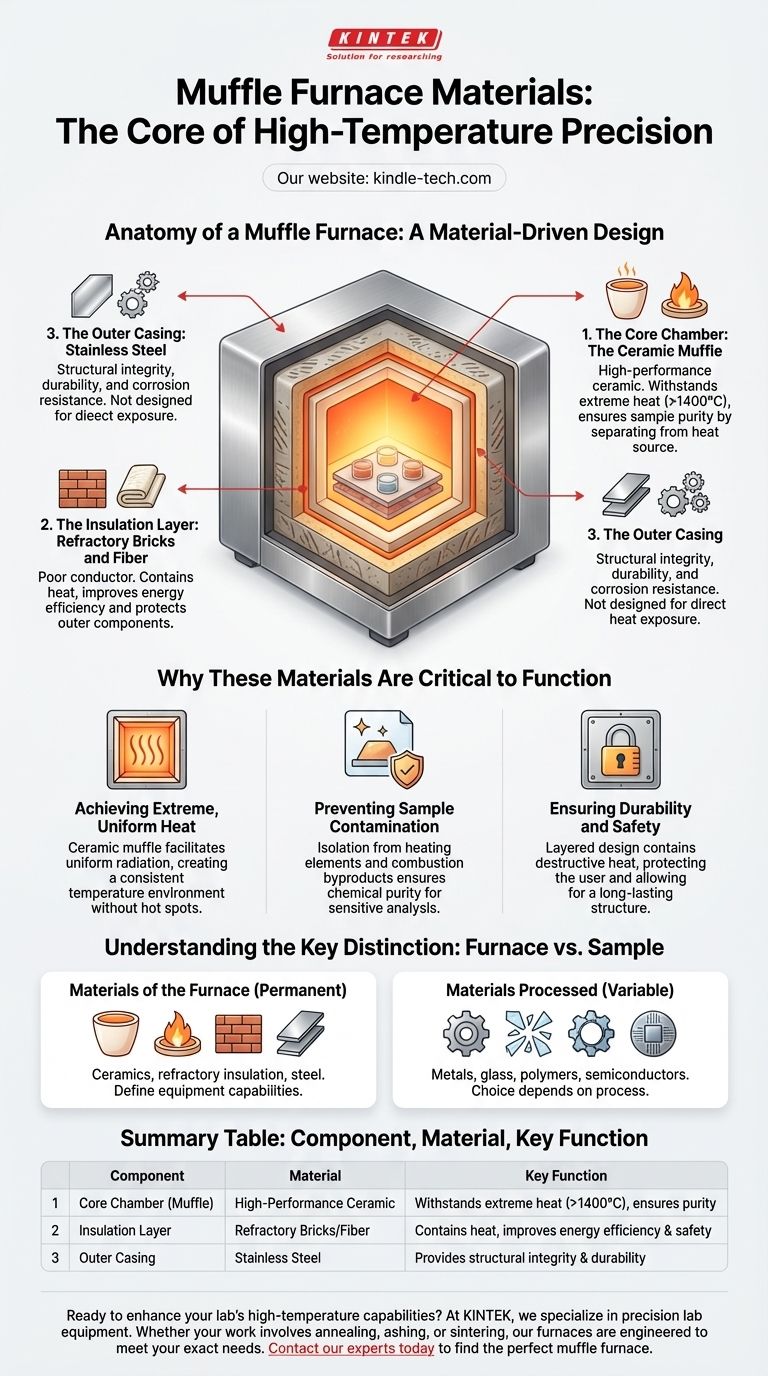
At its core, a muffle furnace is constructed using advanced refractory ceramic materials. This inner chamber, known as the "muffle," is designed to withstand extreme temperatures without melting or degrading. This core is then surrounded by layers of insulation and housed within a durable outer casing, typically made of stainless steel.
The selection of materials is not arbitrary; it is fundamental to the furnace's function. The entire design revolves around using a thermally resistant ceramic muffle to create an isolated, uniformly heated chamber that protects samples from direct contact with the heat source.

The Anatomy of a Muffle Furnace: A Material-Driven Design
The construction of a muffle furnace is a lesson in thermal management. Each material is chosen for a specific role in containing and controlling temperatures that can exceed 1400°C (2550°F).
