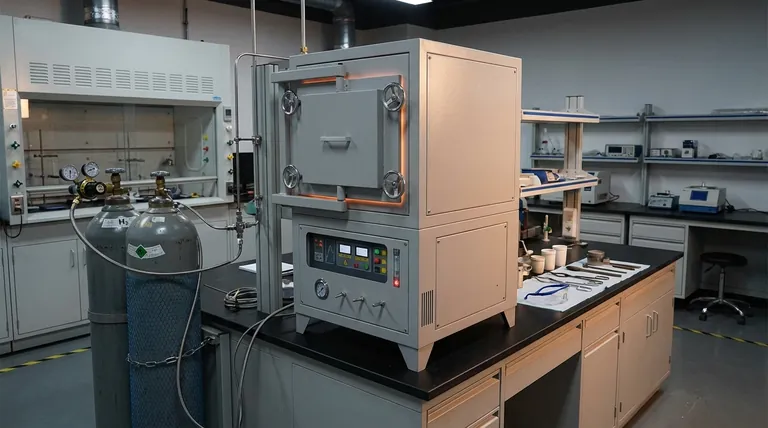
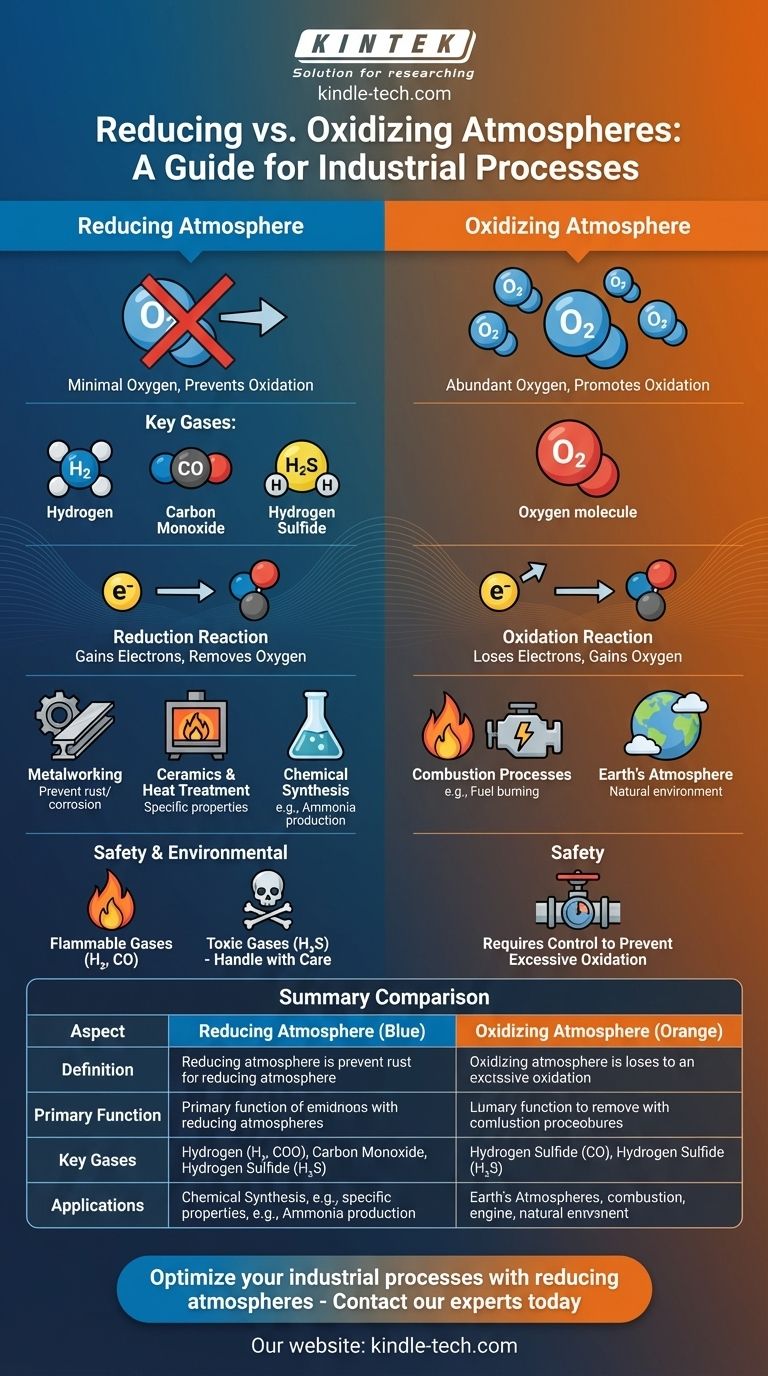
A reducing atmosphere is a gaseous environment where the presence of oxygen and other oxidizing agents is minimized or removed, preventing oxidation processes. Instead, it contains gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide, which promote reduction reactions. This type of atmosphere is often used in industrial processes, such as metalworking and ceramics, to prevent oxidation and achieve specific material properties. Conversely, an oxidizing atmosphere contains ample oxygen, facilitating oxidation reactions. Understanding the distinction between these atmospheres is crucial for applications in material science, manufacturing, and environmental studies.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of a Reducing Atmosphere:
- A reducing atmosphere is characterized by the absence or minimal presence of oxygen and other oxidizing gases.
