At its core, a porcelain crucible is made from a highly refined ceramic clay. This specialized clay is primarily composed of kaolin, a hydrated aluminum silicate, which is then mixed with other materials like quartz (silica) and feldspar before being fired at very high temperatures to achieve its final, durable form.
The specific blend of kaolin, quartz, and feldspar is not accidental. This composition is precisely engineered to give porcelain its signature properties for laboratory work: high resistance to heat and chemical attack, combined with mechanical strength.

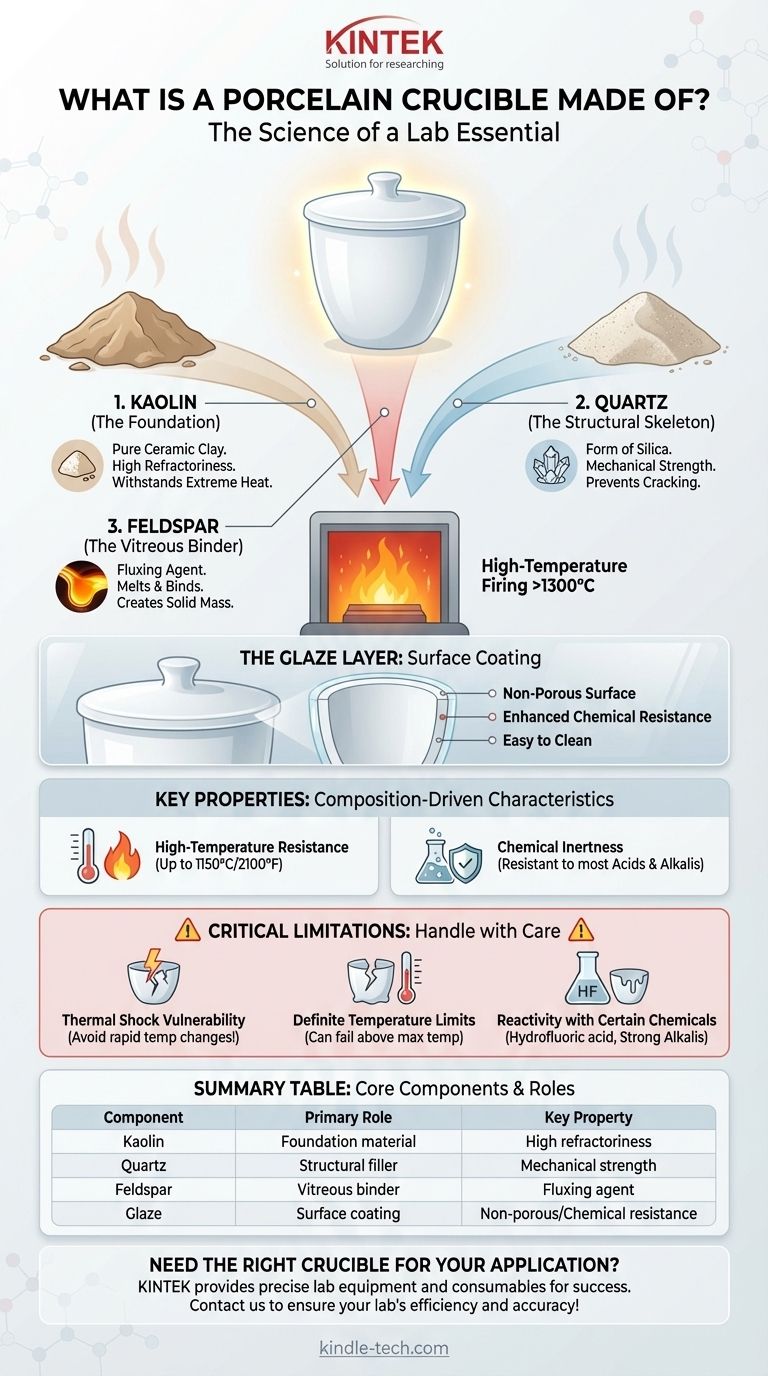
The Core Components of Porcelain
To understand why a porcelain crucible behaves the way it does, we must first look at the role of each primary ingredient. These materials are carefully proportioned to create a final product that is dense, strong, and non-porous.
