The best substitute for tungsten is not a single material; it is a category of materials chosen based on which specific tungsten property you need to replicate. The ideal replacement depends entirely on whether your application demands its extreme hardness, its unmatched melting point, or its high density, as no single element or alloy possesses all three of these characteristics simultaneously.
The search for a tungsten substitute is a lesson in engineering trade-offs. Instead of a one-to-one replacement, the optimal choice depends on isolating the single most critical property for your application—be it hardness, density, or heat resistance—and accepting compromises on others.

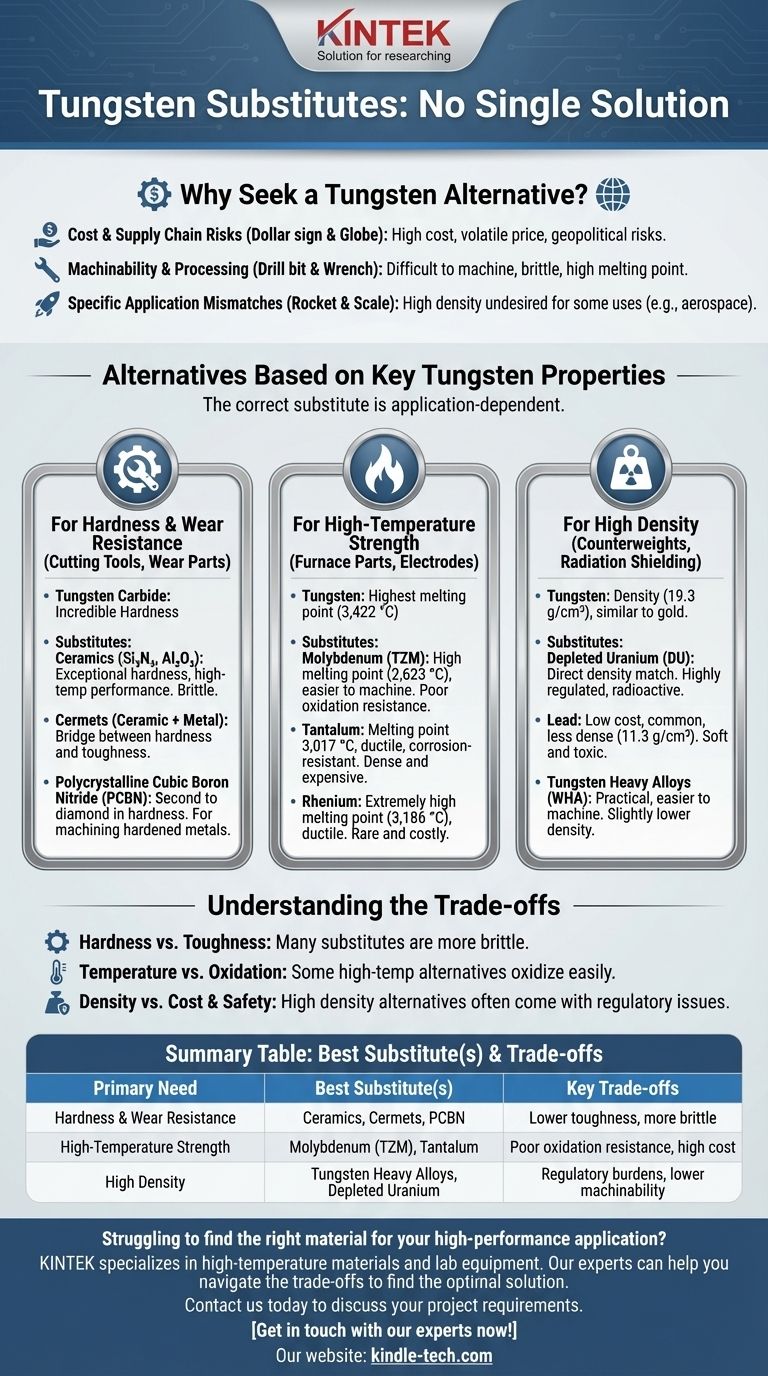
Why Seek a Tungsten Alternative?
Before exploring substitutes, it's crucial to understand the drivers behind the search. Engineers and designers typically move away from tungsten for a few key reasons.
Cost and Supply Chain Risks
Tungsten is expensive and its price can be volatile. A significant portion of the world's supply is concentrated in a few regions, creating geopolitical and supply chain risks that many industries seek to mitigate.
Machinability and Processing
Tungsten is notoriously difficult and costly to machine. It is brittle at room temperature and has an extremely high melting point, requiring specialized equipment and processes for fabrication.