- It contains gases like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), which are capable of donating electrons and promoting reduction reactions.
- Reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons by a substance, often leading to the removal of oxygen from compounds.
-
Purpose and Applications:
- Preventing Oxidation: A reducing atmosphere is used to prevent oxidation, which can degrade materials or alter their properties. For example, in metalworking, it helps maintain the integrity of metals by preventing rust or corrosion.
- Industrial Processes: It is essential in processes like annealing, sintering, and heat treatment of metals and ceramics, where controlled atmospheres are required to achieve specific material characteristics.
- Chemical Reactions: In chemical synthesis, a reducing atmosphere can facilitate reactions that require the reduction of compounds, such as the production of ammonia (NH₃) from nitrogen (N₂) and hydrogen (H₂).
-
Comparison with Oxidizing Atmosphere:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: This environment contains abundant oxygen, promoting oxidation reactions where substances lose electrons. It is common in combustion processes and environments like Earth's atmosphere.
-
Key Differences:
- Reducing atmospheres prevent oxidation, while oxidizing atmospheres promote it.
- Reducing atmospheres are used in processes where oxidation is undesirable, whereas oxidizing atmospheres are used where oxidation is necessary, such as in fuel combustion.
-
Examples of Reducing Gases:
- Hydrogen (H₂): A highly reactive gas that readily donates electrons, making it a strong reducing agent.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Often used in industrial settings to reduce metal oxides to pure metals.
- Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S): A reducing gas that can participate in reduction reactions, though it is less commonly used due to its toxicity.
-
Environmental and Safety Considerations:
- Handling Reducing Gases: Many reducing gases, such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide, are flammable and require careful handling to prevent explosions or fires.
- Toxicity: Some reducing gases, like hydrogen sulfide, are toxic and necessitate proper ventilation and safety protocols.
- Environmental Impact: The use of reducing atmospheres in industrial processes must be managed to minimize environmental harm, such as the release of harmful byproducts.
-
Role in Natural and Industrial Settings:
- Natural Reducing Atmospheres: Rare on Earth but can occur in specific environments, such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents or certain microbial habitats.
- Industrial Reducing Atmospheres: Commonly created in controlled environments for manufacturing processes, such as in furnaces or reactors, to achieve desired material properties or chemical reactions.
By understanding the principles and applications of reducing and oxidizing atmospheres, industries can optimize processes, enhance material performance, and ensure safety and environmental compliance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxidizing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimal oxygen, contains reducing gases (e.g., H₂, CO, H₂S) | Abundant oxygen, promotes oxidation reactions |
| Primary Function | Prevents oxidation, promotes reduction reactions | Facilitates oxidation reactions |
| Applications | Metalworking, ceramics, chemical synthesis, heat treatment | Combustion processes, Earth's atmosphere |
| Key Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) | Oxygen (O₂) |
| Safety Considerations | Flammable gases (e.g., H₂, CO), toxic gases (e.g., H₂S) require careful handling | Less hazardous but requires control to prevent excessive oxidation |
Optimize your industrial processes with reducing atmospheres—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization



















