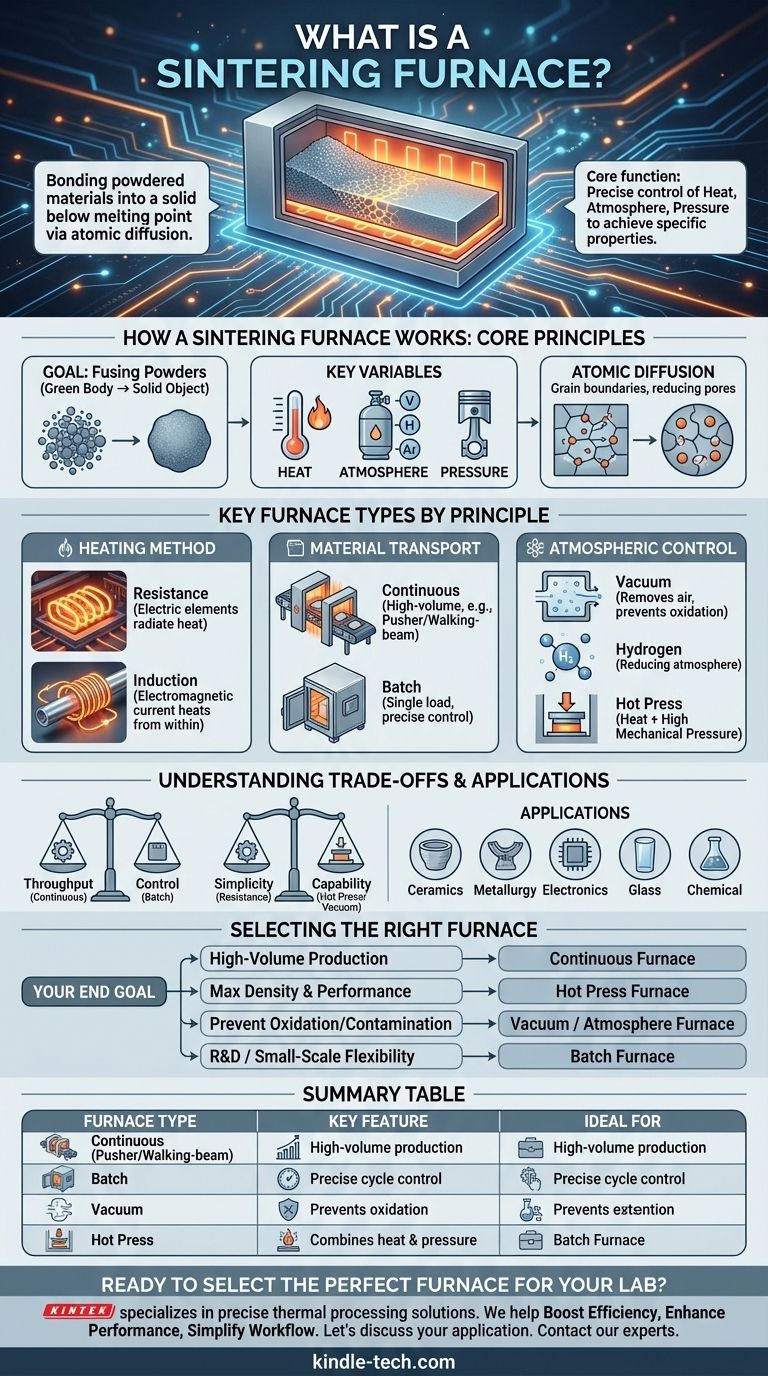
In materials science and manufacturing, a sintering furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing chamber designed to bond powdered materials into a solid, coherent mass. It accomplishes this by heating the material to a temperature below its melting point, allowing atomic diffusion to fuse the particles together, which increases the material's strength and density. These furnaces are essential tools in fields like ceramics, metallurgy, and electronics for creating high-performance components.
The core function of a sintering furnace is not just to apply heat, but to precisely control the environment—including atmosphere, pressure, and temperature—to achieve specific material properties. The "best" furnace is simply the one that provides the exact controls your material requires.
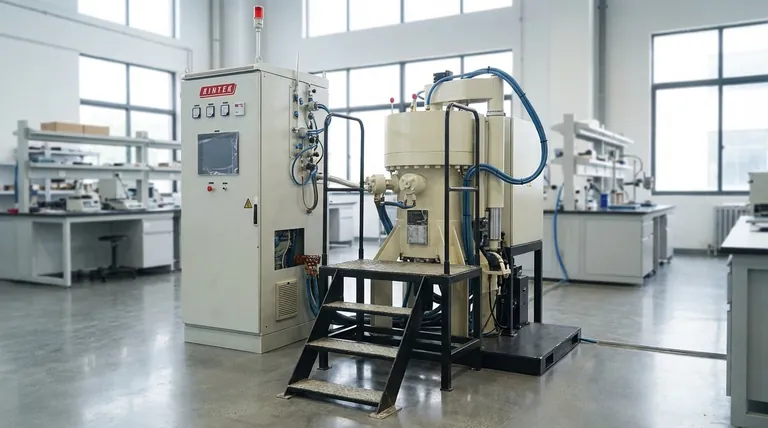

How a Sintering Furnace Works: The Core Principles
A sintering furnace operates on a few fundamental variables that determine the final quality of the product. Understanding these principles is key to selecting the right technology for an application.
