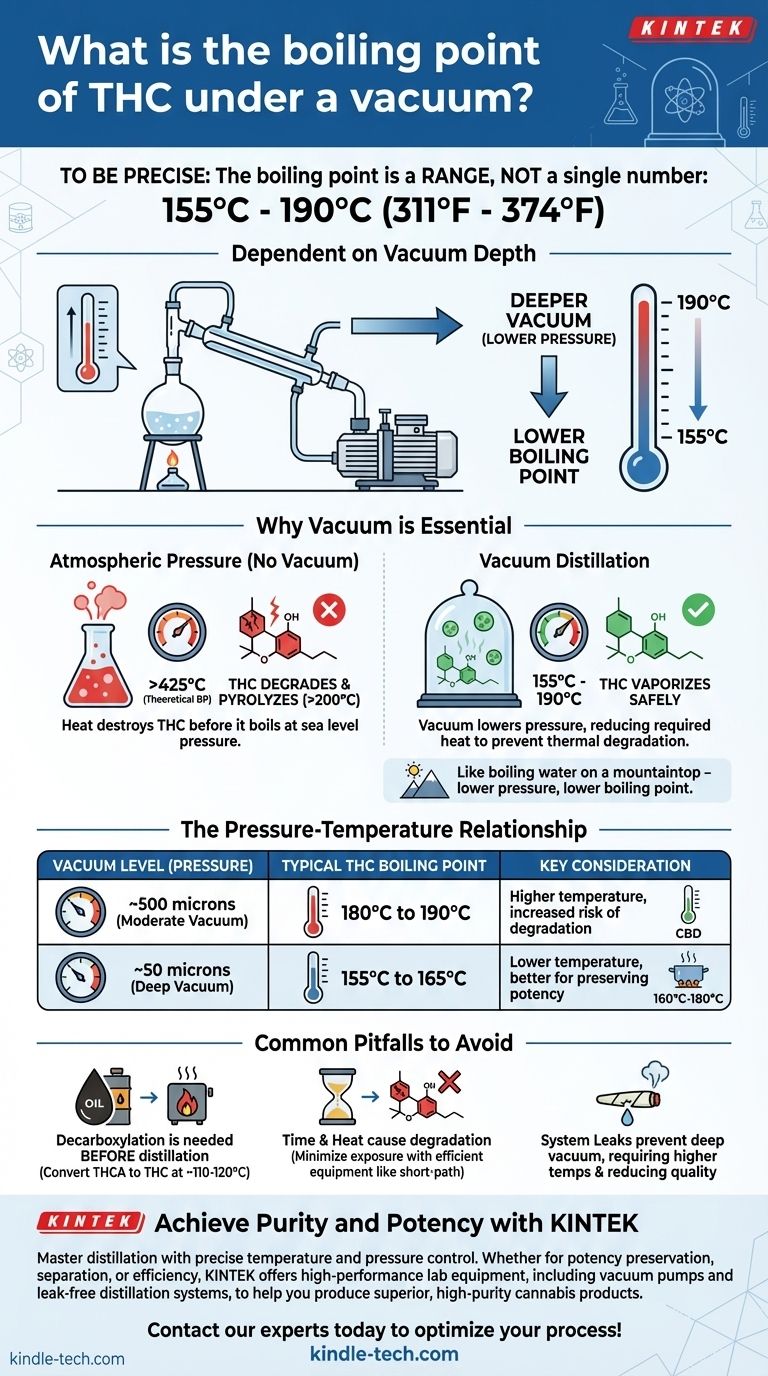
To be precise, the boiling point of THC under a vacuum is not a single number but a range, typically between 155°C and 190°C (311°F to 374°F). The exact temperature is entirely dependent on the depth of the vacuum you can achieve; a stronger vacuum (lower pressure) allows for a lower boiling temperature.
The core principle is not simply to boil THC, but to do so without destroying it. Using a deep vacuum is the essential technique that lowers THC's boiling point to a safe temperature, preventing the thermal degradation that would otherwise occur well before it could ever vaporize at atmospheric pressure.
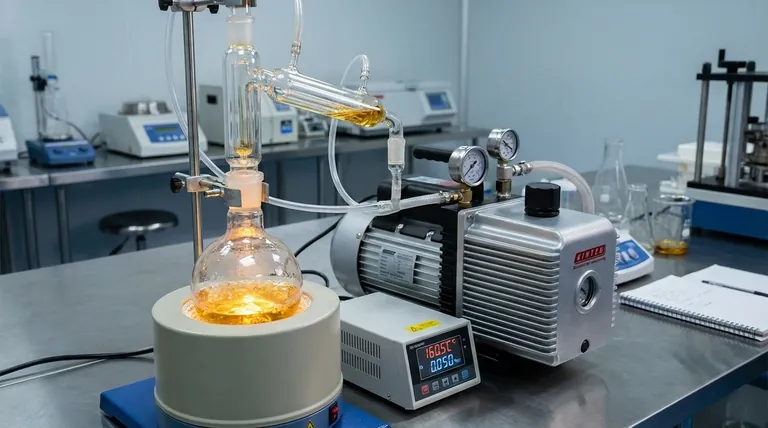

Why Vacuum is Essential for THC Distillation
Attempting to distill THC without a vacuum is a futile effort. The molecule will break down from the intense heat long before it ever reaches its natural boiling point. Understanding this relationship between heat, pressure, and molecular integrity is fundamental.