The Core Chamber: The Ceramic Muffle
The heart of the furnace is the muffle itself, an inner chamber made from a high-performance ceramic. This material is the primary barrier that contains the intense heat.
Ceramics are chosen for their exceptionally high melting points and chemical inertness, ensuring they remain stable even under extreme thermal stress. This allows the furnace to operate reliably for processes like annealing, ashing, and sintering.
The Insulation Layer: Refractory Bricks and Fiber
Surrounding the ceramic muffle is a thick layer of refractory insulation. This is often composed of refractory bricks or ceramic fiber blankets.
This material is a poor conductor of heat. Its purpose is twofold: to prevent heat from escaping, which ensures energy efficiency and stable temperatures, and to protect the furnace's outer components and the user from the dangerous inner heat.
The Outer Casing: Stainless Steel
The external body or housing of the furnace is typically fabricated from textured stainless steel sheets.
Unlike the internal components, the steel casing is not designed for direct heat exposure. It provides structural integrity, durability, and corrosion resistance for the overall unit. The internal refractory insulation is what keeps the external casing at a safe temperature.
Why These Materials Are Critical to Function
Understanding the materials reveals the core principles of how a muffle furnace works: isolation and uniform heating.
Achieving Extreme, Uniform Heat
The ceramic muffle separates the sample chamber from the heating elements (in an electric furnace) or the flame (in a gas-fired furnace). Heat is transferred into the chamber via radiation, creating a highly uniform temperature environment without hot spots.
Preventing Sample Contamination
This separation is the defining feature of a muffle furnace. Because the sample never makes direct contact with the heating source or combustion byproducts, its chemical purity is maintained. This is critical for sensitive analytical procedures like ash content determination or materials research.
Ensuring Durability and Safety
The layered design—a ceramic core, refractory insulation, and a steel exterior—creates a robust and safe piece of equipment. The insulation contains the destructive heat, allowing the durable steel frame to provide a stable and long-lasting structure.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Furnace vs. Sample
A common point of confusion is the distinction between the materials used to build the furnace and the materials processed inside it.
Materials of the Furnace
As established, the furnace itself is constructed from ceramics, refractory insulation, and steel. These materials are permanent and define the equipment's capabilities.
Materials Processed in the Furnace
The materials placed inside the furnace for testing or treatment can be anything from metals and glass to polymers and semiconductors. The choice of sample material depends entirely on the specific process being performed and its ability to withstand the required temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of each material helps you better utilize the equipment for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is performance: The quality of the ceramic muffle and refractory insulation directly dictates the furnace's maximum temperature, heat-up speed, and temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is process purity: Appreciate that the inert ceramic muffle is the key component that prevents contamination and ensures reliable analytical results.
- If your primary focus is safety: Recognize that the layered system of insulation and the steel casing are what stand between you and the thousands of degrees of internal heat.
By understanding its material composition, you move from simply using a tool to truly understanding how it works.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core Chamber (Muffle) | High-Performance Ceramic | Withstands extreme heat (>1400°C), ensures sample purity |
| Insulation Layer | Refractory Bricks/Fiber | Contains heat, improves energy efficiency and safety |
| Outer Casing | Stainless Steel | Provides structural integrity and durability |
Ready to enhance your lab's high-temperature capabilities? The right muffle furnace is built from the right materials. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment designed for durability, safety, and superior performance. Whether your work involves annealing, ashing, or sintering, our furnaces are engineered to meet your exact needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-quality high-temperature furnace required for YSZ electrolytes? Achieve Dense, High-Conductivity Ceramics
- What is the inside material of the muffle furnace? Discover the Refractory Core for High-Temp Precision
- What is the holding time for sintering? A Guide to Optimizing Your Process
- What are the applications of microwave sintering? Faster, More Uniform Ceramic Processing
- What is the importance of ash determination in foods? A Key to Quality, Nutrition & Purity
- What is sintering cycle? A Guide to the Thermal Process for Dense, Strong Parts
- What is the refractory material for the muffle furnace? Choosing the Right Lining for Your Application
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in TiO2/CuxOy nanotubes? Achieve Superior Phase Transformation



















