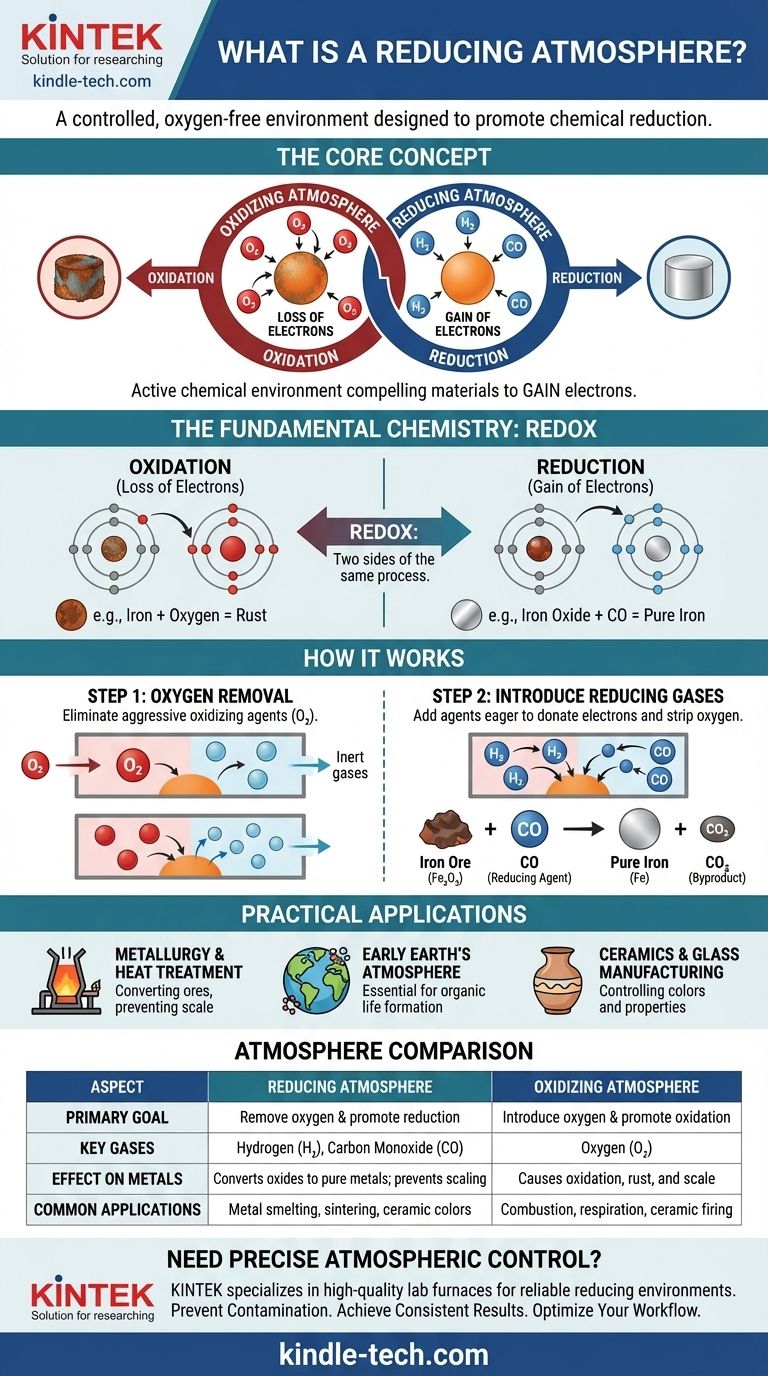
In short, a reducing atmosphere is a controlled gaseous environment where oxygen has been intentionally removed and replaced with gases that prevent oxidation and actively promote chemical reduction. This type of atmosphere is rich in "reducing agents" like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), or hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), which are chemically eager to donate electrons and strip oxygen from other materials.
A reducing atmosphere isn't merely about the absence of oxygen; it is an active chemical environment designed to force a specific reaction. It works by creating a surplus of electrons, compelling materials within it to gain those electrons and revert to a less oxidized state.

The Fundamental Chemistry at Play
To truly grasp a reducing atmosphere, you must first understand the fundamental chemical principle it's built upon: oxidation and reduction. These are two sides of the same coin, a process often called "redox."
Understanding Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation is the loss of electrons. A classic example is iron rusting. Oxygen in the air pulls electrons from the iron atoms, forming iron oxide (rust). The iron is "oxidized."
Reduction is the gain of electrons. It is the chemical opposite of oxidation. A reducing atmosphere facilitates this process by creating an environment where atoms are forced to take on electrons.
Think of it as a chemical tug-of-war for electrons. An oxidizing agent, like oxygen, is strong and pulls electrons away from other materials. A reducing agent, like hydrogen, is generous and donates electrons to other materials.