Kaolin (The Foundation)
Kaolin is the main component. As a very pure form of clay, it provides the base material with high refractoriness, which is the ability to withstand extreme heat without melting or deforming. It also gives the unfired material plasticity, allowing it to be shaped into the crucible form.
Quartz (The Structural Skeleton)
Quartz, a form of silica, is added as a filler. It plays a critical structural role by reducing the amount the crucible shrinks as it dries and is fired. This prevents cracking and adds significant mechanical strength and hardness to the finished product.
Feldspar (The Vitreous Binder)
Feldspar acts as a fluxing agent. During the high-temperature firing process (often exceeding 1300°C or 2372°F), the feldspar melts. This molten glass flows between the particles of kaolin and quartz, binding them together into a single, solid mass.
The Glaze Layer
Finally, most porcelain crucibles are coated with a glaze. This is a glassy layer fused to the surface that makes the crucible non-porous and smooth. The glaze enhances chemical resistance and makes the crucible much easier to clean, preventing cross-contamination between experiments.
How Composition Creates Key Properties
The synergy between these components directly results in the crucible's essential characteristics for lab use.
High-Temperature Resistance
The high melting points of kaolin and quartz are responsible for the crucible's ability to be used at very high temperatures, typically up to 1150°C (2100°F) for glazed porcelain.
Chemical Inertness
The stable, vitrified (glass-like) structure created by the feldspar binder and the glaze makes porcelain highly resistant to the corrosive action of most acids, alkalis, and other chemicals. This ensures the crucible does not react with the sample being heated.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly useful, the composition of porcelain also introduces critical limitations that every user must understand to prevent failure.
Vulnerability to Thermal Shock
This is the most significant weakness of porcelain. Because it is a rigid, crystalline ceramic, it does not expand or contract uniformly. Heating or cooling a crucible too quickly creates internal stress, which will cause it to crack or shatter. Gentle and gradual temperature changes are mandatory.
Definite Temperature Limits
While heat-resistant, porcelain is not indestructible. Heating it above its recommended maximum temperature can cause the feldspar binder to soften, leading to deformation or complete failure. It is not suitable for ultra-high-temperature applications where materials like alumina or zirconia would be required.
Reactivity with Certain Chemicals
Although generally inert, porcelain can be attacked by a few specific substances. Hydrofluoric acid will dissolve the silica in the porcelain, and hot, concentrated alkaline solutions can also slowly etch its surface over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work
Understanding the material science behind your tools is key to successful experiments. Use these guidelines to determine if a porcelain crucible is the right choice for your task.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating: For ashing samples, heating stable chemical compounds, or evaporating liquids below 1150°C, a porcelain crucible is an excellent and cost-effective tool.
- If your process involves rapid temperature changes: You must avoid porcelain. Consider using a metal crucible (like nickel or stainless steel) or a quartz fiber crucible, which are designed to withstand thermal shock.
- If you are working with hydrofluoric acid or strong alkalis: Do not use porcelain. A platinum or specific polymer-based crucible is necessary to avoid destroying your vessel and contaminating your sample.
By respecting both the strengths and the inherent limitations of its composition, you can use the porcelain crucible as the reliable and effective laboratory tool it was designed to be.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Role | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Kaolin | Foundation material | High refractoriness (heat resistance) |
| Quartz | Structural filler | Mechanical strength, reduces shrinkage |
| Feldspar | Vitreous binder | Fluxing agent, binds components during firing |
| Glaze | Surface coating | Non-porous, chemical resistance, easy cleaning |
Need the right crucible for your specific application? The composition of your labware is critical to your experiment's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your laboratory requires. Whether you need standard porcelain crucibles or specialized alternatives for extreme temperatures or reactive chemicals, our experts can help you select the perfect tool. Contact us today to ensure your lab's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible required for LLTO calcination? Ensure Material Purity and Stoichiometry
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles necessary for liquid lead corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Data
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- Why must aluminum alloys be heated in alumina crucibles? Ensure Pure Results in Molten Corrosion Experiments
- What is a crucible porcelain? Choosing the Right High-Temperature Lab Vessel



















