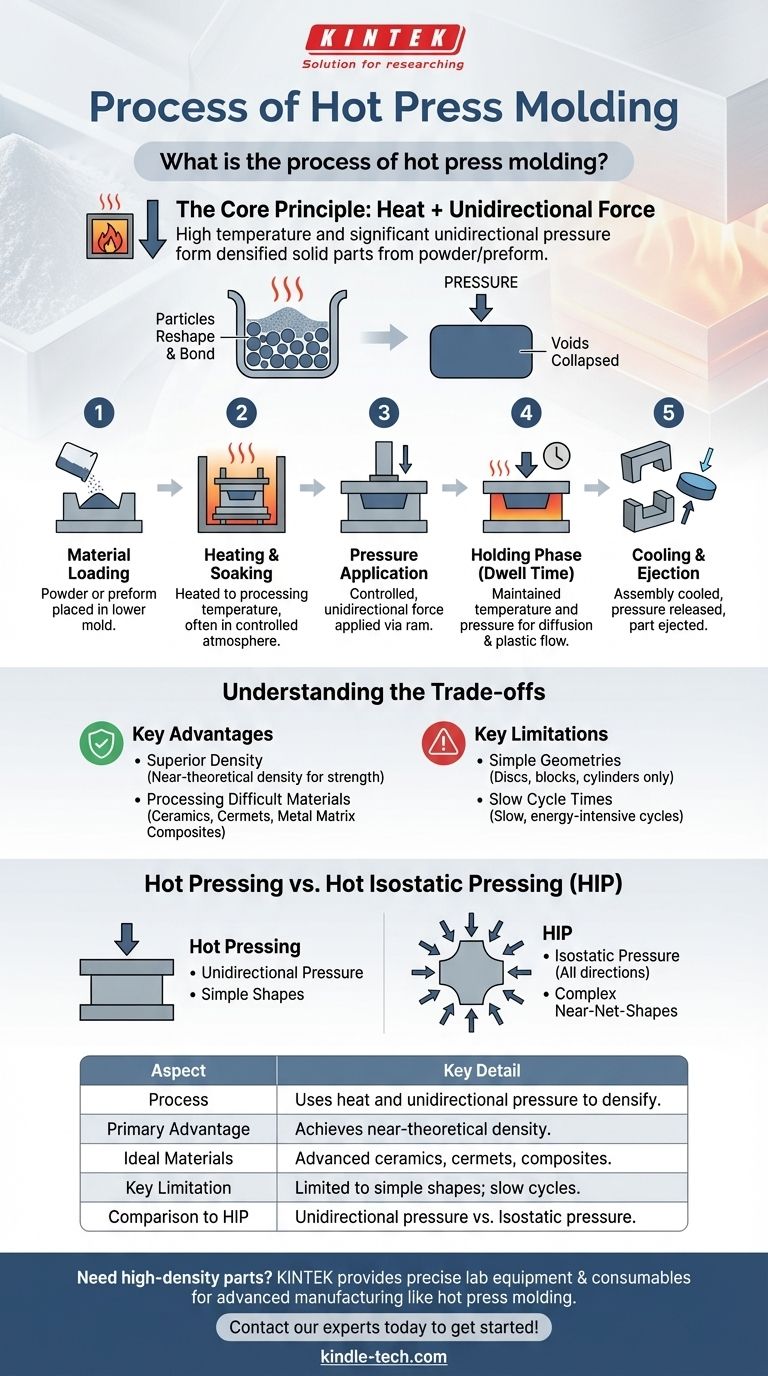
Hot press molding is a manufacturing process that uses high temperature and significant unidirectional pressure to form a densified solid part from a powder or preform. The material is placed inside a heated die cavity, and a ram or platen applies force, simultaneously compacting and heating the material until it consolidates into a dense, solid shape.
The central purpose of hot pressing is to achieve superior material density and mechanical properties, particularly for advanced ceramics, composites, and other materials that are difficult to process using conventional sintering or melting techniques.

The Core Principle: Heat + Unidirectional Force
Hot pressing fundamentally relies on the synergistic effect of high temperature and directional pressure to transform loose powder into a solid object with minimal porosity.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the critical enabler in the process. Raising the material's temperature lowers its yield strength and resistance to deformation, making it easier for particles to reshape and bond. It also accelerates atomic diffusion, which is the primary mechanism for eliminating the final pores.
