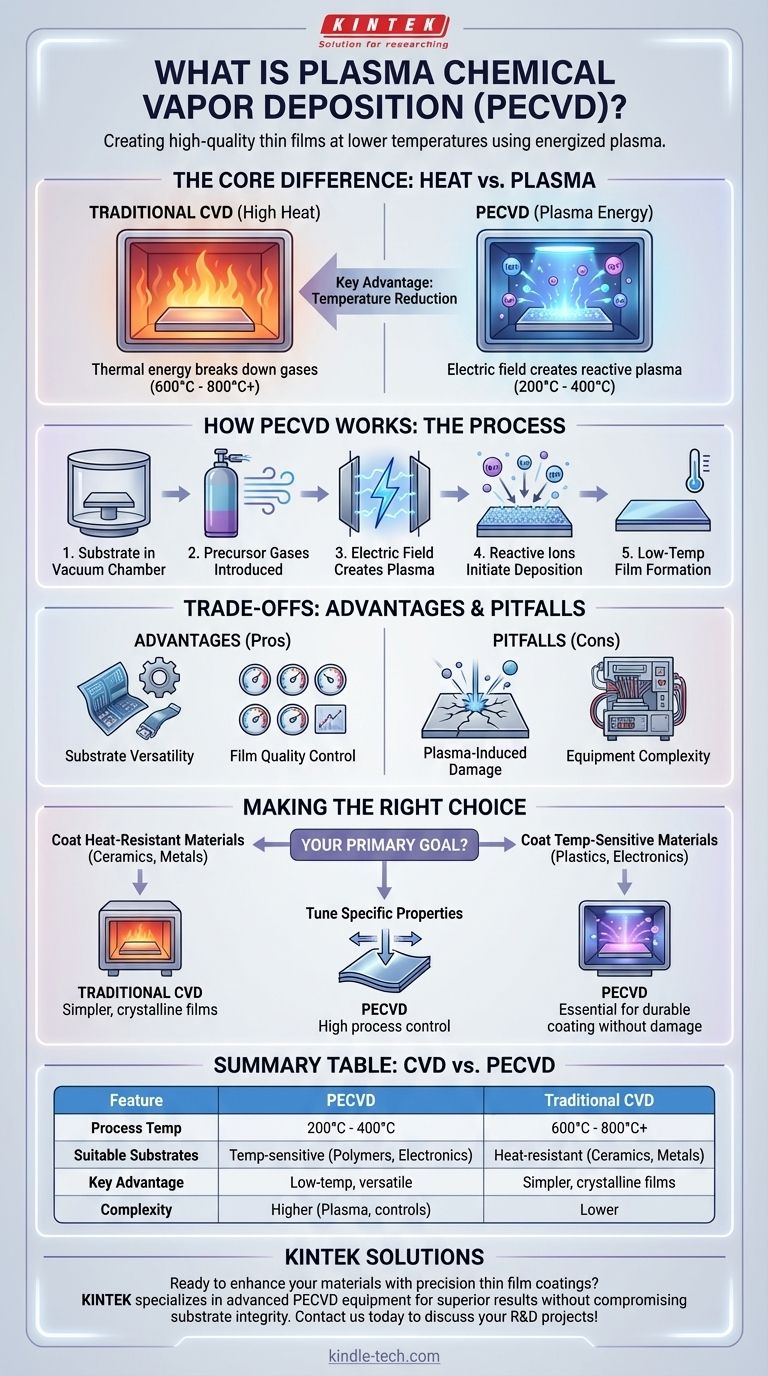
At its core, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process for creating high-quality, durable thin films on a surface. It functions like traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) by introducing precursor gases into a chamber, but with a crucial difference: it uses an energized plasma to drive the chemical reactions needed to form the coating, allowing the process to occur at much lower temperatures.
The central advantage of using plasma is temperature reduction. While standard CVD requires intense heat to break down precursor gases, PECVD achieves the same result with energy from a plasma, making it possible to coat temperature-sensitive materials that would be damaged or destroyed by other methods.

