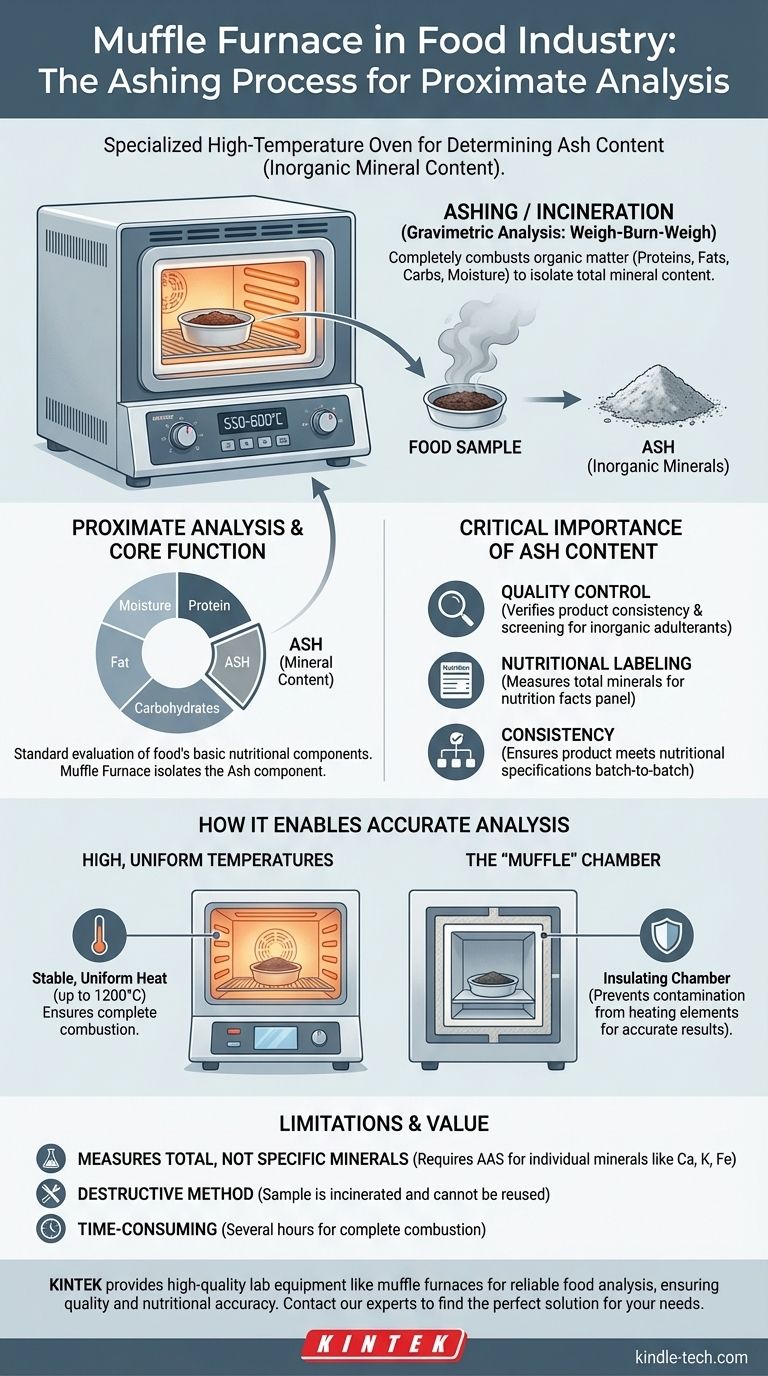
In the food industry, a muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven primarily used for determining the ash content of a food sample. This process, known as ashing or incineration, involves heating a sample at extremely high temperatures (typically 550-600°C) to completely burn away all organic matter. What remains is the ash—the inorganic, non-combustible mineral content of the food.
The core purpose of a muffle furnace in a food lab is not complex heating, but a precise form of analytical destruction. By incinerating a food product, it isolates the total mineral content, which is a fundamental indicator of nutritional value and product quality.

