifaceted, extending far beyond simple containment.
A Critical Protective Barrier
The primary function of the lining is to create a robust thermal and electrical barrier. It separates the superheated molten metal, often exceeding 1500°C, from the vital, water-cooled copper induction coil.
A breach in this lining would lead to a catastrophic failure, as molten metal would instantly destroy the coil and create an extreme safety hazard.
The Crucible for Inductive Heating
The lining material forms the crucible that contains the raw metal charge. When a powerful alternating current flows through the outer coil, it generates a magnetic field.
This field induces massive eddy currents within the metal inside the crucible, generating the intense heat required for melting. The lining must be transparent to the magnetic field while containing the resulting heat.
Ensuring Metallurgical Purity
The chemical composition of the lining is crucial for maintaining the purity of the alloy being melted. The lining material must be chemically compatible with the metal to prevent contamination.
This is why selecting the right refractory is essential for achieving the uniform composition and high quality for which induction furnaces are known.
Key Refractory Materials and Properties
The choice of lining material is dictated by the type of metal being melted and the specific operating conditions of the furnace. The most common categories are acidic and basic refractories.
Acidic Linings (Silica)
Linings made from high-purity silica (SiO₂) are the most common choice, particularly for melting iron and many steel alloys.
Silica is cost-effective and performs well in these applications. However, it will react with basic slags, making it unsuitable for certain refining processes.
Basic Linings (Magnesia)
Linings made from magnesia (MgO) are considered "basic." They are used when melting specific steel alloys or metals that would have a negative chemical reaction with an acidic silica lining.
Magnesia offers superior chemical resistance in these scenarios but is typically more expensive and may require different installation and preheating procedures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Degradation
A furnace lining is a consumable part with a finite lifespan. Understanding its limitations and failure mechanisms is critical for safe and efficient foundry operations.
The Concept of Lining Life
The operational life of a lining is measured in the number of heats (melting cycles) it can endure before it must be repaired or replaced.
This lifespan is affected by the operating temperature, the chemistry of the metal and slag, the speed of heating and cooling, and the physical charging process.
Mechanisms of Failure
Linings degrade over time through several mechanisms:
- Corrosion: Chemical reactions between the refractory material and the molten metal or slag.
- Erosion: Physical wear caused by the movement of the molten metal bath.
- Thermal Shock: Cracking caused by the immense stress of rapid heating and cooling cycles.
The Cost of a Poor Lining
Operating with a worn or improperly chosen lining leads to significant consequences. It reduces energy efficiency, can contaminate and ruin valuable alloys, and dramatically increases the risk of a dangerous metal breakout.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting and maintaining the correct lining is a foundational aspect of running a successful and safe induction furnace operation. Your decision should be guided by your primary metallurgical goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective iron melting: An acidic lining made from high-purity silica is typically the most economical and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is melting specialty steels or reactive alloys: A basic magnesia or other specialized neutral refractory (like alumina) is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure alloy integrity.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and longevity: A strict regimen of lining inspection, wear monitoring, and scheduled replacement is non-negotiable, regardless of the material used.
Ultimately, the lining is the heart of the induction furnace, and its careful management is paramount to achieving optimal performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Protective thermal/electrical barrier between molten metal and water-cooled coil |
| Common Materials | Acidic (Silica/SiO₂) for iron/steel; Basic (Magnesia/MgO) for reactive alloys |
| Lifespan Factor | Measured in heats; affected by temperature, chemistry, and thermal cycling |
| Failure Mechanisms | Corrosion (chemical), Erosion (physical), Thermal Shock (cracking) |
Optimize your melting process with the right refractory solution. The correct furnace lining is paramount for safety, efficiency, and product quality. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice on induction furnace linings and refractory materials. Let our experts help you select the ideal lining for your specific alloy and application. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















