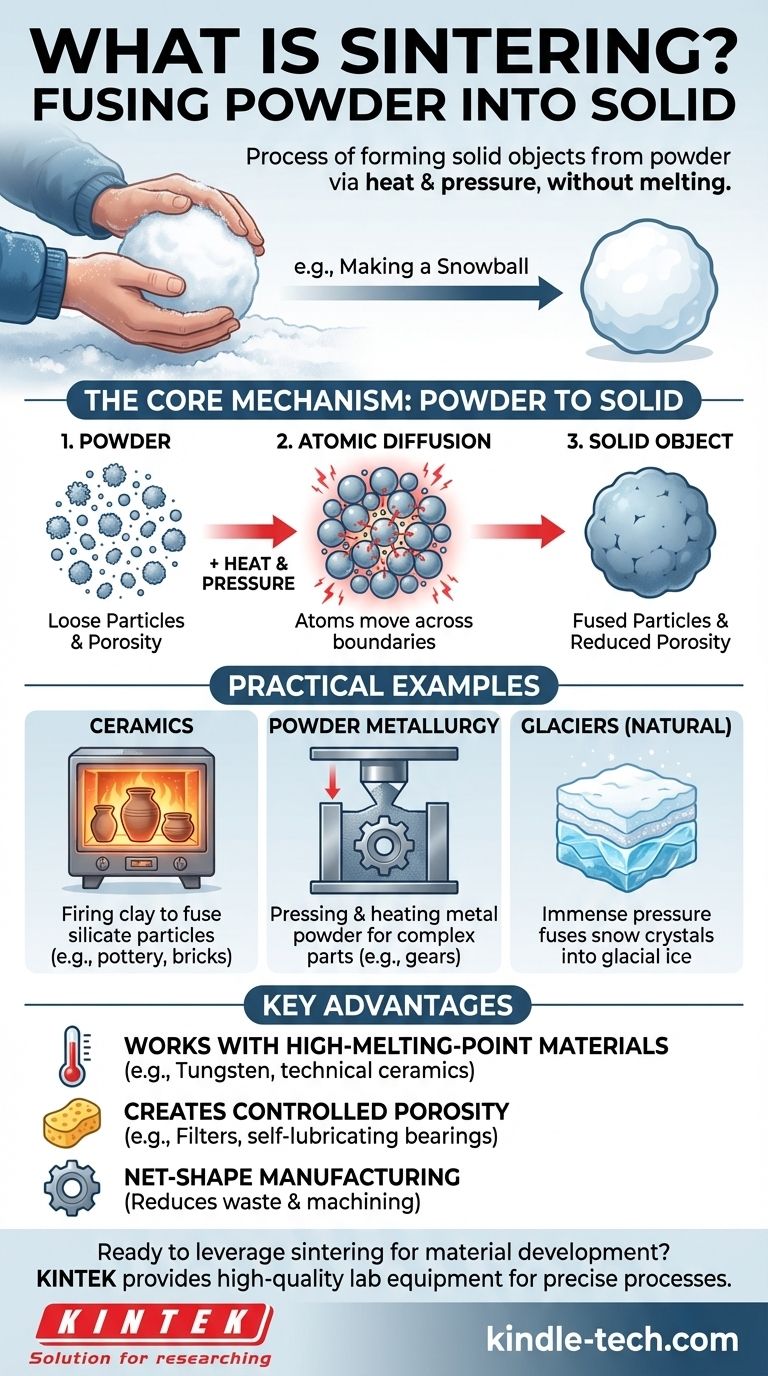
In essence, sintering is the process of forming a solid object from a powder using heat and pressure. It fundamentally works by fusing particles together into a single, strong mass, but crucially, it does so without melting the material to the point of liquefaction. A simple, relatable example is pressing loose snow together in your hands to form a hard, dense snowball.
Sintering is best understood as a microscopic welding process. Instead of melting a material into a liquid and casting it, sintering encourages atoms from individual particles to diffuse across their boundaries, effectively stitching the particles together into a solid piece.
