At its core, the Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) is used to characterize electrochemical reactions by simultaneously driving a reaction at one electrode (the disk) and detecting the resulting products or intermediates at a second, downstream electrode (the ring). This makes it an indispensable tool for evaluating the efficiency and mechanism of electrocatalysts, particularly in fields like energy conversion, such as characterizing platinum catalysts for fuel cells.
The true power of RRDE lies not just in studying a reaction, but in actively capturing and quantifying the chemical species it produces in real-time. This dual-electrode setup provides direct evidence of reaction pathways and catalyst selectivity, something a standard single electrode cannot achieve.
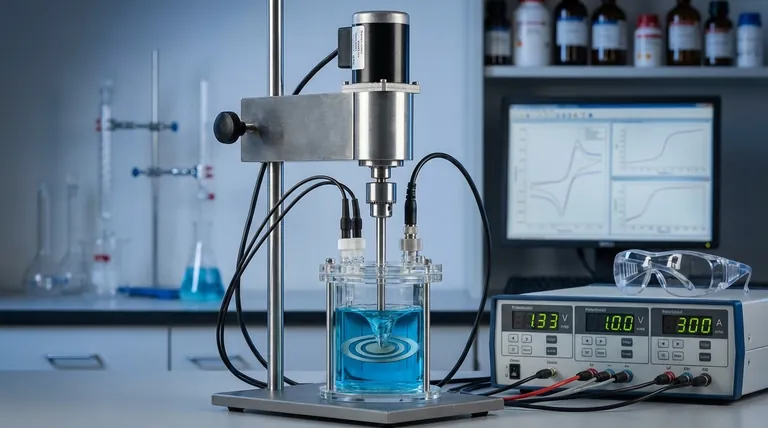

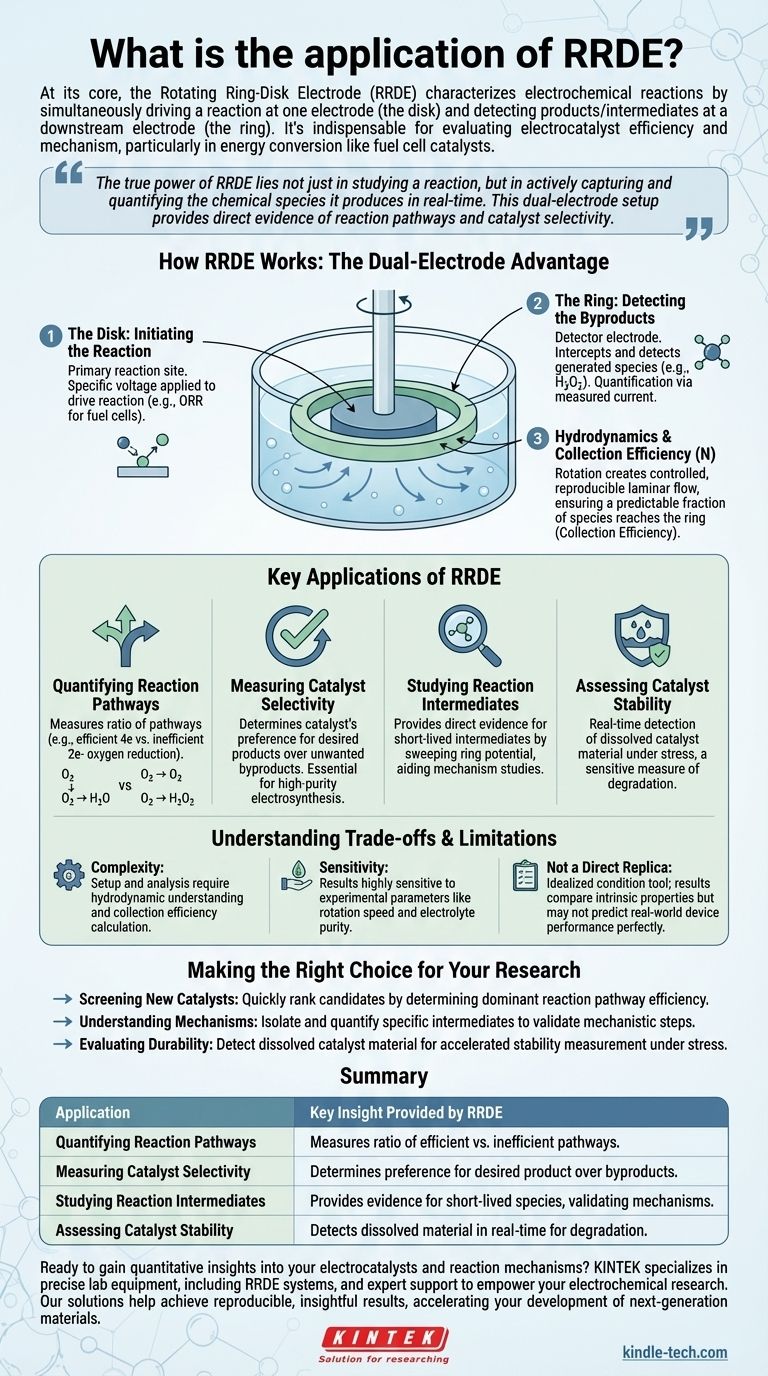
How RRDE Works: The Dual-Electrode Advantage
Understanding the application of RRDE requires first understanding its unique physical setup. It consists of two concentric, electrically isolated electrodes—a central disk and an outer ring—that rotate at high speed in an electrolyte solution.
The Disk: Initiating the Reaction
The disk electrode acts as the primary reaction site. A specific voltage is applied to the disk to drive the electrochemical reaction of interest.
