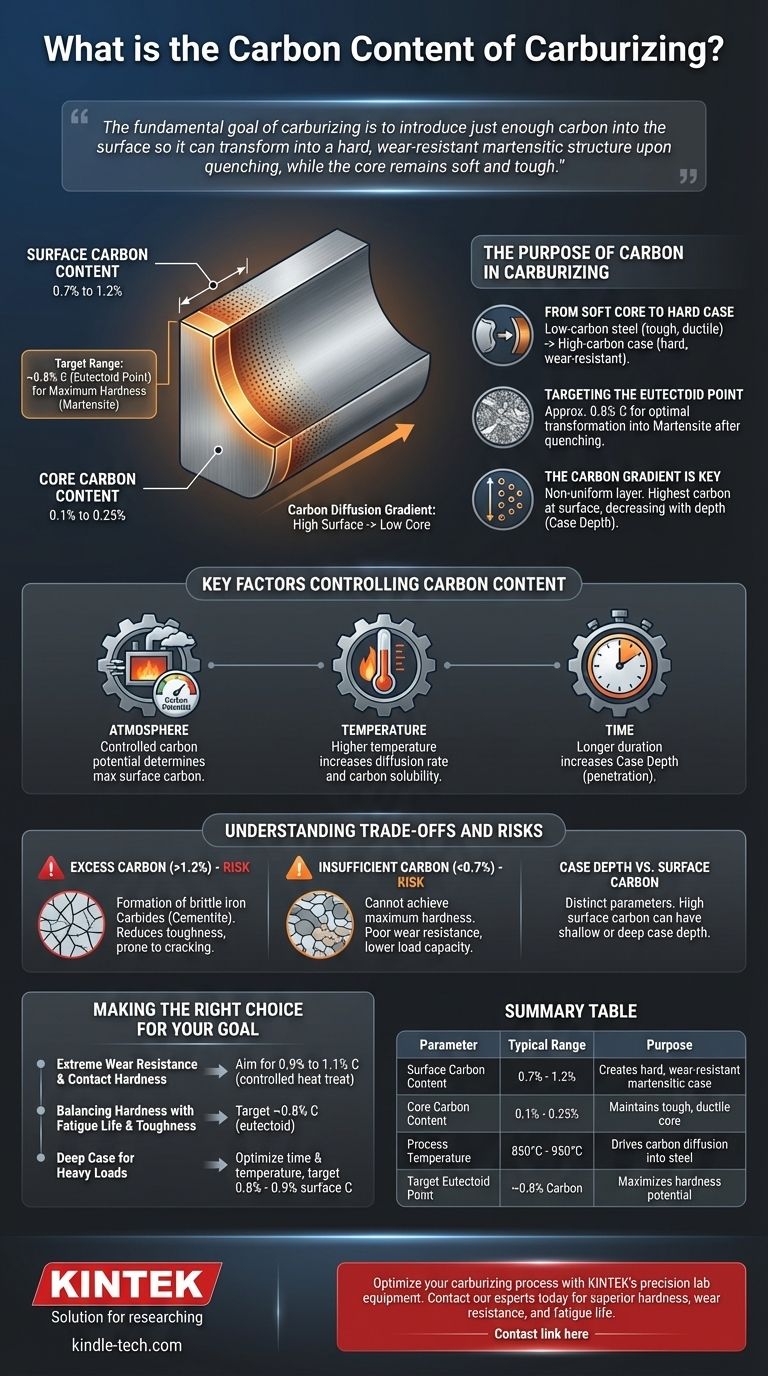
In carburizing, the target surface carbon content typically ranges from 0.7% to 1.2%. This process is not about changing the entire component's chemistry, but about intentionally creating a steep carbon gradient. The carbon level decreases sharply from this high surface concentration down to the steel's original, much lower core carbon content (e.g., 0.1% to 0.25%).
The fundamental goal of carburizing isn't simply to achieve a specific carbon percentage. It is to introduce just enough carbon into the surface so it can transform into a hard, wear-resistant martensitic structure upon quenching, while the core remains soft and tough.
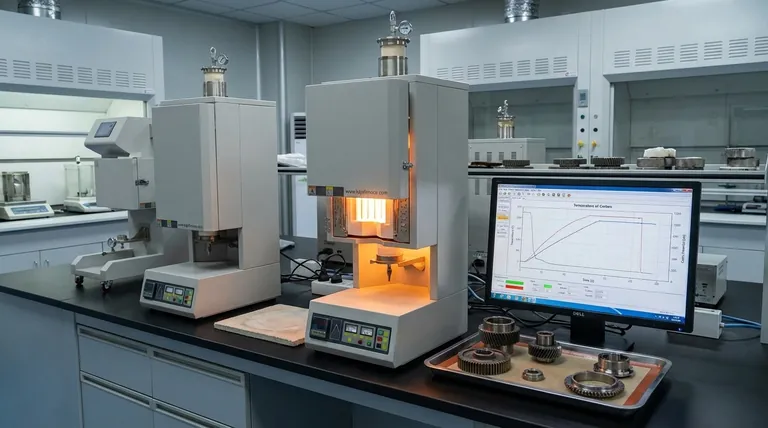

The Purpose of Carbon in Carburizing
From a Soft Core to a Hard Case
Low-carbon steels are inherently tough and ductile, making them resistant to fracture under impact. However, they are too soft to resist abrasion and wear.
