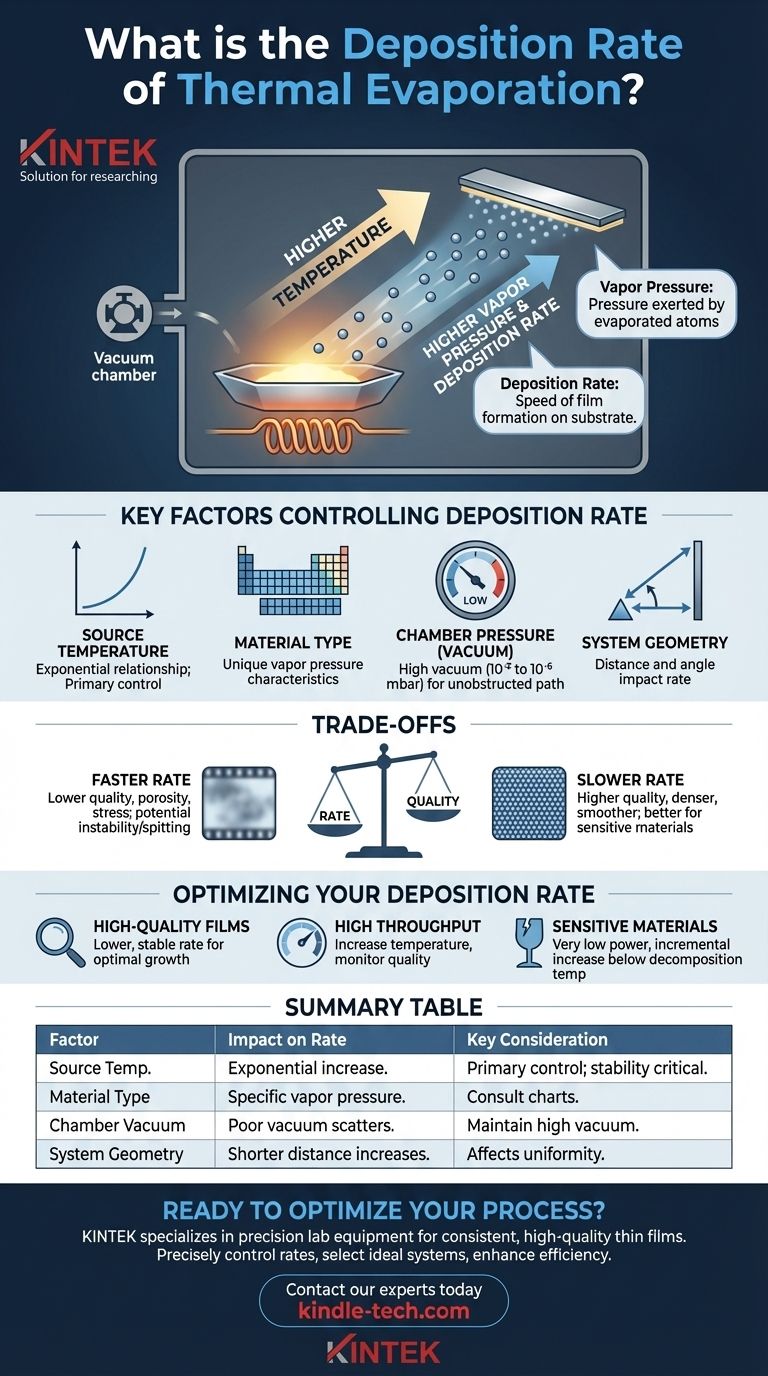
The deposition rate in thermal evaporation is not a single value but a highly variable and controllable parameter. It is determined primarily by the temperature of the source material—a higher temperature creates a higher vapor pressure, which in turn leads to a faster rate of deposition on your substrate.
The core principle to understand is that deposition rate is a direct consequence of your process inputs. You actively control the rate by adjusting the source temperature, which dictates how quickly material atoms evaporate and coat your substrate.

The Fundamental Principle: Vapor Pressure
To control the deposition rate, you must first understand the physics of vapor pressure and its direct relationship with temperature.
The Role of Temperature
Thermal evaporation works by heating a source material in a high-vacuum chamber. This is typically done by passing a high electric current through a holder, known as a "boat" or "crucible."
