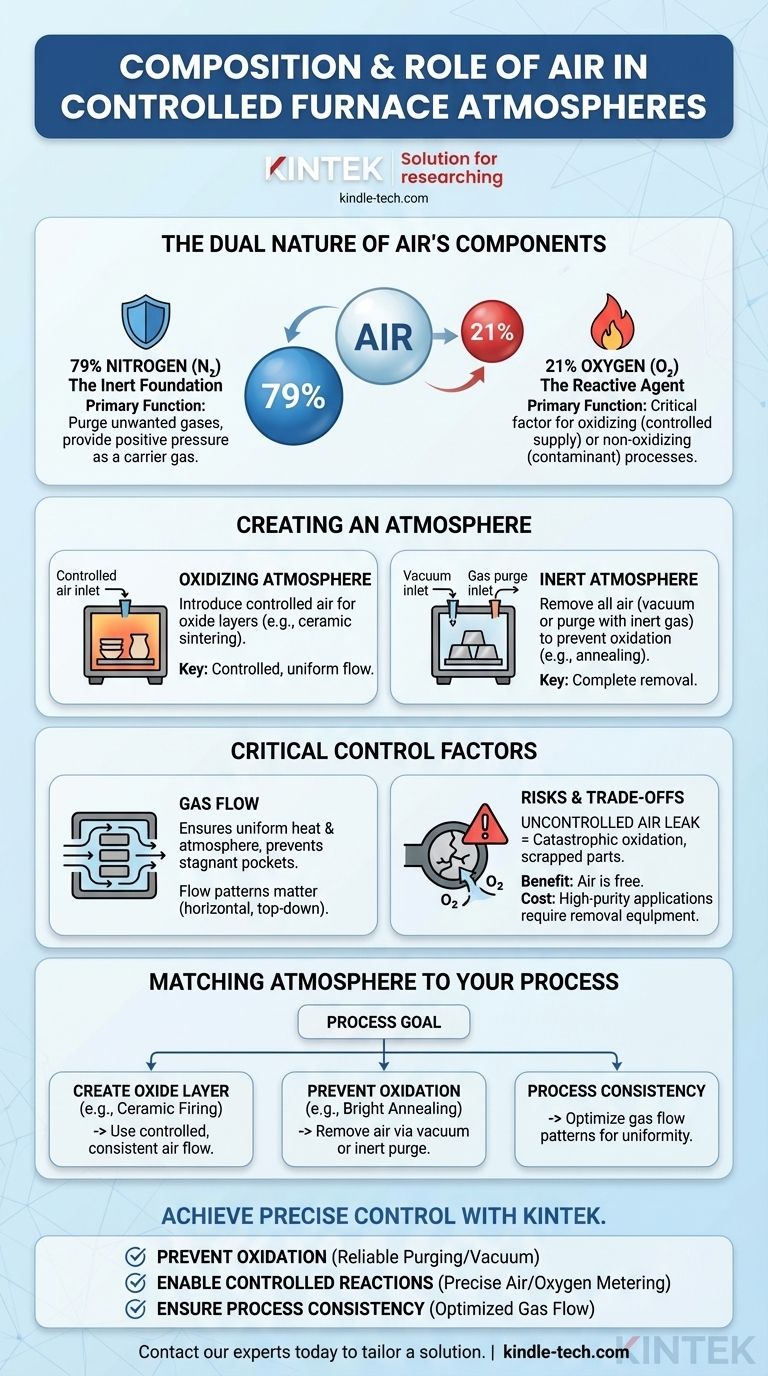
In furnace operations, air is best understood not as a single atmosphere but as a raw material source for two distinct gases: nitrogen and oxygen. Its composition is approximately 79% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. The role of air is therefore entirely dependent on which of these components is desired for the thermal process and which is considered a contaminant to be removed.
The fundamental role of air in a controlled furnace is determined by process requirements. It can either be a deliberate source of oxygen for oxidizing atmospheres or an impurity that must be purged and replaced with an inert gas to prevent unwanted reactions like scaling.

The Dual Nature of Air's Components
To understand how to use air, you must first understand the vastly different properties of its two primary components at high temperatures.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Inert Foundation
Nitrogen is largely non-reactive under most heat-treating conditions. Because of this inertness, it is often used as a safe and cost-effective carrier gas.
Its primary functions are to purge unwanted atmospheric gases (like oxygen) from the furnace chamber before a cycle and to provide positive pressure to prevent outside air from leaking in.
Oxygen (O₂): The Reactive Agent
Oxygen is extremely reactive, especially at the elevated temperatures found inside a furnace. Its presence is the single most critical factor determining whether a process is oxidizing or non-oxidizing.