The Role of Oxygen Removal
The first and most critical step in creating a reducing atmosphere is the removal of free oxygen (O₂) and other oxidizing gases.
Oxygen is a highly aggressive oxidizing agent. Its presence makes it nearly impossible to perform a reduction reaction, as it will relentlessly pull electrons from any available source. Removing it prevents this unwanted oxidation from occurring.
The Function of Reducing Gases
Simply removing oxygen creates a neutral, or inert, atmosphere. To make it a reducing atmosphere, specific gases are introduced.
These gases—typically hydrogen (H₂) or carbon monoxide (CO)—act as powerful reducing agents. They have a stronger affinity for oxygen than many other elements, meaning they will actively "steal" oxygen atoms from compounds like metal oxides.
For example, when iron ore (iron oxide, Fe₂O₃) is heated in a furnace with carbon monoxide, the CO strips the oxygen from the iron, leaving behind pure liquid iron and creating carbon dioxide (CO₂) as a byproduct. The iron ore has been "reduced" to iron.
Practical Applications and Context
Reducing atmospheres are not just a theoretical concept; they are a critical tool in many industrial and scientific processes where precise chemical control is necessary.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
This is the most common application. Blast furnaces use a reducing atmosphere rich in carbon monoxide to transform metal ores into pure metals. It's also used in annealing and sintering to prevent the formation of oxides (scale) on the surface of metals during high-temperature processing.
Early Earth's Atmosphere
Scientists theorize that Earth's primordial atmosphere was a reducing one, containing methane, ammonia, and water vapor but virtually no free oxygen. This environment was essential for the formation of the complex organic molecules that eventually led to life.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
The atmosphere inside a kiln has a profound effect on the final product. A reducing atmosphere can be used to create specific colors and properties in ceramic glazes and glass by changing the oxidation state of the metal oxides used as colorants. For example, copper oxide produces green in an oxidizing fire but a deep red in a reducing one.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Oxidizing vs. Reducing
The opposite of a reducing atmosphere is an oxidizing atmosphere, which is rich in oxygen. Our planet's current atmosphere is a prime example.
The Oxidizing Atmosphere
An oxidizing atmosphere promotes the loss of electrons. It's essential for processes like combustion (burning) and cellular respiration (breathing), but it is destructive in other contexts, causing corrosion, spoilage, and degradation.
Why Atmospheric Control is Critical
The choice between a reducing, inert, or oxidizing atmosphere is determined entirely by the desired outcome. Using the wrong one is not just inefficient; it can be catastrophic to a process.
Attempting to smelt metal in an oxygen-rich environment would fail, instead producing more oxides and scale. Conversely, firing a ceramic that requires oxidation in a reducing atmosphere would result in incorrect and unpredictable colors.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the purpose of a specific atmosphere comes down to identifying the desired chemical transformation.
- If the primary goal is to prevent degradation: An inert or reducing atmosphere is used to remove oxygen, the primary agent of corrosion and tarnish.
- If the primary goal is to transform a material from an oxide to its pure form: A reducing atmosphere is required to actively strip oxygen atoms from the material (e.g., turning ore into metal).
- If the primary goal is to control the final properties of a compound: The balance between oxidation and reduction is used to manipulate the electron state of elements, thereby controlling outcomes like color in ceramics or conductivity in semiconductors.
Ultimately, knowing whether an atmosphere is designed to donate or accept electrons is the key to predicting and controlling chemical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxidizing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Remove oxygen & promote reduction (gain of electrons) | Introduce oxygen & promote oxidation (loss of electrons) |
| Key Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Oxygen (O₂) |
| Effect on Metals | Converts metal oxides to pure metals; prevents scaling | Causes oxidation, leading to rust and scale |
| Common Applications | Metal smelting, annealing, sintering, specific ceramic glazes | Combustion, respiration, firing certain ceramics |
Need Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab Processes?
Whether you are sintering metals, developing specialized ceramic glazes, or conducting research that requires an oxygen-free environment, the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab furnaces and reactors designed for precise atmospheric control, including creating reliable reducing environments.
We help you:
- Prevent Contamination: Ensure your materials are not degraded by unwanted oxidation.
- Achieve Consistent Results: Get the precise chemical transformations you need, batch after batch.
- Optimize Your Workflow: With equipment designed for reliability and ease of use.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how our solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of furnaces are used for powder metallurgy sintering? Choose the Right Furnace for Your PM Production
- What is the heat treatment for hydrogen annealing? Prevent Embrittlement & Clean Metal Surfaces
- What products use annealing? Enhance Formability and Durability in Metal Manufacturing
- What is the function of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in biomass carbonization? Optimize Your Carbon Research
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What is the role of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in nitrogen fixation? Master Catalyst Precision Engineering
- Why Use High-Temperature Furnaces with Steam Generators for LOCA? Simulate Reactor Accidents with 1373 K Precision



