The Foundation: Understanding Chemical Vapor Deposition
What is the Basic CVD Process?
In any CVD process, the object to be coated (the substrate) is placed inside a reaction chamber under a vacuum.
Gaseous chemical precursors are then introduced into the chamber. These gases flow over the substrate, where a chemical reaction is triggered, causing a solid material to deposit onto the surface and form a thin, uniform film.
Why is CVD Used?
CVD is a highly versatile technique used to create films with specific, desirable properties. The resulting coatings are durable and can be engineered for high purity or resistance to corrosion and abrasion.
Because the precursor is a gas, it can evenly coat all surfaces of a complex, three-dimensional object. This "non-line-of-sight" capability is a significant advantage over many other coating techniques.
The Key Enhancement: The Role of Plasma
Breaking Down Molecules Without Heat
The chemical reactions in traditional CVD are initiated by thermal energy, often requiring temperatures of 600°C to 800°C or higher. Many materials, such as plastics, polymers, or fully fabricated semiconductor wafers, cannot withstand this heat.
PECVD solves this problem by using an electric field to ionize the precursor gases, creating a plasma. This plasma is a high-energy state of matter that contains ions, electrons, and free radicals which are highly reactive.
The Impact of Lower Temperatures
The reactive particles within the plasma can initiate the deposition reaction at much lower temperatures, typically in the 200°C to 400°C range.
This single difference dramatically expands the range of possible applications. It allows for the deposition of durable, high-performance films on substrates that would otherwise be incompatible with the CVD process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Advantage: Substrate Versatility
The primary benefit of PECVD is its ability to coat materials that cannot tolerate high heat. This includes flexible electronics, medical implants made of polymers, and low-melting-point metals.
Advantage: Film Quality Control
While lower temperature is the main driver, the plasma parameters (power, frequency, pressure) provide additional variables for controlling the properties of the final film, such as its density, stress, and chemical composition.
Potential Pitfall: Plasma-Induced Damage
The high-energy ions within the plasma can, if not properly controlled, physically bombard the substrate and the growing film. This can introduce defects or impurities into the coating, which is a critical concern in high-precision applications like microelectronics.
Potential Pitfall: Equipment Complexity
PECVD systems are inherently more complex and expensive than many thermal CVD reactors. They require sophisticated power supplies, gas handling systems, and vacuum technology to generate and maintain a stable plasma.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between traditional CVD and PECVD hinges almost entirely on the temperature tolerance of your substrate and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-resistant materials (like ceramics or refractory metals): Traditional high-temperature CVD may be a simpler, more cost-effective choice that can yield highly crystalline films.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials (like plastics, polymers, or complete electronic devices): PECVD is the essential and often only viable option for applying a durable, high-quality coating.
- If your primary focus is tuning specific film properties like mechanical stress or refractive index: The additional control parameters offered by PECVD can provide a level of process control that is difficult to achieve with thermal methods alone.
Ultimately, PECVD empowers engineers and scientists to apply the powerful benefits of vapor deposition to a much broader universe of materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD | Traditional CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 200°C - 400°C | 600°C - 800°C+ |
| Suitable Substrates | Temperature-sensitive materials (polymers, plastics, electronics) | Heat-resistant materials (ceramics, refractory metals) |
| Key Advantage | Low-temperature processing, substrate versatility | Simpler equipment, highly crystalline films |
| Complexity | Higher (plasma generation, sophisticated controls) | Lower |
| Film Quality Control | Excellent (via plasma parameters) | Good (via temperature/gas flow) |
Ready to enhance your materials with precision thin film coatings?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge deposition techniques like PECVD. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive polymers, developing flexible electronics, or creating medical implants, our solutions can help you achieve superior coating results without compromising your substrate integrity.
Our expertise in plasma-enhanced processes ensures you get the right equipment for your specific application needs, with optimal film quality and process control.
Contact us today to discuss how PECVD technology can advance your research and development projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















