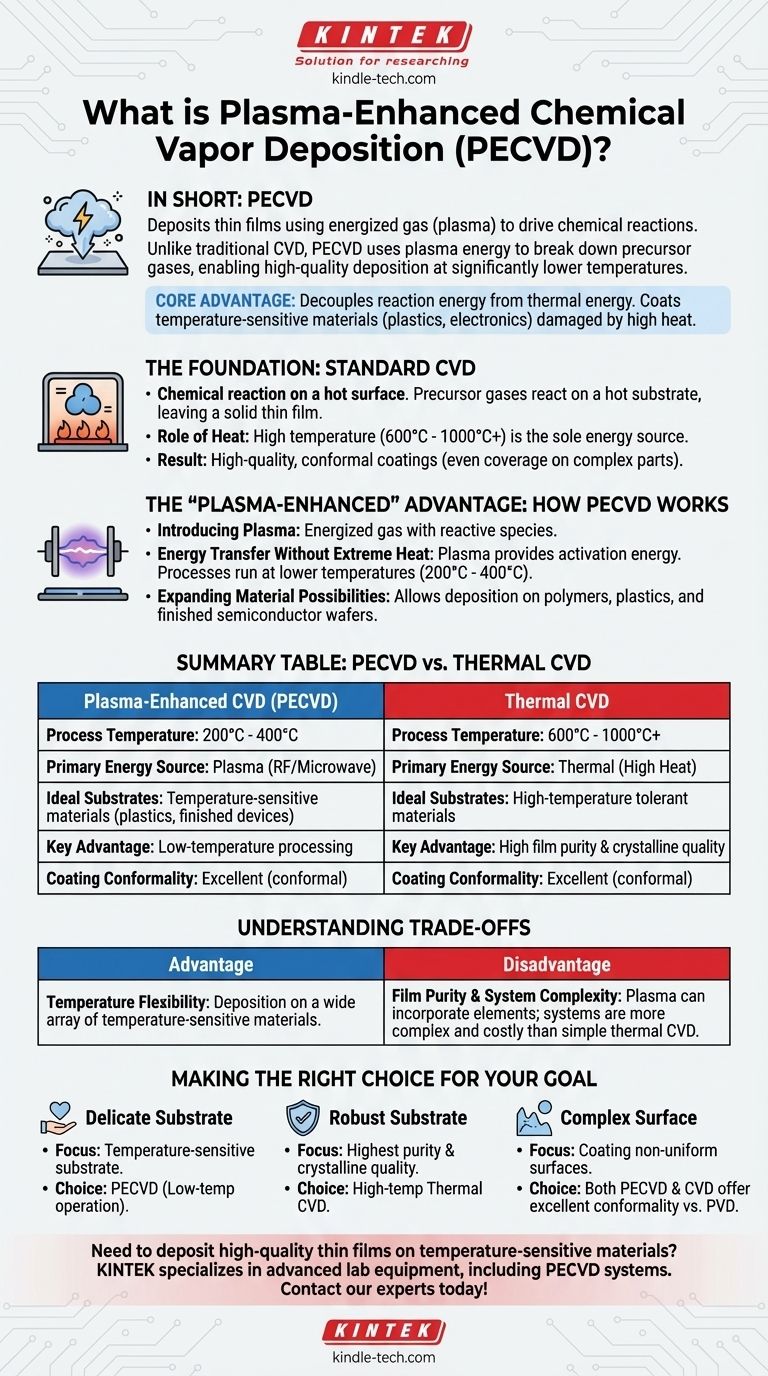
In short, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process for depositing thin films onto a surface that uses an energized gas, or plasma, to drive the necessary chemical reactions. Unlike traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) which relies on high heat, PECVD uses the energy from the plasma to break down precursor gases. This fundamental difference allows for high-quality film deposition at significantly lower temperatures.
The core advantage of PECVD is its ability to decouple the reaction energy from thermal energy. This allows for the coating of temperature-sensitive materials, like plastics or completed electronic devices, that would be damaged or destroyed by the high heat of conventional CVD processes.

