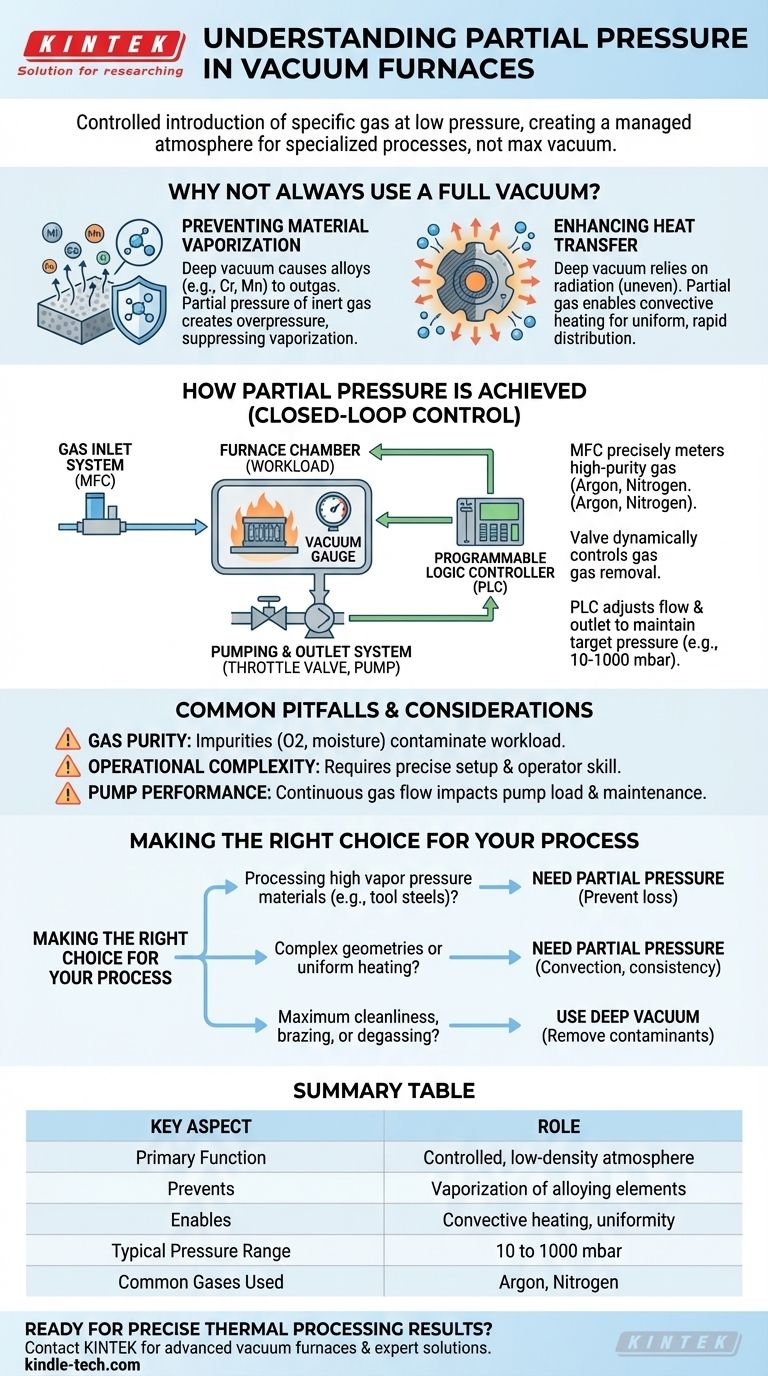
In a vacuum furnace, partial pressure is the controlled introduction and maintenance of a specific gas at a low but defined pressure. Instead of aiming for the highest possible vacuum (the lowest pressure), this technique creates a precisely managed, low-density atmosphere for specialized thermal processes.
The core purpose of partial pressure is to change the furnace environment from a pure vacuum to a specific, controlled atmosphere. This is critical for preventing material damage like vaporization or for improving process outcomes like heat uniformity, which a deep vacuum cannot achieve alone.
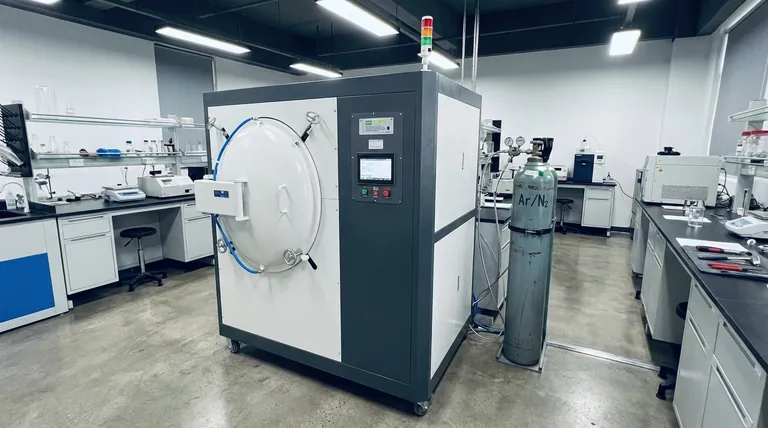

Why Not Always Use a Full Vacuum?