The Role of Pressure
While heat makes the material malleable, the unidirectional pressure provides the driving force. This applied force pushes particles into intimate contact, collapses voids, and conforms the material to the precise shape of the die cavity.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
The hot pressing cycle is a carefully controlled sequence designed to achieve full densification and the desired final shape.
1. Material Loading
The process begins by placing the starting material, typically a fine powder or a pre-compacted shape called a "preform," into the lower part of the mold or die.
2. Heating and Soaking
The entire die assembly is heated to a specific processing temperature. This is often done within a controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnace to prevent oxidation of the material and the tooling, which is often made of graphite.
3. Pressure Application
Once the target temperature is reached, a hydraulic or mechanical press applies a controlled, unidirectional force through a ram or plunger. This pressure is maintained throughout the consolidation phase.
4. Holding Phase (Dwell Time)
The material is held at peak temperature and pressure for a specific duration. This "dwell time" allows for plastic flow and diffusion to occur, closing any remaining porosity and ensuring a uniformly dense part.
5. Cooling and Ejection
After the holding phase, the assembly is cooled in a controlled manner. Once it is cool enough to be stable, the pressure is released, the die is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Hot pressing is a powerful but specialized technique. Its advantages in material quality come with significant limitations in speed and geometric complexity.
Key Advantage: Superior Density
The primary reason to use hot pressing is to achieve near-theoretical density. This results in parts with exceptional mechanical strength, hardness, and performance, which is critical for demanding applications like armor plating or cutting tools.
Key Advantage: Processing Difficult Materials
This method is ideal for non-oxide ceramics (like silicon carbide), cermets, and certain metal matrix composites that do not sinter well through heat alone.
Key Limitation: Simple Geometries
Because the pressure is applied in only one direction, hot pressing is limited to producing relatively simple shapes like discs, blocks, and cylinders. Complex features like undercuts or internal cavities are not possible.
Key Limitation: Slow Cycle Times
The necessary heating, soaking, and cooling cycles make hot pressing a slow and energy-intensive process. This makes it unsuitable for high-volume manufacturing and contributes to a higher per-part cost.
Hot Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
It is crucial to distinguish hot pressing from a related process, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), as they serve different purposes. The provided reference appears to describe HIP.
Direction of Pressure
Hot Pressing uses unidirectional pressure from a ram. Hot Isostatic Pressing uses an inert gas (like argon) to apply isostatic (equal from all directions) pressure to the part.
Tooling and Shape Capability
Hot pressing requires a rigid die that defines the part's final shape, limiting complexity. HIP places the part in a pressure vessel, allowing for the densification of much more complex, near-net-shape components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal consolidation process depends entirely on your material and final part requirements.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in a simple shape (e.g., a ceramic target): Hot pressing is a direct, reliable, and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is densifying a complex, pre-formed part (e.g., an aerospace casting): Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior technology.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of polymer or metal parts: Far faster methods like injection molding or conventional die compaction and sintering are more economical.
Ultimately, hot pressing is a precision tool for creating high-performance materials where final density and mechanical properties are more important than production speed or geometric complexity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses heat and unidirectional pressure to densify powder/preform. |
| Primary Advantage | Achieves near-theoretical density for superior mechanical properties. |
| Ideal Materials | Advanced ceramics (e.g., silicon carbide), cermets, metal matrix composites. |
| Key Limitation | Limited to simple shapes (discs, blocks); slow cycle times. |
| Comparison to HIP | Unidirectional pressure vs. isostatic (all-around) pressure. |
Need to create high-density ceramic or composite parts with superior mechanical properties?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced manufacturing processes like hot press molding. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools to achieve optimal material density and performance for your specific application.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to maintain a high-vacuum environment within a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize Cu-SiC Sintering
- What is the purpose of phased heating and holding protocols in high-temperature furnaces? Enhance Glass Purity
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- Why is maintaining a high vacuum environment in a Vacuum Hot-Pressing Furnace necessary for titanium alloy preparation?
- Why is precise pressure control necessary for Mo-Na targets? Achieve Maximum Density and Structural Integrity



















