In essence, sintering is the process of transforming a fragile, compacted powder into a solid, dense object using heat. This is achieved by heating the material to a high temperature, but crucially, below its melting point. At this temperature, the individual particles fuse together through atomic diffusion, eliminating the pores between them and creating a strong, coherent mass.
Sintering is not a melting process. Instead, it is a solid-state transformation where heat and pressure compel individual particles to bond, systematically removing porosity and converting a delicate "green" body into a durable, dense ceramic piece.
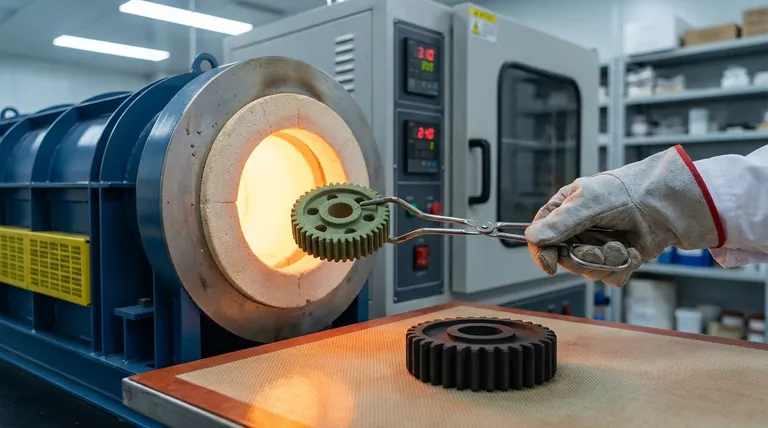

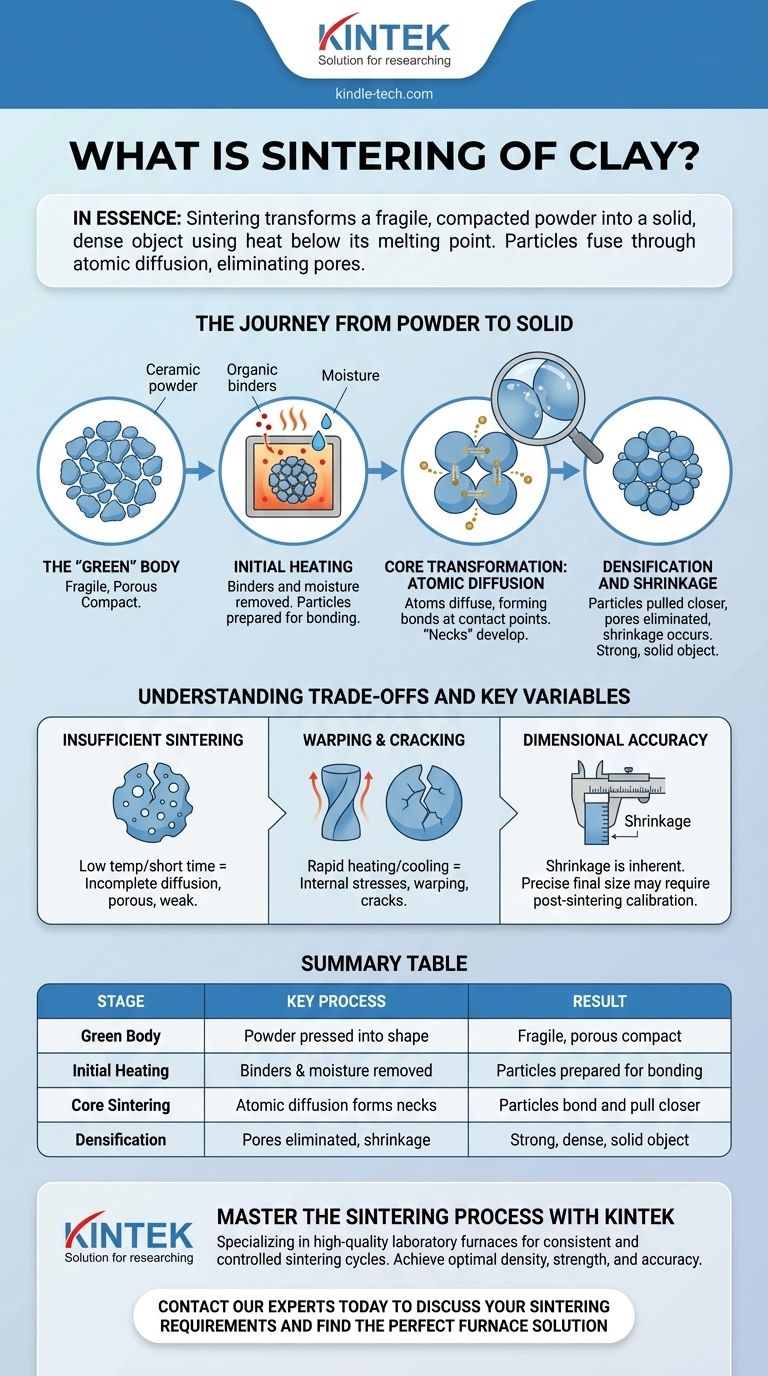
The Journey from Powder to Solid
To truly understand sintering, it's best to view it as a multi-stage journey where a shaped powder undergoes a fundamental structural transformation.