While a deep vacuum is excellent for removing contaminants and preventing oxidation, it can be detrimental to certain materials and processes. Introducing a controlled partial pressure of a gas like argon or nitrogen solves several key challenges.
Preventing Material Vaporization
At high temperatures, a deep vacuum can cause certain alloying elements with high vapor pressures (like chromium, manganese, or zinc) to essentially "boil" off the surface of the material. This is known as outgassing or sublimation.
A partial pressure of an inert gas creates a controlled "overpressure" on the material's surface. This physical barrier suppresses the vaporization of these volatile elements, ensuring the final product maintains its intended chemical composition and integrity.
Enhancing Heat Transfer
A deep vacuum is an excellent thermal insulator. Heat can only travel via radiation, which can lead to uneven temperatures, especially with complex parts that have shadowed areas.
By introducing a gas, you enable convective heating. The gas molecules transfer heat throughout the chamber and around the workload, resulting in significantly more uniform and rapid temperature distribution.
How Partial Pressure Control is Achieved
A partial pressure system is a sophisticated control loop that balances gas being introduced with gas being pumped out. This is managed by a dedicated programmable logic controller (PLC).
The Gas Inlet System
A mass flow controller (MFC) is used to precisely meter a specific amount of high-purity gas (typically argon or nitrogen) into the furnace chamber. The operator sets the desired flow rate via the PLC.
The Pumping and Outlet System
While the gas is being introduced, the vacuum pumps (e.g., a rotary vane pump) continue to operate. A pneumatic throttling or adjustable outlet valve is placed between the chamber and the pumps.
This valve dynamically opens or closes to control how quickly gas is removed from the chamber.
The Closed-Loop Control
A vacuum gauge constantly measures the pressure inside the furnace and sends this reading to the PLC. The PLC compares the actual pressure to the desired setpoint.
It then adjusts both the incoming gas flow via the MFC and the outgoing gas removal via the outlet valve to maintain the target partial pressure with high precision, often within a range of 10 to 1000 mbar.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Using partial pressure introduces a higher level of process control, but it also comes with specific challenges that must be managed for successful operation.
Gas Purity and Contamination
The effectiveness of the process depends entirely on the purity of the gas being introduced. Any impurities in the gas supply, such as oxygen or moisture, will be introduced directly into the hot zone, potentially contaminating the workload.
Increased Operational Complexity
Operating a partial pressure system is inherently more complex than simply pumping down to a deep vacuum. It requires careful setup of flow rates and pressure setpoints specific to the material and process, demanding a higher level of operator skill.
Impact on Pump Performance
Running with a continuous gas flow places a different type of load on the vacuum pumps compared to high-vacuum operation. This must be considered for system maintenance and longevity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing whether to use a partial pressure system depends entirely on the specific goal of your thermal process.
- If you are processing materials with high vapor pressures (e.g., tool steels, certain alloys): Using partial pressure is essential to prevent the vaporization and loss of critical alloying elements.
- If you need highly uniform heating for complex geometries or dense loads: A partial pressure of an inert gas will dramatically improve heat transfer through convection, reducing cycle times and ensuring consistent results.
- If your primary goal is maximum cleanliness, brazing, or degassing: A deep, clean vacuum without the addition of another gas is the correct approach to remove all atmospheric contaminants.
Ultimately, mastering partial pressure control transforms a vacuum furnace from a simple heating chamber into a highly adaptable and precise processing tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Partial Pressure Control |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates a controlled, low-density atmosphere for specialized thermal processes. |
| Prevents | Vaporization of alloying elements (e.g., chromium, manganese) at high temperatures. |
| Enables | Convective heating for more uniform and rapid temperature distribution. |
| Typical Pressure Range | 10 to 1000 mbar (millibar). |
| Common Gases Used | Argon, Nitrogen. |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing results?
Partial pressure control is essential for preventing material degradation and ensuring uniform heating in your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces with advanced partial pressure systems, to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories.
Our experts can help you select the right equipment to enhance your process efficiency and material outcomes. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