Carburizing solves this by diffusing carbon atoms into the surface of the steel at high temperatures (typically 850-950°C or 1560-1740°F). This creates a high-carbon steel "case" on the outside of a low-carbon steel core.
Targeting the Eutectoid Point
The ideal carbon content for maximum hardness in steel is at or slightly above the eutectoid point, which is approximately 0.8% carbon.
At this concentration, the steel's microstructure can transform almost entirely into martensite after quenching. Martensite is the extremely hard, brittle phase that gives carburized components their exceptional wear resistance.
The Carbon Gradient is Key
Carburizing does not create a uniform layer. It produces a diffusion gradient, with the highest carbon concentration at the immediate surface.
This carbon level gradually decreases with depth until it matches the original chemistry of the base material. The thickness of this carbon-enriched layer is known as the case depth.
Key Factors Controlling Carbon Content
The final surface carbon content and the case depth are not accidental; they are precisely controlled by three primary process variables.
The Carburizing Atmosphere
The medium surrounding the part (gas, liquid, or solid pack) has a specific carbon potential. This is a measure of its ability to transfer carbon to the steel.
In modern gas carburizing, the atmosphere is carefully controlled to maintain a specific carbon potential, which directly determines the maximum carbon content the steel's surface will absorb.
Temperature
Higher process temperatures increase the rate at which carbon atoms diffuse into the steel. This allows for a deeper case to be formed in a shorter amount of time.
Temperature also affects the maximum amount of carbon that the steel's austenite phase can dissolve.
Time
The duration of the carburizing cycle directly impacts the case depth. The longer the steel is held at temperature in the carbon-rich atmosphere, the farther the carbon atoms will penetrate into the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Achieving the correct carbon content is a balancing act. Deviating from the optimal range introduces significant risks to the component's performance.
The Risk of Excess Carbon (>1.2%)
If the surface carbon content becomes too high (hypereutectoid), a network of brittle iron carbides (cementite) can form along the grain boundaries of the steel.
These carbides act as internal stress points, drastically reducing the toughness and fatigue life of the case and making it prone to chipping or cracking under load.
The Problem of Insufficient Carbon (<0.7%)
If the surface carbon is too low, the steel cannot achieve its maximum potential hardness upon quenching.
The resulting microstructure will be a mix of hard martensite and softer phases. This leads to a component with poor wear resistance and a lower load-bearing capacity than intended.
Case Depth vs. Surface Carbon
It is crucial to understand that case depth and surface carbon are two different, though related, parameters.
You can have a high surface carbon with a shallow case (short cycle) or a moderate surface carbon with a deep case (long cycle). The application dictates the ideal combination of both.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal surface carbon content depends entirely on the component's intended service conditions.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and contact hardness: Aim for a slightly hypereutectoid surface content (0.9% to 1.1%), but ensure post-carburizing heat treatment is controlled to prevent brittle carbide networks.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness with fatigue life and toughness: Target the eutectoid composition (around 0.8% C) to achieve excellent hardness without inducing the brittleness associated with excess carbides.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very deep case for heavy loads: This is more about extending the process time and controlling temperature to drive diffusion, while maintaining an optimal surface carbon content (e.g., 0.8% - 0.9%).
Ultimately, controlling the carbon content in carburizing is about precisely engineering a composite material—a tough, ductile core protected by a hard, durable shell.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Carbon Content | 0.7% - 1.2% | Creates hard, wear-resistant martensitic case |
| Core Carbon Content | 0.1% - 0.25% | Maintains tough, ductile core |
| Process Temperature | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) | Drives carbon diffusion into steel |
| Target Eutectoid Point | ~0.8% Carbon | Maximizes hardness potential |
Optimize your carburizing process with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Achieving the perfect carbon content (0.7%-1.2%) is critical for creating components with superior hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life. KINTEK specializes in furnaces and atmosphere control systems that deliver precise, repeatable carburizing results—ensuring your steel parts meet exact performance specifications.
Whether you're processing gears, bearings, or other critical components, our solutions help you:
- Maintain exact carbon potential for optimal case hardness
- Control temperature and atmosphere with precision
- Prevent issues like brittle carbide networks or insufficient hardness
Ready to enhance your heat treatment outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific carburizing requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does furnace cooling occur in the heat treatment process? A Guide to Controlled Slow Cooling
- What critical process conditions does a vacuum sintering furnace provide for titanium? Expert Diffusion Bonding Guide
- What type of environment does a high-vacuum bell jar furnace provide? Precision for Plasma Nano-Coatings
- What role do furnaces play in argyrodite electrolytes? Essential Tools for High-Performance Phase Formation
- What temperature is needed for metal casting? Achieve Perfect Casts with the Right Superheat
- What is the significance of using high-vacuum heat treatment furnaces and rapid quenching for zirconium alloys?
- What are the 4 heat treatments of steel? Master Hardness, Toughness & More
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