Specific Application Mismatches
In some cases, one of tungsten's signature properties can be a liability. Its high density, for example, is undesirable in aerospace applications where weight is a primary concern.
Alternatives Based on Key Tungsten Properties
The correct substitute is always application-dependent. Below are the most viable alternatives, categorized by the primary tungsten property they aim to replace.
For Hardness & Wear Resistance (Cutting Tools, Wear Parts)
In its carbide form (tungsten carbide), tungsten is prized for its incredible hardness.
- Ceramics: Materials like Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) and Alumina (Al₂O₃) offer exceptional hardness and good high-temperature performance. They are often used in high-speed cutting inserts.
- Cermets: These are composites of ceramic (cer) and metal (met), such as titanium carbide-nitride. They provide a bridge between the hardness of ceramics and the toughness of cemented carbides.
- Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN): Second only to diamond in hardness, PCBN is extremely effective for machining hardened ferrous metals. It is a premium, high-performance alternative.
For High-Temperature Strength (Furnace Parts, Electrodes)
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal (3,422 °C / 6,192 °F), making it essential for extreme-heat applications.
- Molybdenum (and its alloys, like TZM): This is the most common and practical substitute. It has a high melting point (2,623 °C), is less dense than tungsten, and is easier to machine. Its primary weakness is poor oxidation resistance above 600 °C.
- Tantalum: With a melting point of 3,017 °C, tantalum is a strong contender. It is more ductile and has better corrosion resistance than tungsten, but it is also very dense and expensive.
- Rhenium: Often alloyed with tungsten or molybdenum, pure rhenium has an extremely high melting point (3,186 °C) and remains ductile even after being worked. However, its rarity and extreme cost limit it to highly specialized aerospace and electronic applications.
For High Density (Counterweights, Radiation Shielding)
Tungsten's density (19.3 g/cm³) is nearly identical to gold, making it ideal for concentrating mass in a small volume.
- Depleted Uranium (DU): For applications demanding the absolute highest density, DU (approx. 19.1 g/cm³) is a direct alternative. It is primarily used in military and aerospace for kinetic energy penetrators and counterweights, but its use is heavily regulated due to its low-level radioactivity and toxicity.
- Lead: While significantly less dense (11.3 g/cm³), lead is a very common and low-cost material for radiation shielding and ballast. It is soft and toxic, which limits its structural applications.
- Tungsten Heavy Alloys (WHA): These are not substitutes but rather more practical forms of tungsten, where tungsten powder is sintered with a binder like nickel, iron, or copper. They offer slightly lower density but are far easier to machine.
Understanding the Trade-offs: No Perfect Substitute
Choosing an alternative to tungsten means you must be aware of what you are giving up.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
Many materials that rival tungsten carbide's hardness, like ceramics, are significantly more brittle. They cannot withstand the same level of impact or shock, making them unsuitable for applications involving vibration or interrupted cuts.
The Temperature vs. Oxidation Barrier
Molybdenum is an excellent high-temperature substitute, but it oxidizes catastrophically in air at high temperatures. Tungsten performs better in this regard. Using molybdenum often requires a vacuum, an inert atmosphere, or protective coatings.
The Density vs. Cost & Safety Equation
While Depleted Uranium matches tungsten's density, it comes with immense regulatory, safety, and political burdens. For most commercial applications, the complexity of using DU makes it a non-starter.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the best substitute, define your non-negotiable requirement first.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness for cutting or wear: Your best options are ceramics (for cost-effectiveness) or PCBN (for ultimate performance), but you must design for their lower toughness.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Molybdenum and its TZM alloy are your most practical first choice, provided you can manage their poor oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is maximum density for weighting or shielding: Tungsten Heavy Alloys (WHA) offer the best balance of performance and machinability for most applications, while lead remains the choice for low-cost, non-structural shielding.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction with good all-around performance: Consider advanced steels or molybdenum, as they often provide 80% of the performance for a fraction of the cost and fabrication difficulty.
Ultimately, replacing tungsten requires a precise definition of your engineering problem, not a search for a miracle material.
Summary Table:
| Primary Need | Best Substitute(s) | Key Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Ceramics, Cermets, PCBN | Lower toughness, more brittle |
| High-Temperature Strength | Molybdenum (TZM), Tantalum | Poor oxidation resistance, high cost |
| High Density | Tungsten Heavy Alloys, Depleted Uranium | Regulatory burdens, lower machinability |
Struggling to find the right material for your high-performance application?
KINTEK specializes in high-temperature materials and lab equipment. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between materials like molybdenum, tantalum, and advanced ceramics to find the optimal solution for your specific needs in thermal processing, research, and development.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our materials and expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications



