The Foundation: Understanding Standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
To grasp the significance of PECVD, we must first understand the principles of conventional CVD.
The Core Principle: A Chemical Reaction on a Surface
At its heart, any CVD process involves introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing a substrate (the part to be coated).
These gases decompose and react on the hot substrate's surface, leaving behind a solid thin film. The excess gaseous byproducts are then pumped out of the chamber.
The Role of Heat
In traditional CVD methods, such as Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), high temperature is the sole energy source used to break the chemical bonds of the precursor gases and initiate the deposition reaction.
This often requires temperatures ranging from 600°C to over 1000°C, which severely limits the types of materials that can be used as substrates.
The Result: High-Quality, Conformal Coatings
A major advantage of the CVD family of techniques is their ability to produce conformal coatings. Because the precursor is a gas, it can reach and coat all surfaces of a complex or non-uniform part.
This overcomes the "line-of-sight" limitations common in other methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), ensuring even coverage on all features of the substrate.
The "Plasma-Enhanced" Advantage: How PECVD Works
PECVD fundamentally alters the energy input of the CVD process, opening up a vast new range of applications.
Introducing Plasma: An Energized Gas
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. By applying a strong electric or magnetic field to a gas at low pressure, its atoms are broken apart into a mix of ions, electrons, and highly reactive neutral radicals.
This energized gas, the plasma, contains a tremendous amount of chemical energy without being intensely hot in the thermal sense.
Energy Transfer Without Extreme Heat
In PECVD, this plasma provides the activation energy needed to break down the precursor gases. The reactive radicals created in the plasma readily form the desired film on the substrate's surface.
Because the energy comes from the plasma itself, the substrate does not need to be heated to extreme temperatures. PECVD processes can run at much lower temperatures, typically from 200°C to 400°C.
Expanding Material and Substrate Possibilities
This low-temperature operation is the key benefit of PECVD. It allows for the deposition of high-quality thin films on materials that cannot withstand high heat.
This includes polymers, plastics, and, critically, finished semiconductor wafers that already contain sensitive electronic circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PECVD vs. Thermal CVD
Choosing a deposition technique requires an objective understanding of its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantage: Temperature Flexibility
The primary reason to choose PECVD is its low-temperature capability. It makes deposition possible on a wide array of temperature-sensitive materials that are incompatible with thermal CVD.
Disadvantage: Film Purity
High-temperature thermal CVD processes often produce films with higher purity and better crystalline structure. The energetic environment of plasma can sometimes incorporate other elements, like hydrogen from the precursor gases, into the growing film.
While PECVD films are of excellent quality for many applications, the highest-purity films are often grown with high-temperature methods on substrates that can tolerate the heat.
Disadvantage: System Complexity
A PECVD system is inherently more complex than a simple thermal CVD furnace. It requires RF or microwave power supplies, impedance matching networks, and more sophisticated chamber engineering to generate and sustain the plasma. This can lead to higher equipment and maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between PECVD and a conventional CVD method depends entirely on your substrate material and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film on a temperature-sensitive substrate (like a polymer or a finished electronic device): PECVD is the clear and often only viable choice due to its low-temperature operation.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and crystalline quality for a robust, heat-tolerant substrate: A high-temperature thermal process like LPCVD may be the superior option.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-uniform surfaces where line-of-sight is a problem: Both PECVD and other CVD methods offer an excellent solution compared to PVD techniques.
Ultimately, selecting the correct deposition method requires matching the process capabilities to your specific material constraints and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Thermal CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 200°C - 400°C | 600°C - 1000°C+ |
| Primary Energy Source | Plasma (RF/Microwave) | Thermal (High Heat) |
| Ideal Substrates | Temperature-sensitive materials (plastics, finished devices) | High-temperature tolerant materials |
| Key Advantage | Low-temperature processing | High film purity & crystalline quality |
| Coating Conformality | Excellent (conformal) | Excellent (conformal) |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films on temperature-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PECVD systems, to meet your specific research and production needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for coating polymers, electronics, and other delicate substrates. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your thin film deposition process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















