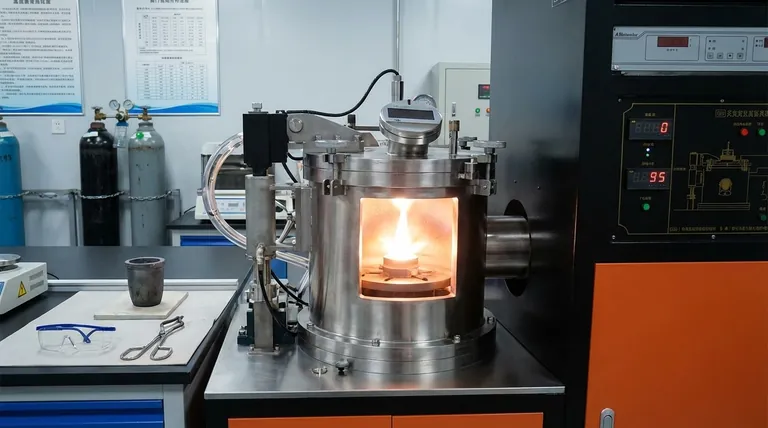
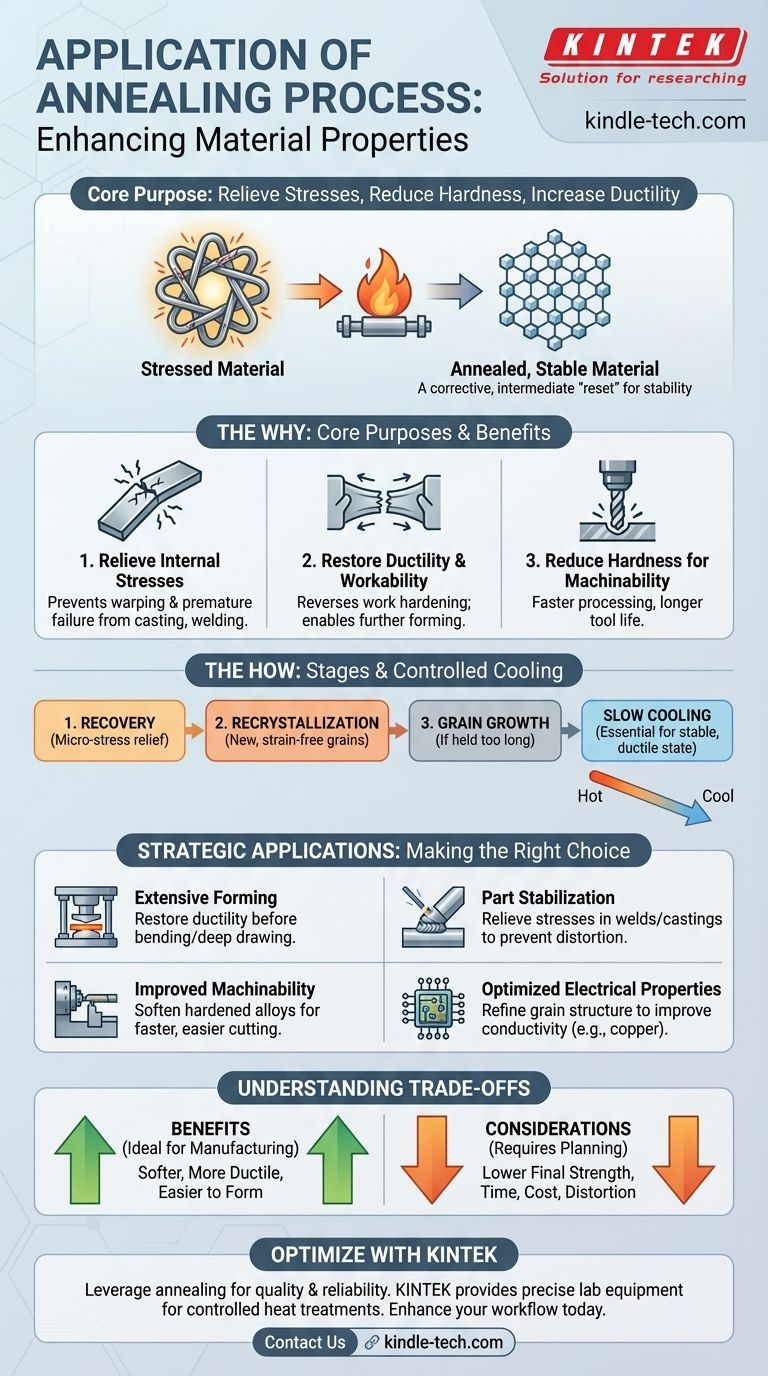
In essence, the annealing process is applied to relieve internal stresses, reduce hardness, and increase the ductility of a material. This heat treatment makes a metal more workable and less prone to failure by reversing the negative effects of fabrication processes like casting, welding, and cold forming.