The "Green" Body: The Starting Point
The process begins with a ceramic powder, which is often pressed into a desired shape using molds and high pressure.
This initial object is called a "green" body or a compact. While it holds its shape, it is mechanically weak, porous, and fragile.
Initial Heating: Clearing the Way
As the green body is heated in a furnace, the first phase occurs at lower temperatures.
During this stage, any residual moisture or organic binders—additives used to help shape the powder—are burned off, preparing the particles for direct contact.
The Core Transformation: Atomic Diffusion
As the temperature rises, the core of the sintering process begins. The atoms on the surfaces of the adjacent particles become more mobile.
These atoms start to move, or diffuse, across the boundaries between particles. This creates small "necks" or bonds at every point of contact.
Think of it like a collection of soap bubbles. Where two bubbles touch, their walls merge, and they begin to pull closer together, reducing the total empty space.
The Result: Densification and Shrinkage
As these bonds grow, the particle centers are pulled closer together. This systematically eliminates the tiny pores and gaps that existed in the green body.
This elimination of void space causes the entire object to become denser and stronger. It also results in a predictable amount of shrinkage, a critical factor in manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Successful sintering depends on the precise control of several factors. Mismanaging them can lead to flawed or failed pieces.
Insufficient Sintering
If the temperature is too low or the time in the furnace is too short, the diffusion process will be incomplete.
The result is a piece that remains porous, weak, and unsuitable for its intended function.
Warping and Cracking
The heating and cooling cycles must be carefully managed. If a piece is heated or cooled too quickly, internal stresses can build up.
These stresses can cause the object to warp out of shape or, in more severe cases, develop cracks.
The Challenge of Dimensional Accuracy
Because sintering inherently involves shrinkage, achieving exact final dimensions is a significant challenge.
For applications requiring very tight tolerances, a post-sintering calibration step is often necessary, where the piece may be re-pressed or machined to its final, precise size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of sintering allows you to control the outcome of your ceramic or powder-based project.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You must ensure the piece reaches the optimal sintering temperature and is held there long enough for pore elimination to complete.
- If your primary focus is precise dimensional accuracy: You must carefully calculate the material's shrinkage rate and plan for post-sintering calibration or machining.
- If you are troubleshooting a failed piece: First, examine it for signs of incomplete sintering (porosity and low strength) or for stress fractures caused by improper heating and cooling cycles.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about precisely controlling heat and time to guide a simple powder through its transformation into a durable, functional object.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Green Body | Powder is pressed into shape | Fragile, porous compact |
| Initial Heating | Binders and moisture are removed | Particles prepared for bonding |
| Core Sintering | Atomic diffusion forms necks between particles | Particles bond and pull closer |
| Densification | Pores are eliminated, shrinkage occurs | Strong, dense, solid object |
Master the sintering process for your laboratory ceramics with KINTEK.
Whether you are developing new ceramic materials, troubleshooting sintering defects like warping or porosity, or require precise dimensional control, the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory furnaces designed for consistent and controlled sintering cycles.
We provide the reliable tools you need to achieve optimal density, strength, and accuracy in your ceramic projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering requirements and find the perfect furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















