There is no single "best" heating element for every furnace. The ideal choice is determined entirely by the furnace's required operating temperature and specific application. The most common types are resistance wires, silicon carbide rods, and molybdenum disilicide rods, each optimized for a different temperature range.
The selection of a furnace heating element is a direct trade-off between the maximum temperature you need to achieve and the cost and complexity you are willing to accept. Matching the element material to the required heat range is the most critical decision.

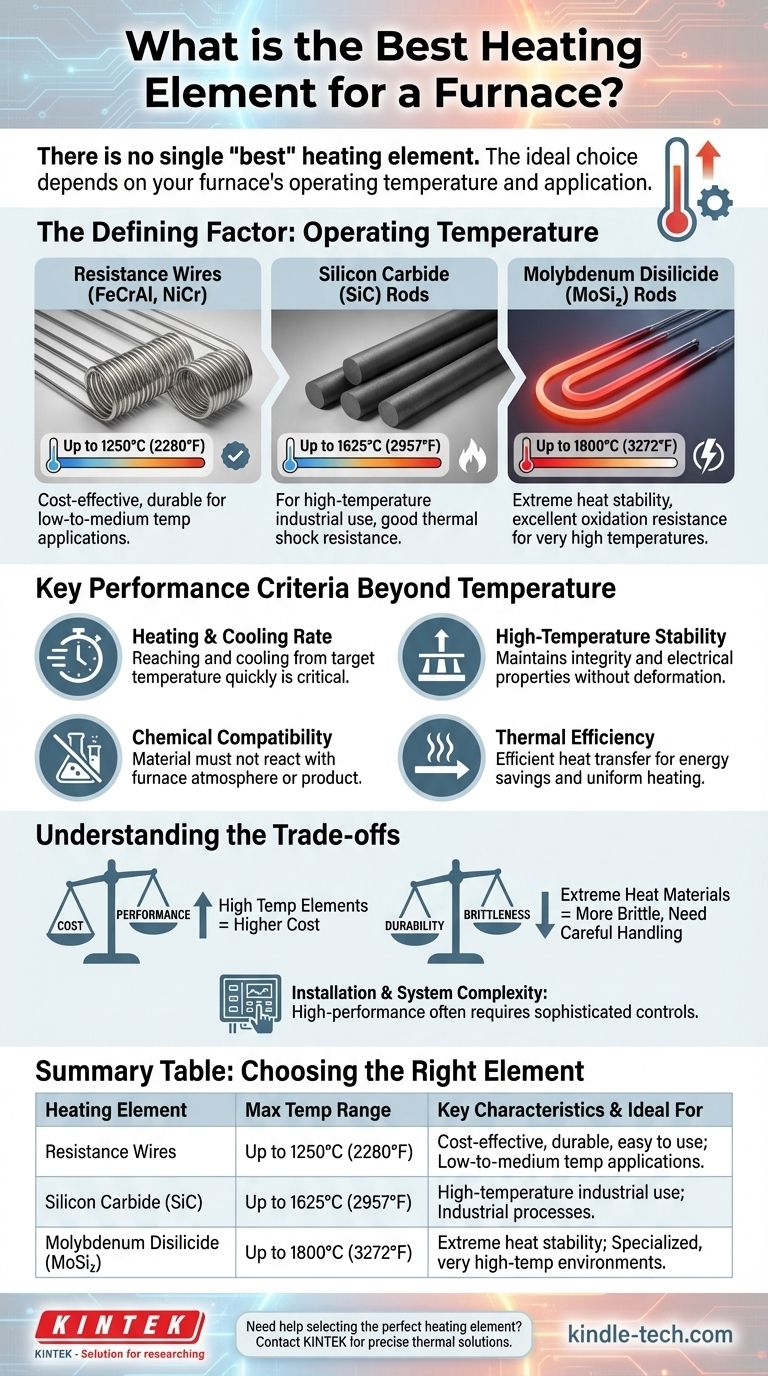
The Defining Factor: Operating Temperature
The material composition of a heating element dictates its maximum service temperature, its lifespan, and its resistance to thermal shock. Using an element outside its designed temperature range leads to rapid failure and inconsistent performance.
Resistance Wires (e.g., FeCrAl, NiCr)
These are the workhorses for low-to-medium temperature applications, typically up to around 1250°C (2280°F). They offer an excellent balance of cost, durability, and ease of use.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods
When temperatures need to exceed the limits of metallic wires, silicon carbide is the next step. These elements are common in industrial processes requiring temperatures up to 1625°C (2957°F).
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Rods
For the most demanding, very high-temperature applications, molybdenum disilicide (often referred to as silicon-molybdenum) is the standard. These elements can operate consistently in air at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
Key Performance Criteria Beyond Temperature
While temperature is the primary driver, several other factors define a high-quality heating element system. A well-designed furnace must account for all of them.
Heating and Cooling Rate
The ability to reach and cool down from a target temperature quickly is a critical performance specification. For example, some processes require heating an empty furnace to 2000°F (1093°C) in as little as five minutes.
High-Temperature Stability
A superior heating element must maintain its structural integrity and electrical properties without deforming at peak temperatures. This ensures a long service life and predictable, repeatable heating cycles.
Chemical Compatibility
The element material must not react with the atmosphere inside the furnace or the product being processed. Such reactions can contaminate the workpiece and degrade the element itself, compromising the quality of the final product.
Thermal Efficiency
An effective element exhibits good thermal conductivity to transfer heat efficiently to the furnace chamber while minimizing heat loss. This translates directly to energy efficiency and uniform heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these compromises is key to choosing the right system.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct and steep correlation between an element's maximum operating temperature and its cost. High-temperature materials like molybdenum disilicide are significantly more expensive than standard resistance wires.
Durability and Brittleness
Materials designed for extreme heat, like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide, are often more brittle than metallic wires. They require more careful handling and can be more susceptible to failure from mechanical or thermal shock.
Installation and System Complexity
High-performance elements often require more sophisticated power controllers and mounting hardware. As the references note, poor design or improper installation are common sources of problems, negating the benefits of a superior element.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate element, start by defining the absolute maximum temperature your process requires.
- If your primary focus is on applications below 1250°C (2280°F): Resistance wire elements provide the most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is on industrial processes between 1250°C and 1625°C (2957°F): Silicon carbide (SiC) rods offer the necessary performance for this demanding range.
- If your primary focus is on specialized, extreme-heat environments above 1625°C (2957°F): Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) is the essential choice for stability and longevity.
Ultimately, the best heating element is the one that reliably and efficiently meets the specific temperature demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Maximum Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Wires (FeCrAl, NiCr) | Up to 1250°C (2280°F) | Cost-effective, durable, easy to use | Low-to-medium temperature applications |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods | Up to 1625°C (2957°F) | High-temperature industrial use, good thermal shock resistance | Industrial processes requiring high heat |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Rods | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) | Extreme heat stability, excellent oxidation resistance | Specialized, very high-temperature environments |
Need help selecting the perfect heating element for your furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with precise thermal solutions. Our experts can help you choose the right heating element to ensure optimal temperature control, efficiency, and longevity for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C



