Annealing should be viewed not as a final step, but as a crucial intermediate process. It is a strategic tool used to "reset" a material's properties, making it more stable and workable for subsequent manufacturing operations or to ensure its long-term structural integrity.

The Core Purpose: Reversing Material Stress and Hardness
Annealing is a corrective heat treatment. Its applications are best understood by looking at the problems it solves, which are typically introduced during earlier manufacturing stages.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like casting, forging, and welding introduce immense internal stresses into a material as it cools unevenly. These hidden stresses can cause a part to warp over time or lead to premature cracking and failure under load.
Annealing heats the material to a temperature where its atoms can rearrange themselves into a more orderly, lower-energy state. This relieves the internal stresses and creates a more uniform and stable internal structure.
Restoring Ductility and Workability
When you bend, draw, or form a metal at room temperature (a process called cold working), it becomes stronger but also harder and more brittle. This phenomenon is known as work hardening.
If you continue to work a hardened material, it will eventually crack. Annealing reverses the effects of work hardening, restoring the material's ductility (its ability to deform without breaking), which allows for further forming and shaping.
Reducing Hardness for Better Machinability
Extremely hard materials are difficult and slow to cut, drill, or machine. This not only increases production time but also causes rapid wear on cutting tools.
By reducing the material's hardness, annealing significantly improves its machinability. A softer material is easier to process, leading to faster production cycles and longer tool life.
How Annealing Achieves These Results
The transformation is not magic; it is a controlled manipulation of the material's crystalline structure. The process is defined by its three stages and, most critically, its cooling rate.
The Three Stages of Transformation
As the material is heated, it progresses through three distinct stages:
- Recovery: Internal stresses begin to be relieved at a microscopic level.
- Recrystallization: New, strain-free grains start to form, replacing the deformed grains created by work hardening. This is where hardness is significantly reduced and ductility is restored.
- Grain Growth: If held at temperature for too long, the new grains will begin to merge and grow larger, which can sometimes negatively affect material properties.
The Critical Role of Controlled Cooling
After holding the metal at the annealing temperature, it is cooled at a very slow and controlled rate. This slow cooling is essential.
It allows the newly formed crystalline structure to settle into its most stable, low-stress, and ductile state. Cooling too quickly would trap stresses and create a harder, more brittle structure, defeating the purpose of the anneal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, annealing is a process with specific outcomes and inherent trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Softness vs. Final Strength
Annealing's primary outcome is a softer, more ductile, and less strong material. While this is ideal for manufacturing and forming, it is often the opposite of what is required for the final product's service life.
Because of this, annealing is frequently an intermediate step. After all machining and forming are complete, a part may undergo a different heat treatment, like hardening and tempering, to achieve the final desired strength and toughness.
Time, Cost, and Distortion
The annealing process requires specialized furnaces, precise temperature control, and long cycle times, especially during the slow cooling phase. This adds both time and cost to the overall manufacturing workflow.
Furthermore, heating a component to high temperatures can cause distortion, especially in large or complex parts. This must be anticipated and planned for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Apply annealing strategically based on the specific problem you need to solve in your manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is extensive forming: Anneal the material before or between forming operations to restore ductility and prevent cracking during deep drawing, bending, or stamping.
- If your primary focus is stabilizing a part after fabrication: Use annealing to relieve internal stresses in welded assemblies or cast components to prevent future distortion and improve structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Anneal a hardened or tough alloy to soften it, thereby reducing machining time and extending the life of your cutting tools.
- If your primary focus is optimizing electrical properties: In some materials, such as copper, annealing can improve electrical conductivity by refining the grain structure.
Ultimately, annealing is a foundational tool for controlling a material's mechanical properties to suit your manufacturing needs.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Key Benefit of Annealing |
|---|---|
| Extensive Forming | Restores ductility, prevents cracking during bending or stamping. |
| Part Stabilization | Relieves internal stresses in welds or castings to prevent distortion. |
| Improved Machinability | Softens hardened alloys for faster machining and longer tool life. |
| Optimized Electrical Properties | Refines grain structure to improve conductivity in materials like copper. |
Optimize Your Material Properties with KINTEK
Does your manufacturing process involve welding, casting, or cold working? The annealing process is a critical step to relieve internal stresses, restore ductility, and improve the machinability of your materials, ensuring higher quality and more reliable final products.
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled heat treatments. Our expertise helps laboratories and manufacturers achieve optimal material performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your workflow and material integrity. Let's build something stronger together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering



