The Goal: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering transforms a loosely packed collection of particles, known as a "green body," into a dense, solid object. The high heat encourages atoms to move across the boundaries of the particles, creating strong chemical bonds and reducing the porous space between them.
The Key Variables: Heat, Atmosphere, and Pressure
Every sintering process is a careful balance of three factors. Heat provides the energy for atomic diffusion. The atmosphere inside the furnace—whether a vacuum, an inert gas like argon, or a reactive gas like hydrogen—prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation. In some cases, external pressure is applied to dramatically accelerate densification.
Key Furnace Types by Operating Principle
Sintering furnaces are best categorized by how they generate heat, how they move material through the furnace, and how they control the processing environment.
Heating Method: Resistance vs. Induction
The most common distinction is the method of heat generation.
Resistance furnaces use electric heating elements to convert electrical energy into heat, which then radiates to the material. This is a common and versatile approach.
Induction furnaces use electromagnetic induction. A powerful alternating current creates a magnetic field that induces an electric current directly within the metallic or conductive material, causing it to heat itself from the inside out.
Material Transport: Continuous vs. Batch
Furnaces are also defined by their production flow.
Continuous furnaces are designed for high-volume production. Pusher furnaces move materials through the heat zones on a series of trays or "boats" in a continuous train. Walking-beam furnaces use a more complex mechanism that lifts, advances, and lowers the material, which can reduce friction and part stress.
Batch furnaces, such as many vacuum or hot press models, process a single load at a time. This method offers precise control over the entire cycle and is ideal for research, small-scale production, or materials requiring complex heating and cooling profiles.
Atmospheric Control: Specialized Process Furnaces
Many advanced materials demand highly controlled environments to achieve their desired properties.
A vacuum sintering furnace removes air from the chamber to create a vacuum. This is critical for preventing oxidation and contamination, leading to higher purity and better performance in reactive materials.
A hydrogen sintering furnace is used for materials that require a reducing atmosphere, often for sintering or annealing specific metals and alloys.
A hot press sintering furnace combines high temperature with high mechanical pressure in a vacuum. This dual action dramatically accelerates the densification process, making it possible to create nearly 100% dense materials with exceptionally fine grain structures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering furnace involves balancing capability with operational complexity and cost. No single design is universally superior.
Continuous vs. Batch Processing
Continuous furnaces, like pusher and walking-beam models, offer excellent throughput for mass production but are less flexible. Batch furnaces provide superior control and versatility for complex processes or multiple product types but have lower output.
Simplicity vs. Capability
A basic resistance furnace is relatively simple and affordable. In contrast, a hot press or a highly controlled vacuum furnace is a far more complex and expensive system, justified only when the material properties absolutely demand it.
Production Scale
Furnaces are available in a range of sizes, from small lab-scale units to large industrial models capable of processing hundreds of units per cycle. The choice depends entirely on production demand and facility space.
Where Are Sintering Furnaces Used?
The applications for sintering are vast and cut across numerous high-tech industries.
These furnaces are foundational in ceramics, metallurgy, electronics, glass manufacturing, and the chemical industry. They are used for powder roasting, high-temperature experiments, creating refractory materials, and producing specialized components for machinery and buildings.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice depends on your end goal. The material you are working with and the properties you need to achieve will dictate the technology required.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a consistent part: A continuous pusher or walking-beam furnace provides the necessary throughput.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and performance: A hot press sintering furnace is the definitive choice due to the addition of high pressure.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or contamination in sensitive materials: A vacuum or controlled-atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen) furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-scale custom jobs: A versatile batch furnace offers the best flexibility for experimenting with different materials and process cycles.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select a furnace that functions as a precise tool for your specific material engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous (Pusher/Walking-beam) | High-volume production | Mass manufacturing of consistent parts |
| Batch | Precise cycle control | R&D, small-scale production, complex materials |
| Vacuum | Prevents oxidation/contamination | Sensitive, high-purity materials |
| Hot Press | Combines heat & high pressure | Maximum density and fine grain structures |
Ready to Select the Perfect Sintering Furnace for Your Lab?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to achieving your material properties and production goals. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise thermal processing solutions your laboratory needs.
We can help you:
- Boost Efficiency: Find the ideal furnace for your production scale, from R&D to high-volume output.
- Enhance Material Performance: Leverage controlled atmospheres (vacuum, hydrogen) and pressure for superior results.
- Simplify Your Workflow: Get expert guidance on the best technology for ceramics, metallurgy, and electronics.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the sintering furnace that will drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of the tempering process? Understanding the Hardness vs. Toughness Trade-off
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in TiO2 synthesis? Unlock High-Performance Photocatalytic Properties
- What is the necessity of a high-temperature calcination process in the synthesis of CoWO4 nanomaterials? Unlock Purity
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a box resistance furnace play in the pretreatment of coal gangue? Enhance ZSM-5 Zeolite Synthesis Results
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- What is the primary application of a high-temperature muffle furnace in Li-LSX zeolite catalyst regeneration?
- Why must the Silicalite-1 seed layer undergo calcination? Unlock Superior Zeolite Film Growth Today



