The Core Function: Ashing for Proximate Analysis
Proximate analysis is the standard evaluation of a food's basic nutritional components: moisture, protein, fat, carbohydrates, and ash. The muffle furnace is the essential tool for the ash component of this analysis.
What is Ashing?
Ashing is a form of gravimetric analysis, a "weigh-burn-weigh" method. A food sample of a known weight is placed in a crucible and heated in the muffle furnace for several hours until only a grayish-white ash remains.
The process completely combusts organic substances like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, as well as any moisture. The remaining material is weighed, and the percentage of ash in the original sample is calculated.
Why Ash Content is Critical
Measuring the ash content of a food product provides crucial information for both quality control and nutritional labeling.
It serves as a direct measure of the total amount of minerals within the food. This is a key metric for verifying that a product meets its nutritional specifications and for ensuring consistency from batch to batch. Abnormally high ash content can also indicate the presence of inorganic adulterants.
How a Muffle Furnace Enables Accurate Analysis
A muffle furnace is specifically designed to provide the controlled, high-temperature environment necessary for reliable ashing. Its design ensures the integrity of the analytical process.
High, Uniform Temperatures
Muffle furnaces can reach temperatures far exceeding a standard oven, often up to 1200°C or higher. For food ashing, they provide the stable, uniform heat required to ensure complete combustion of all organic material.
The "Muffle" for Contamination Control
The key feature is the "muffle"—an insulating chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements. This design prevents any flakes or contaminants from the heating elements from falling into the sample, which would corrupt the final weight measurement and lead to inaccurate results.
Beyond Ashing: Other Applications
While ashing is its primary role in food science, the furnace can also be used for determining volatile content and performing loss-on-ignition tests. These are variations of the same principle, measuring weight loss after heating to specific temperatures.
Understanding the Limitations
While indispensable for its primary function, it's important to recognize what a muffle furnace does not do. This understanding prevents misapplication of the data it generates.
It Measures Total, Not Specific, Minerals
A muffle furnace provides the total ash content only. It cannot differentiate between individual minerals like calcium, potassium, or iron. To determine the concentration of specific minerals, more advanced analytical techniques such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) are required.
It is a Destructive Method
The ashing process completely incinerates the sample. The material used for the test is destroyed and cannot be used for any other form of analysis.
The Process is Time-Consuming
Proper ashing can take several hours to ensure complete combustion. This, combined with the high energy consumption of the furnace, makes it a relatively slow and resource-intensive analytical step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data from a muffle furnace is foundational for any serious food quality or research program. Its application depends on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Using a muffle furnace to monitor ash content is a simple and effective method for verifying product consistency and screening for inorganic contamination.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: Determining total ash is the mandatory first step for reporting the mineral content on a nutrition facts panel.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Understanding how ingredients and processing changes affect the mineral profile of a new product begins with this fundamental measurement.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace provides an essential piece of data, forming the bedrock of food analysis for safety, nutrition, and quality assurance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Ash Content Determination (Proximate Analysis) |
| Process | Gravimetric Analysis (Weigh-Burn-Weigh) |
| Typical Temperature | 550-600°C |
| Key Benefit | Precise, Contamination-Free Mineral Measurement |
| Limitation | Measures Total Minerals Only (Not Specific Minerals) |
Ensure your food products meet the highest standards of quality and nutritional accuracy.
The precise data from a muffle furnace is the foundation of reliable food analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces, designed for the rigorous demands of food laboratories. Our products help you achieve consistent, accurate results for quality control and nutritional labeling.
Ready to enhance your lab's analytical capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your food testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an incubator? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What heat can a muffle furnace produce? Achieve Precise High Temperatures Up to 1800°C
- Which material is used in a muffle furnace? The Key to High-Temperature Performance and Purity



