Even trace amounts of oxygen can cause undesirable scaling, decarburization, and discoloration on the surface of many metals. In other processes, like firing certain ceramics, a controlled supply of oxygen is essential for achieving the desired material properties.
How Air is Used to Create an Atmosphere
The "control" in a controlled atmosphere comes from managing the composition and movement of the gases within the furnace. Air is the starting point for several distinct approaches.
Creating an Oxidizing Atmosphere
For processes that require an oxide layer, such as specific ceramic sintering or metal passivation, air is intentionally introduced into the furnace.
The key is control. Simply leaving the furnace open to the room is not sufficient. A controlled flow of air ensures that every part is exposed to a uniform concentration of oxygen, resulting in consistent product quality.
Creating an Inert Atmosphere
For most metal heat treatments, including annealing, hardening, and brazing, oxygen is a contaminant. The primary goal is to remove all air from the chamber.
This is typically achieved in two ways: by pulling a vacuum to physically remove the air molecules, or by purging the chamber with a high-purity inert gas, like nitrogen, to displace the air.
The Critical Role of Gas Flow
Controlling the gas composition is only half the battle. Controlling its flow is equally critical for maintaining part quality and protecting furnace components.
A regular, stable flow of gas ensures uniform heat transfer and prevents stagnant pockets of unwanted residual gases. Depending on the furnace design, this flow may be engineered to be horizontal, top-down, or bottom-up to optimize results for specific part geometries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Using air or its components involves balancing cost, complexity, and the specific chemical reactions required for your material.
The High Cost of Uncontrolled Air
The most significant risk in many furnace operations is an uncontrolled air leak. A crack in a seal or a faulty connection can introduce oxygen into what should be an inert atmosphere.
This unwanted oxygen can cause catastrophic oxidation of the workpiece, leading to scrapped parts and wasted production time. It is a common and costly failure mode.
The Benefit of Air as a Raw Material
Air's primary advantage is that it is free and abundant. For processes that can tolerate or require oxygen, using filtered, compressed air is the most economical choice for an atmosphere.
Conversely, for high-purity applications, the cost shifts. The expense is no longer the gas itself but the equipment needed to remove the air—vacuum pumps and the high-purity inert gases required for purging.
Matching the Atmosphere to Your Process
Your process goal dictates your atmospheric strategy. There is no single "best" atmosphere, only the correct one for the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating an oxide layer (e.g., ceramic firing): Use a controlled and consistent flow of air to provide the necessary oxygen for the chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation (e.g., bright annealing steel): You must diligently remove air from the furnace, typically by using a vacuum or purging with an inert gas like pure nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Pay close attention to gas flow patterns, as this ensures uniform temperature and atmospheric exposure for every part in the load.
Ultimately, mastering your furnace environment means understanding that controlling the atmosphere is how you control the final properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Air Component | Primary Role in Furnace Atmosphere | Common Process Application |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Inert carrier gas for purging and pressure control | Annealing, brazing, hardening (non-oxidizing) |
| Oxygen (O₂) | Reactive agent for creating oxide layers | Ceramic sintering, metal passivation (oxidizing) |
Achieve precise control over your furnace atmosphere with KINTEK.
Whether your process requires a perfectly inert environment for bright annealing or a controlled oxidizing atmosphere for ceramic sintering, the right lab equipment is critical. Uncontrolled air can lead to costly defects like scaling and decarburization, while precise gas management ensures consistent, high-quality results batch after batch.
KINTEK specializes in furnaces and atmosphere control systems designed for laboratory and industrial heat treatment. Our solutions help you:
- Prevent Oxidation: Implement reliable purging and vacuum systems to protect sensitive materials.
- Enable Controlled Reactions: Precisely meter air or oxygen for processes that require it.
- Ensure Process Consistency: Optimize gas flow patterns for uniform results across your entire load.
Don't let atmospheric inconsistencies compromise your material properties. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can tailor a furnace solution to your specific application and ensure your thermal processes deliver the performance you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do atmosphere tube or box furnaces support sintering of LiFePO4? Optimize Battery Cathode Performance
- Why are laboratory vacuum or atmosphere furnaces necessary for non-gold metallic nanofoams? Ensure Material Integrity
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace influence Si-O-C ceramics? Control Your Pyrolysis Environment
- What are the factors affecting the heat treatment process? Master Temperature, Time, Cooling & Atmosphere
- What is a controlled atmosphere furnace for heat treatment? Master Surface Chemistry and Metallurgy
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing process? Prevent Oxidation for a Perfect Metal Finish
- What is the function of a high-strength hydrogen atmosphere sintering furnace? Essential for Molybdenum Targets
- How are inert gases utilized in the thermal treatment of metals? Protect Your Alloys with Nitrogen & Argon Atmospheres



















