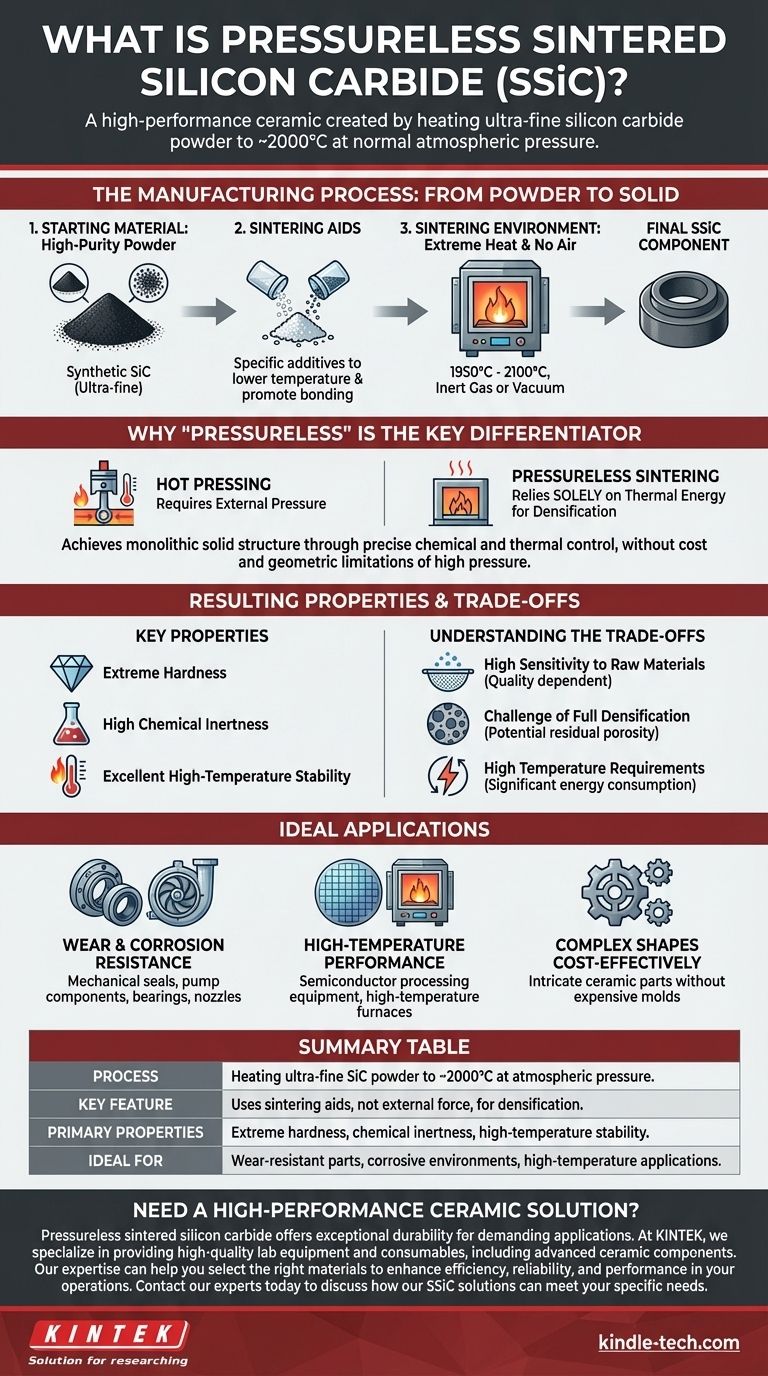
In short, pressureless sintered silicon carbide (SSiC) is a high-performance ceramic. It is created by heating an extremely pure, ultra-fine silicon carbide powder to very high temperatures (around 2000°C) until the particles fuse together into a solid, dense object. The defining feature of this process is that it occurs at normal atmospheric pressure, relying on chemical additives and precise temperature control rather than external force.
The core principle of pressureless sintering is to achieve the exceptional hardness, density, and temperature resistance of silicon carbide without the cost and geometric limitations of manufacturing methods that require high external pressure.

The Manufacturing Process: From Powder to Solid
The creation of SSiC is a precise, multi-step process designed to produce a material with minimal internal flaws. Each step is critical to the final properties of the component.
The Starting Material: High-Purity Powder
The process begins with synthetically produced silicon carbide. Natural silicon carbide, known as moissanite, is too rare for industrial use.
This synthetic SiC is milled into an ultra-fine, high-purity powder. The small particle size is essential for enabling the particles to bond effectively during heating.
The Role of Sintering Aids
A small amount of specific additives, known as sintering aids, are mixed with the SiC powder.
These additives are the key to making the "pressureless" process work. They help reduce the temperature needed for densification and promote the bonding between SiC grains without requiring external mechanical force.
The Sintering Environment: Extreme Heat and No Air
The mixture is then heated in a controlled furnace to between 1950°C and 2100°C.
This is done in an inert gas or vacuum atmosphere. This controlled environment is crucial to prevent the silicon carbide from reacting with oxygen at such extreme temperatures, which would compromise its integrity.
Why "Pressureless" is the Key Differentiator
The term "pressureless" distinguishes this method from other ceramic manufacturing processes like hot pressing, where immense external pressure is applied alongside heat.
Relying on Temperature, Not Force
As the name implies, this method relies solely on thermal energy to consolidate the powder into a dense ceramic part.
The heat activates the sintering aids and gives the SiC atoms enough energy to diffuse and form strong bonds, effectively fusing the powder into a monolithic solid.
Resulting Material Properties
This process creates a theoretically dense ceramic with the exceptional properties inherent to silicon carbide.
Key characteristics include extreme hardness, high chemical inertness, and excellent stability at high temperatures, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the pressureless sintering method is not without its challenges. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
High Sensitivity to Raw Materials
The success of the process is highly dependent on the quality of the initial SiC powder. Particle size, purity, and the specific sintering aids used all have a dramatic impact on the final product's density and strength.
The Challenge of Full Densification
Achieving 100% theoretical density without pressure is difficult. Any residual porosity (tiny voids) can become a weak point, potentially reducing the material's overall mechanical strength compared to hot-pressed alternatives.
High Temperature Requirements
The extremely high temperatures required translate to significant energy consumption and require specialized, expensive furnace equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Pressureless sintered silicon carbide is not a universal solution, but it is an outstanding choice for specific engineering challenges.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear and corrosion resistance: SSiC is an ideal material for mechanical seals, pump components, bearings, and nozzles used in abrasive or chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Its ability to maintain strength and inertness at high temperatures makes it suitable for components in semiconductor processing equipment and high-temperature furnaces.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes cost-effectively: Compared to methods requiring expensive pressing molds, pressureless sintering can be a more economical route for creating intricate ceramic parts.
Ultimately, pressureless sintering is an advanced manufacturing technique that leverages material science to create highly durable ceramic components by substituting mechanical force with precise chemical and thermal control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating ultra-fine SiC powder to ~2000°C at atmospheric pressure. |
| Key Feature | Uses sintering aids, not external force, for densification. |
| Primary Properties | Extreme hardness, chemical inertness, high-temperature stability. |
| Ideal For | Wear-resistant parts, corrosive environments, high-temperature applications. |
Need a high-performance ceramic solution for your laboratory or industrial process?
Pressureless sintered silicon carbide offers exceptional durability for demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components. Our expertise can help you select the right materials to enhance efficiency, reliability, and performance in your operations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our SSiC solutions can meet your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges



