The Problem with Heat and THC
At normal atmospheric pressure (sea level, ~760 Torr), the theoretical boiling point of Delta-9-THC is extremely high, around 425°C (797°F).
However, THC is a sensitive organic molecule. It begins to degrade, or pyrolyze, into other compounds like Cannabinol (CBN) and unknown byproducts at temperatures starting around 200°C (392°F). Boiling it at atmospheric pressure would destroy the very compound you are trying to isolate.
How Vacuum Lowers the Boiling Point
A vacuum drastically reduces the ambient pressure inside the distillation apparatus. With less pressure pushing down on the liquid, the THC molecules require far less energy (heat) to escape into a vapor phase.
Think of it like boiling water on a mountaintop. At high altitudes, the air pressure is lower, so water boils at a temperature below the standard 100°C (212°F). A vacuum pump creates an artificial, extreme "mountaintop" inside your glassware.
The Pressure-Temperature Relationship
The most critical concept to grasp is that boiling point is not a fixed property. It is a variable that is directly tied to pressure. There is no single "vacuum boiling point" for THC, only a boiling point at a specific vacuum level.
Understanding Vacuum Levels
In distillation, a vacuum is measured in units of pressure like Torr or, more commonly, microns (1 Torr = 1000 microns). A lower number signifies less pressure and a deeper, more effective vacuum.
A typical laboratory vacuum pump might pull a vacuum of 500 microns. A high-performance diffusion or turbomolecular pump can achieve a much deeper vacuum, often below 50 microns.
Practical Temperature Ranges
The distillation temperature for THC changes significantly with the quality of the vacuum:
- Moderate Vacuum (e.g., ~500 microns): The boiling point will be on the higher end, roughly 180°C to 190°C.
- Deep Vacuum (e.g., ~50 microns): The boiling point drops significantly, falling into the 155°C to 165°C range.
This principle is also what allows for fractional distillation, the separation of different cannabinoids. CBD, for example, has a slightly higher boiling point than THC under the same vacuum, typically boiling at 160°C to 180°C.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Successfully distilling THC requires more than just heating a flask under vacuum. Several factors can compromise the quality and purity of the final product.
Decarboxylation vs. Distillation
Crude cannabis extract primarily contains THCA, the non-psychoactive acidic precursor to THC. Distillation requires pure THC. Therefore, a separate process called decarboxylation (heating the crude oil gently, often around 110-120°C) must be performed before distillation to convert THCA into THC.
The Risk of Degradation
Even at lower vacuum temperatures, time is your enemy. The longer the THC molecule is exposed to heat, the more likely it is to degrade into CBN. Efficient equipment, like a short-path distillation apparatus or a wiped-film evaporator, is designed to minimize this exposure time, preserving potency and purity.
The Impact of System Leaks
Even a microscopic leak in your distillation setup will prevent the vacuum pump from reaching its lowest possible pressure. This forces you to increase the temperature to achieve boiling, which in turn increases the risk of thermal degradation and results in a lower-quality product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your distillation strategy should be dictated by your end goal. The interplay between temperature and pressure is your primary tool for control.
- If your primary focus is preserving maximum potency: Aim for the deepest vacuum your equipment can reliably hold. This allows you to distill at the lowest possible temperature, minimizing degradation into CBN.
- If your primary focus is separating THC from other cannabinoids: You must achieve a deep, stable vacuum and have precise temperature control to carefully fractionate compounds based on their unique boiling points.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Ensure your system is perfectly sealed. A leak-free setup that reaches a deep vacuum quickly will shorten run times and produce a purer distillate.
Ultimately, mastering THC distillation is about controlling pressure to protect the integrity of your product.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Level (Pressure) | Typical THC Boiling Point Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate Vacuum (~500 microns) | 180°C to 190°C | Higher temperature, increased risk of degradation |
| Deep Vacuum (~50 microns) | 155°C to 165°C | Lower temperature, better for preserving potency |
Achieve Purity and Potency in Your Cannabis Extracts with KINTEK
Mastering THC distillation requires precise control over temperature and pressure to prevent degradation and ensure a high-quality final product. Whether your goal is to preserve maximum potency, separate cannabinoids, or improve process efficiency, the right laboratory equipment is essential.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum pumps and distillation systems designed for the demanding needs of cannabis extraction and purification. Our reliable, leak-free setups help you achieve the deep vacuums necessary for safe, low-temperature distillation, protecting your valuable compounds and enhancing your yield.
Ready to optimize your distillation process? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's specialized lab equipment can meet your specific needs and help you produce superior, high-purity cannabis products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is pressure-assisted sintering? Achieve Denser, Stronger Materials Faster
- What is the process of hot-pressing sintering? Achieve Superior Density for High-Performance Materials
- What is the process of hot press molding? A Guide to High-Density Material Manufacturing
- What is the hot pressing method of sintering? A Guide to High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the sintering process of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Density and Complex Shapes



