As the source material heats up, its atoms gain thermal energy. Eventually, they gain enough energy to break free from the surface and enter a gaseous state, a process known as evaporation.
From Vapor Pressure to Deposition Rate
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by these evaporated atoms within the chamber. The hotter the source material gets, the more atoms evaporate, and the higher the vapor pressure becomes.
This stream of vapor travels through the vacuum and condenses on the cooler substrate, forming the thin film. A higher vapor pressure means a denser stream of atoms reaches the substrate per unit of time, resulting in a higher deposition rate.
Key Factors Controlling Deposition Rate
While temperature is your primary control knob, several interconnected factors determine the final deposition rate.
Source Temperature
This is your most direct control. Increasing the power to the heating element raises the source temperature, increases vapor pressure, and accelerates the deposition rate. This relationship is exponential, so small changes in temperature can cause large changes in rate.
The Material Being Evaporated
Every material has a unique temperature-to-vapor-pressure relationship. Materials like aluminum and silver evaporate at different temperatures to achieve the same vapor pressure.
Because of this, you must consult vapor pressure charts for your specific material to determine the required temperature range for your desired deposition rate.
Chamber Pressure (Vacuum Level)
Thermal evaporation is performed in a high vacuum (typically 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar) for a critical reason. This low pressure removes most air molecules, ensuring the evaporated atoms have a clear, unobstructed path from the source to the substrate.
A poor vacuum would cause evaporated atoms to collide with air molecules, scattering them and drastically reducing the effective deposition rate and film purity.
System Geometry
The physical arrangement of your chamber plays a significant role. The distance and angle between the evaporation source and the substrate directly impact the rate. Just like a spray paint can, the closer the substrate is to the source, the higher the rate of deposition will be.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply aiming for the fastest possible deposition rate is often a mistake. The rate you choose involves critical trade-offs between speed and quality.
Rate vs. Film Quality
Depositing too quickly can result in a lower-quality film. Atoms may not have enough time to settle into an ordered, dense structure on the substrate, leading to films that are porous or have high internal stress.
Slower deposition rates generally give atoms more time to arrange themselves, often resulting in denser, smoother, and higher-purity films.
Rate vs. Process Stability
Aggressively heating a source to achieve a high rate can make the process unstable. Some materials may "spit" or eject small molten droplets when overheated, creating significant defects on the substrate.
Maintaining a stable, moderate temperature is often key to a repeatable and reliable deposition process.
Temperature vs. Material Integrity
For sensitive materials like organic compounds or certain alloys, excessive heat can cause them to decompose or break down. In these cases, a carefully controlled, lower deposition rate is essential to preserve the material's chemical structure in the final film.
Optimizing Your Deposition Rate
Your ideal rate depends entirely on the goal of your specific application. Use these guidelines to make an informed choice.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, dense films: Opt for a lower, more stable deposition rate to allow for optimal film growth.
- If your primary focus is process speed and high throughput: Carefully increase the source temperature while monitoring film quality to find the maximum rate that still meets your specifications.
- If you are depositing a sensitive or complex material: Begin with very low power and increase it incrementally to find a stable evaporation rate that occurs well below the material's decomposition temperature.
Mastering thermal evaporation lies in understanding and controlling the relationship between temperature, vapor pressure, and your desired film properties.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Deposition Rate | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Source Temperature | Higher temperature exponentially increases rate. | Primary control knob; stability is critical. |
| Material Type | Vapor pressure vs. temperature is material-specific. | Consult vapor pressure charts for your material. |
| Chamber Vacuum | Poor vacuum scatters atoms, reducing effective rate. | Maintain high vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar). |
| System Geometry | Shorter source-to-substrate distance increases rate. | Affects film uniformity and thickness profile. |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Evaporation Process?
Achieving the perfect balance between deposition rate and film quality is key to your research or production success. The right lab equipment is fundamental to this control.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal evaporation needs. We provide the reliable tools and expert support to help you:
- Precisely control deposition rates for consistent, high-quality thin films.
- Select the ideal system and components for your specific materials and application goals.
- Enhance your lab's efficiency with durable, high-performance evaporation sources and vacuum systems.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