For example, when studying the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) for a fuel cell, the disk is held at a potential where oxygen is forced to react.
The Ring: Detecting the Byproducts
The ring electrode acts as a detector. It is positioned to intercept any chemical species that are generated at the disk and flung outward by the rotational force.
The ring's potential is set specifically to react with a target product or intermediate. If that species is present, a current is measured at the ring, confirming its existence and allowing for its quantification.
The Role of Hydrodynamics
The rotation of the electrode is critical. It creates a well-defined and reproducible flow of solution, pulling fresh reactants toward the disk and then pushing products outward in a laminar fashion over the ring.
This controlled flow acts like a conveyor belt, ensuring that a predictable fraction of the species produced at the disk will reach the ring.
The Concept of Collection Efficiency
This predictable fraction is known as the collection efficiency (N). It is a constant determined by the precise geometry of the ring and disk electrodes.
Knowing this value is what allows researchers to translate the current measured at the ring into a quantitative measure of the products being generated at the disk.
Key Applications of RRDE
The unique ability to generate and detect species in one controlled experiment gives RRDE several powerful applications in materials science and electrochemistry.
Quantifying Reaction Pathways
Many reactions can proceed through multiple pathways, some more desirable than others. RRDE can definitively measure the ratio of these pathways.
The most common example is the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The efficient, direct pathway produces only water (a 4-electron process). An inefficient pathway produces hydrogen peroxide (a 2-electron process), which can damage fuel cell components.
By setting the ring to detect hydrogen peroxide, RRDE can precisely calculate the percentage of peroxide produced, providing a clear metric of the catalyst's efficiency.
Measuring Catalyst Selectivity
This principle extends to any reaction where a catalyst might produce multiple products. RRDE allows you to measure how selective a catalyst is for producing the desired chemical versus unwanted byproducts.
This is invaluable in fields like electrosynthesis, where the goal is to create high-purity value-added chemicals.
Studying Reaction Intermediates
RRDE is one of the few techniques that can provide direct evidence for the existence of short-lived reaction intermediates.
By sweeping the ring potential while a reaction occurs on the disk, researchers can identify the electrochemical signatures of transient species, which is crucial for piecing together complex reaction mechanisms.
Assessing Catalyst Stability
The technique can also be used to study catalyst degradation. By holding the disk at a high potential to induce corrosion, the ring can be set to detect dissolved metal ions.
This provides a real-time, highly sensitive measure of how quickly a catalyst is dissolving or degrading under operational stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, RRDE is a specialized tool with certain constraints that are important to recognize.
Complexity in Setup and Analysis
RRDE experiments are more complex to set up and control than standard electrochemical methods. The analysis requires a firm understanding of the system's hydrodynamics and the collection efficiency calculation.
Sensitivity to Experimental Conditions
The results are highly sensitive to experimental parameters like rotation speed, potential scan rate, and electrolyte purity. Meticulous control and consistency are required for reproducible data.
Not a Direct Replica of Real-World Devices
RRDE is a fundamental research tool that provides insights under idealized conditions. The hydrodynamic environment in an RRDE setup is very different from that in a real-world device like a fuel cell's gas diffusion electrode or a commercial electrolyzer.
The results are therefore excellent for comparing the intrinsic properties of catalysts but may not be a perfect predictor of performance in an applied system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Using RRDE effectively means aligning its capabilities with your specific research question.
- If your primary focus is screening new catalysts: Use RRDE to quickly determine the dominant reaction pathway (e.g., the 4-electron vs. 2-electron pathway in ORR) to rank candidates by efficiency.
- If your primary focus is understanding a reaction mechanism: Design experiments to isolate and quantify specific chemical intermediates to validate your proposed mechanistic steps.
- If your primary focus is evaluating catalyst durability: Use the ring to detect dissolved catalyst material from the disk, providing a direct and accelerated measure of stability under electrochemical stress.
Ultimately, RRDE empowers you to move beyond simply observing a reaction to quantitatively understanding its underlying pathways and products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Insight Provided by RRDE |
|---|---|
| Quantifying Reaction Pathways | Measures the ratio of efficient vs. inefficient pathways (e.g., 4e- vs. 2e- oxygen reduction). |
| Measuring Catalyst Selectivity | Determines a catalyst's preference for producing a desired product over unwanted byproducts. |
| Studying Reaction Intermediates | Provides direct evidence for short-lived species to validate complex reaction mechanisms. |
| Assessing Catalyst Stability | Detects dissolved catalyst material in real-time to evaluate degradation under stress. |
Ready to gain quantitative insights into your electrocatalysts and reaction mechanisms?
The unique dual-electrode setup of a Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) provides the direct, quantitative data you need to accurately characterize catalyst efficiency, selectivity, and stability. This is essential for advancing research in energy conversion, fuel cells, and electrosynthesis.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment, including RRDE systems, and expert support to empower your electrochemical research. Our solutions are designed to help you achieve reproducible and insightful results, accelerating your development of next-generation materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an RRDE system can enhance your research: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key precautions for a gold disc electrode? Ensure Accurate Results & Long Lifespan
- What is a glassy carbon electrode made of? The Engineered Material Powering Electrochemical Analysis
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- How can mechanical damage to the PTFE electrode stand and its components be prevented? Ensure Long-Term Lab Reliability
- What is the polishing cloth for electrodes? A Guide to Achieving Reproducible Electrochemical Results
- What characteristics make glassy carbon electrodes suitable as anodes? Ideal for Pure Molten Salt Electrolysis
- Is graphite sensitive to heat? Unlock its full potential in extreme environments.
- How should an electrode be positioned for modification via drop-coating? Master the Upside-Down Technique



