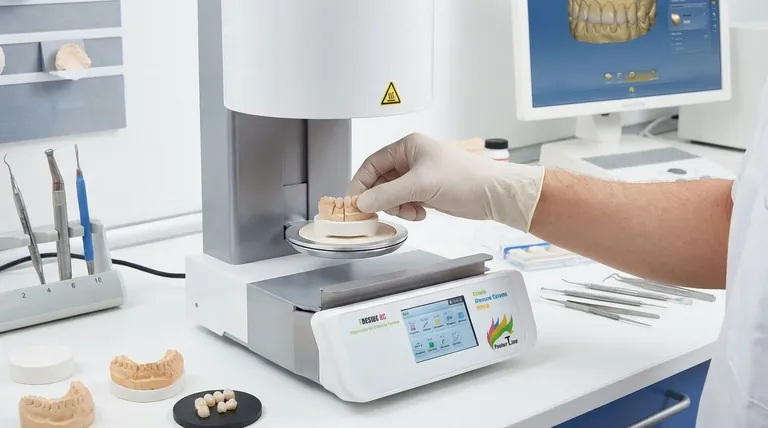

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering transforms a collection of individual particles into a coherent, solid object. The process relies on two key inputs: heat and pressure. While sometimes one is more dominant, they often work in tandem to achieve the final result.
The Role of Heat
Heat provides the energy necessary for the process to occur. It doesn't melt the material, but it agitates the atoms within the particles, making them mobile enough to move. This atomic mobility is the engine of sintering.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure serves to compact the powder, forcing the individual particles into intimate contact. This reduces the empty space (porosity) between them and shortens the distance that atoms need to travel to bond with neighboring particles.
Atomic Diffusion Explained
At the heart of sintering is atomic diffusion. Energized by heat and pushed together by pressure, atoms begin to migrate from their own particle and cross the boundary to bond with an adjacent one. As millions of atoms make this jump, the boundaries between the original particles slowly disappear, and the separate grains fuse into a single, unified material.
Practical Examples of Sintering
The principle of sintering is applied across a vast range of industries, from heavy manufacturing to nature itself.
Manufacturing Ceramics
This is a classic example of sintering. When clay is fired in a kiln to make pottery or bricks, the heat causes the tiny silicate particles to fuse together. This process gives the final ceramic object its strength and solidity, transforming it from fragile, dry clay into a durable material.
Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy. To create complex metal parts like gears or self-lubricating bearings, manufacturers press fine metal powder into a mold and then heat it. This allows them to create intricate shapes from materials with very high melting points, with minimal waste.
A Natural Example: Glaciers
Nature provides a powerful, large-scale example of pressure-driven sintering. Over centuries, immense pressure from the weight of accumulating snow compacts the lower layers. This pressure fuses the individual ice crystals (snowflakes) into a solid, dense mass of glacial ice, all without any melting involved.
Understanding the Advantages
Sintering isn't just an alternative to melting and casting; it offers unique capabilities that make it essential for creating advanced materials.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is the go-to method for materials that are extremely difficult to melt, such as tungsten (used for lightbulb filaments) and most technical ceramics. It allows for the fabrication of solid parts at temperatures well below the material's melting point.
Creating Controlled Porosity
Because the process starts with a powder, engineers can precisely control the final density of the object. This is used to create porous metal or ceramic filters, as well as self-lubricating bearings that are designed to hold oil within their porous structure.
Net-Shape Manufacturing
The process can produce parts that are very close to their final desired dimensions, often referred to as "net-shape" or "near-net-shape." This dramatically reduces the need for expensive and wasteful secondary machining operations.
Applying Sintering to Your Goal
Understanding when to use sintering is key to leveraging its strengths for a specific manufacturing or material design challenge.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-temperature materials like ceramics or tungsten: Sintering is often the most effective and sometimes the only practical manufacturing method available.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal parts with high precision: Powder metallurgy, a form of sintering, offers an economical and low-waste solution.
- If your primary focus is designing a material with controlled porosity, such as a filter or a self-lubricating bearing: Sintering gives you direct control over the final density and internal structure of the part.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational technology that enables the creation of materials and components that would be impossible to produce through traditional melting methods.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fusing powder particles using heat and pressure without full melting. |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion across particle boundaries. |
| Common Examples | Manufacturing ceramics, powder metallurgy parts, glacial ice formation. |
| Primary Advantages | Works with high-melting-point materials, enables controlled porosity, allows for net-shape manufacturing. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material development?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are working with advanced ceramics, metal powders, or developing porous materials, our solutions help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific sintering applications and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















